Exploring the World of Prasanthus suecicus: A Remarkable Moss
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
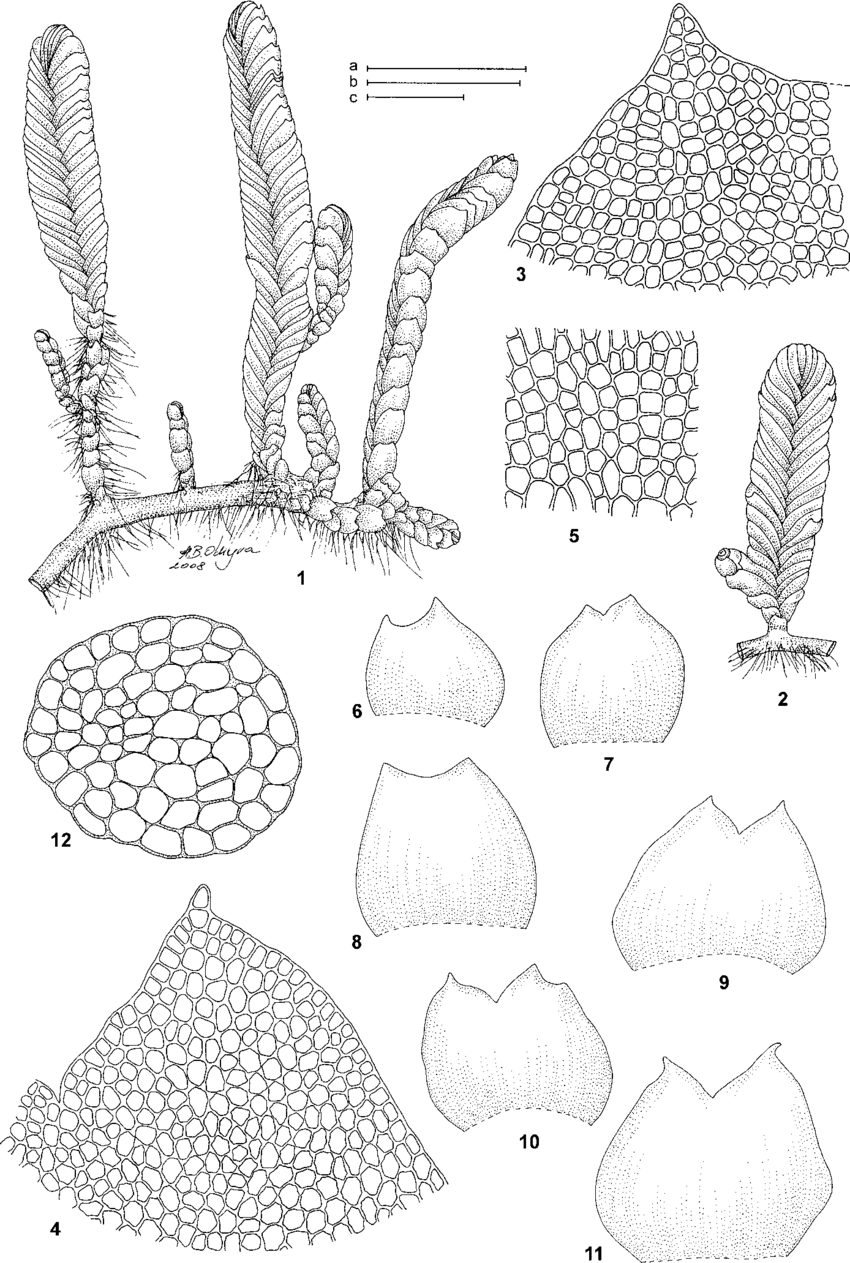
Prasanthus-suecicus-1-2-Habit-3-4-Cells-at-leaf-apex-5-Basal-leaf-cells-6-11.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Prasanthus-suecicus-1-2-Habit-3-4-Cells-at-leaf-apex-5-Basal-leaf-cells-6-11_fig1_233609923
Introduction
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of tiny, yet remarkable plants. Among them is the Prasanthus suecicus (Gottsche) Lindb., a member of the Gymnomitriaceae family, commonly known as Prasanthus. This unassuming moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate world of bryophytes.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Prasanthus suecicus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the Marchantiophyta division, which encompasses liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. Despite their small stature, mosses play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Prasanthus suecicus is a small, acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the gametophyte (the leafy, green plant body). Its leaves are ovate to lanceolate, arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. The distinctive feature of this moss lies in its reddish-brown coloration, particularly noticeable in the older portions of the plant.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Prasanthus suecicus is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, found in regions such as Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including moist, shaded areas, rotting logs, and soil-covered rocks. This moss is often found in coniferous and mixed forests, where it forms dense mats or cushions on the ground or tree bases.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Prasanthus suecicus plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat

48221_2439_5.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/2439
for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Prasanthus suecicus is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found Prasanthus suecicus to be a significant component of the understory vegetation in old-growth forests. Its presence was closely linked to the availability of decaying wood
Prasanthus-suecicus-1-2-Habit-3-4-Cells-at-leaf-apex-5-Basal-leaf-cells-6-11_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Global-distribution-of-Prasanthus-suecicus-New-localities-in-Asia-and-on-Prince-Edward_fig2_233609923
and moist conditions, highlighting its role in nutrient cycling and ecosystem dynamics.
Technical Table
14ce36d3d539b6003af3c169ae07222ac65c113819ef from: https://baike.baidu.com/item/穗枝苔/62779339

70438_2439_1.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/prasanthus-1004541

Cotoneaster-suecicus-Skogsholm-a-HA8A6824.jpg from: https://woerlein.de/produkt/cotoneaster-suecicusx-skogholm-immergruene-boeschungsmispel/

cotoneaster-x-suecicus-coral-beauty.jpeg from: https://www.gardentags.com/plant-encyclopedia/cotoneaster-x-suecicus-coral-beauty/28512
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Gymnomitriaceae |
| Genus | Prasanthus
 e1fd4befc468a4dddf5ca25f5c1fb0b4.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/cotoneaster-suecicus-coral-beauty–734016439246426283/ |
| Species | Prasanthus suecicus (Gottsche) Lindb. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Color | Reddish-brown (older portions) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, rotting logs, soil-covered rocks |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
The Prasanthus suecicus (Gottsche) Lindb. moss, a member of the Gymnomitriaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is significant. From its unique morphology and adaptations to its ecological roles, this moss serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. As we continue to explore and appreciate the world of mosses,

_MG_0124.JPG from: https://maisbotanico.blogspot.com/2013/10/os-musgos-as-hepaticas-e-os-antoceros.html

ssp__22320.1511407161.jpg from: https://www.nativewildflowers.net/sphagnum-moss/
Prasanthus suecicus invites us to ponder the intricate web of life that exists beneath our feet, reminding us of the importance of preserving and protecting these often-overlooked wonders of nature.
