
56f3f4984a36f008ccb2d557fe98e5f5.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/543598617494511971/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the

perianth-mouth-stacked.jpg from: https://mosswalks.blogspot.com/2013/07/bryophytes-from-snow-lake.html?m=1
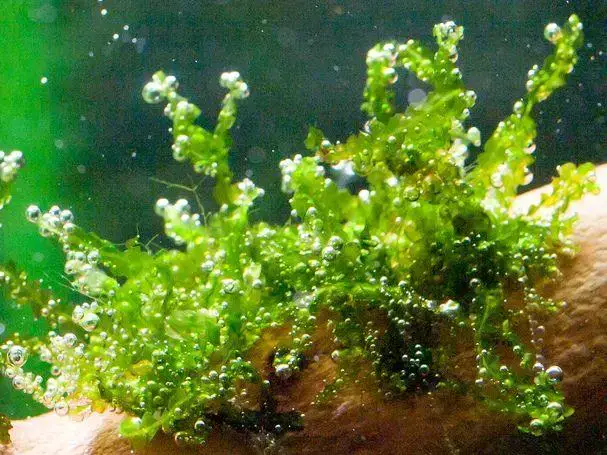
Telaranea blepharostoma (Steph.) Fulford moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Lepidoziaceae family. Also known simply as
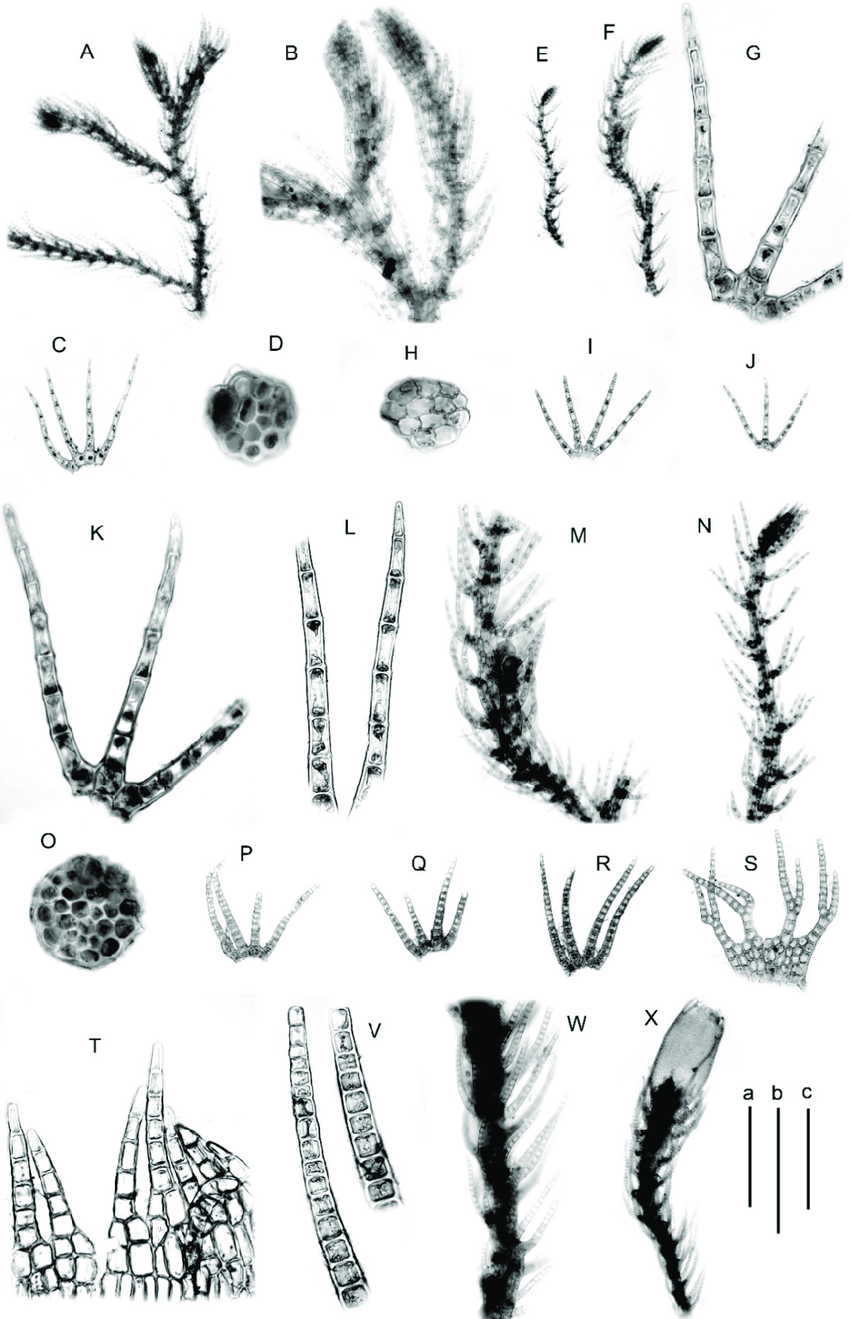
A-D-Blepharostoma-prima-from-S-45-12-16-VBGI-E-N-B-pseudominor-from.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-D-Blepharostoma-prima-from-S-45-12-16-VBGI-E-N-B-pseudominor-from_fig3_346411478
Telaranea, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Marchantiophyta marvel, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Telaranea