image from: https://www.baike.com/wikiid/4355543150966325721
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm of Acroporium macroturgidum Dixon, a remarkable moss species that belongs to the Sematophyllaceae family. Often referred to simply as Acroporium

image from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/Sematophyllaceae/6536687
, this unassuming plant holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be uncovered by enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Acroporium macroturgidum Dixon, it’s essential to understand its place within the grand scheme of things. This moss is a member of the Bryophyta phylum, which encompasses a diverse array of non-vascular plants commonly known as

image from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/01_Semat.html
bryophytes. Within this phylum, Acroporium falls under the class Bryopsida, a group that includes the true mosses.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Acroporium macroturgidum Dixon is a true marvel of nature, with its delicate fronds and intricate structures. This moss is characterized by its
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Acroporium-hyalinum-var-turgidum-A-Habit-of-stem-B-Sporophyte-C-D-Leaves-E-Leaf_fig4_329961872
slender, creeping stems that form dense mats or cushions. Its leaves are

image from: https://ourgardenworks.com/growing-moss-on-rocks/
small, ovate to lanceolate in shape, and arranged spirally along the stem. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its inflated alar cells, which give the leaf bases a distinctive appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
While Acroporium macroturgidum Dixon may seem unassuming, its distribution is truly remarkable. This moss can be found across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia

image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/20719304532/
, and even Australia. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock outcrops to stream banks and damp soil.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Acroporium macroturgidum Dixon plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and paving the way for other plant species to establish themselves. Additionally, they serve as microhabitats