blepharostoma, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. As members of the Jungermanniopsida class, liverworts like Telaranea are renowned for their intricate and delicate structures, making them a true delight for nature lovers and botanists alike.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
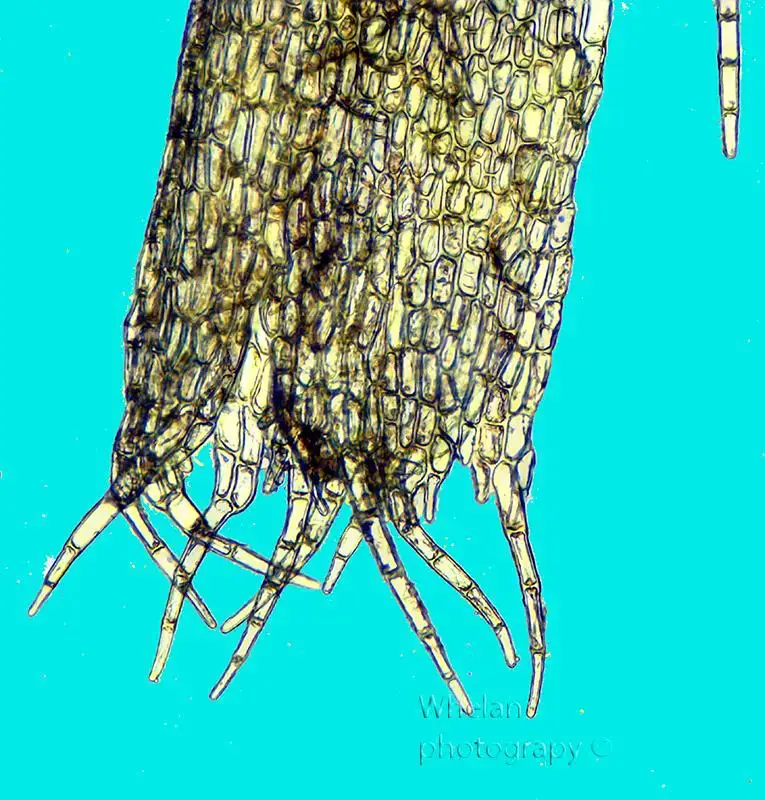
Telaranea blepharostoma is a small, creeping liverwort that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its slender stems are adorned with overlapping leaves, each bearing a distinctive shape and intricate cellular patterns. The leaves are often deeply divided or lobed, adding to the plant’s intricate beauty. One of the most striking features of this moss is its blepharostoma, or eyelash-like structures, which adorn the leaf margins, lending it a whimsical and enchanting appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America.
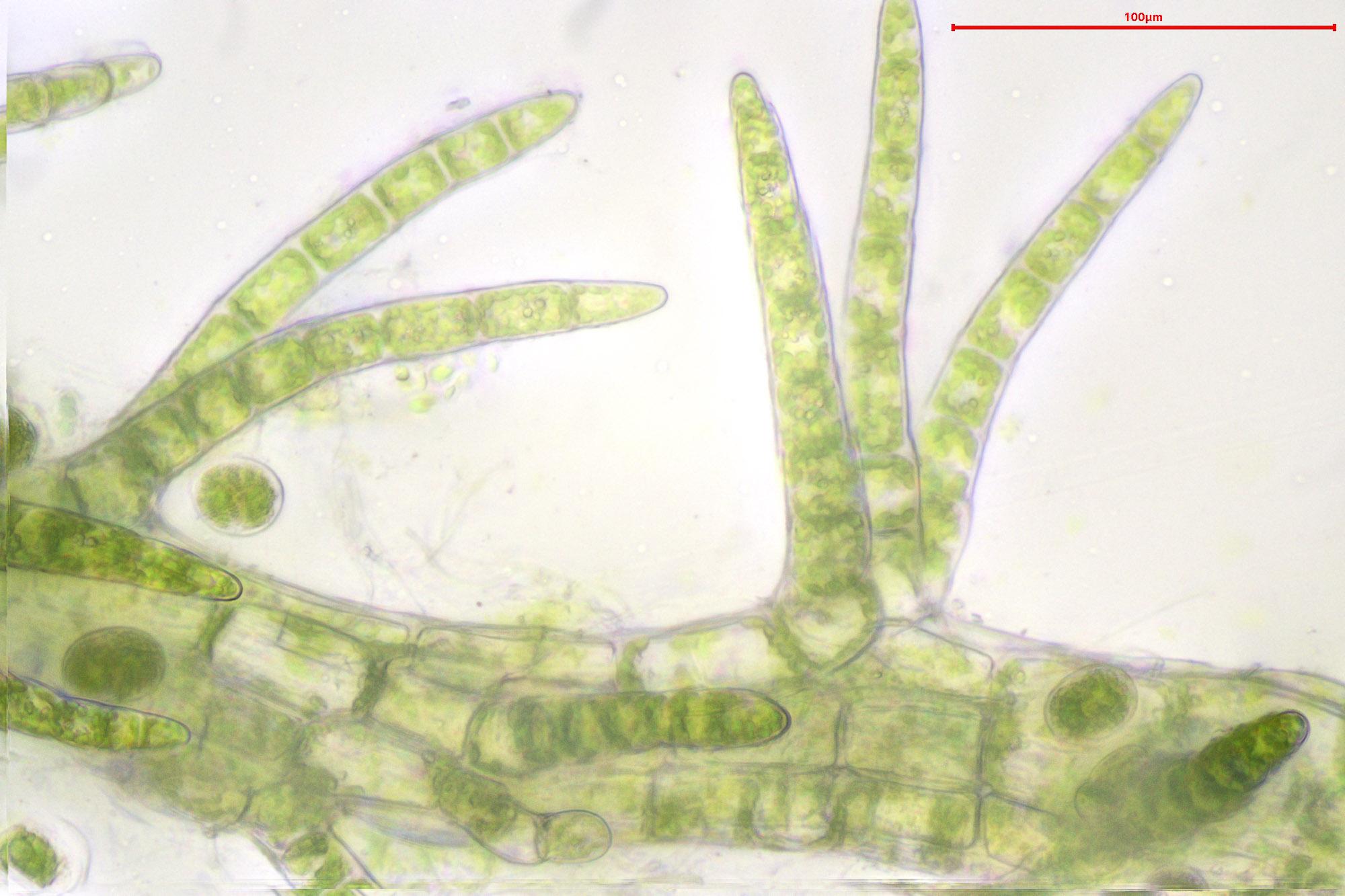
2021-11-17-20-59-19.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/blepharostoma-trichophyllum/
Telaranea blepharostoma thrives in moist, shaded environments, often inhabiting decaying logs, tree bark, and damp soil in forests and woodlands. Its ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats has contributed to its successful dispersal and survival.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Telaranea blepharostoma plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as sponges, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating a microhabitat for other organisms to thrive. They also contribute to soil formation and nutrient cycling, breaking down organic matter and releasing essential nutrients into the environment.
Moreover, Telaranea exhibits remarkable adaptations that allow it to survive in challenging conditions. Its ability to undergo desiccation and revive when moisture becomes available is a testament to its resilience. Additionally, the intricate leaf structures and blepharostoma aid in water retention and protection from drying out, ensuring the plant’s survival in periods of drought.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the ecological significance of Telaranea blepharostoma can be found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. In these temperate rainforests, the moss plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. Its presence contributes to the overall biodiversity, providing shelter and sustenance for a myriad of invertebrates and other organisms that call these forests home.
Technical Table

A-B-Blepharostoma-minor-from-J-91-51-15-VBGI-C-O-B-trichophyllum-from_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-B-Blepharostoma-minor-from-J-91-51-15-VBGI-C-O-B-trichophyllum-from_fig5_346411478

Blepharostoma-trichophyllum-Pearl-moss.jpg from: https://praeclara.ru/2021/03/09/blepharostoma-trichophyllum-pearl-moss/

blepharostoma-trichophyllum-pearl-moss-247×247.jpg from: https://www.premiumbuces.com/blepharostoma-trichophyllum-pearl-moss/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Telaranea blepharostoma (Steph.) Fulford
 maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7GLSIIKXEU |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Structure | Deeply divided or lobed, with blepharostoma
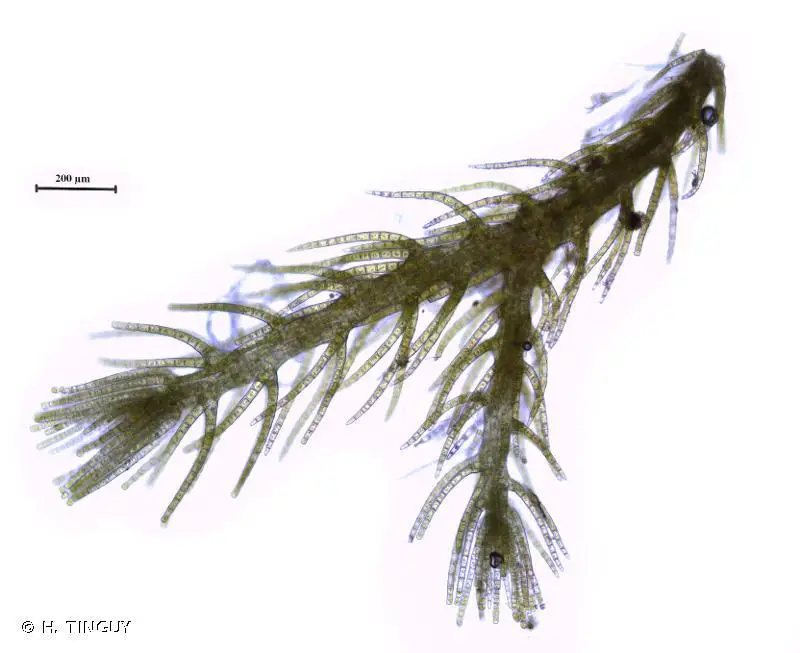 198490.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6645 (eyelash-like structures) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (decaying logs, tree bark, damp soil) |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, South America |
Conclusion
The Telaranea blepharostoma moss is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the intricate beauty and ecological significance of bryophytes. From its delicate morphology to its vital roles in various ecosystems, this unassuming plant deserves our appreciation and admiration. As we continue to explore the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems like
Figures-494-500-Phloeopora-gilbertae-Klimaszewski-Webster-494-habitus-in-dorsal-view.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figures-494-500-Phloeopora-gilbertae-Klimaszewski-Webster-494-habitus-in-dorsal-view_fig59_299408087
Telaranea are waiting to be discovered and celebrated for their unique contributions to our planet’s biodiversity?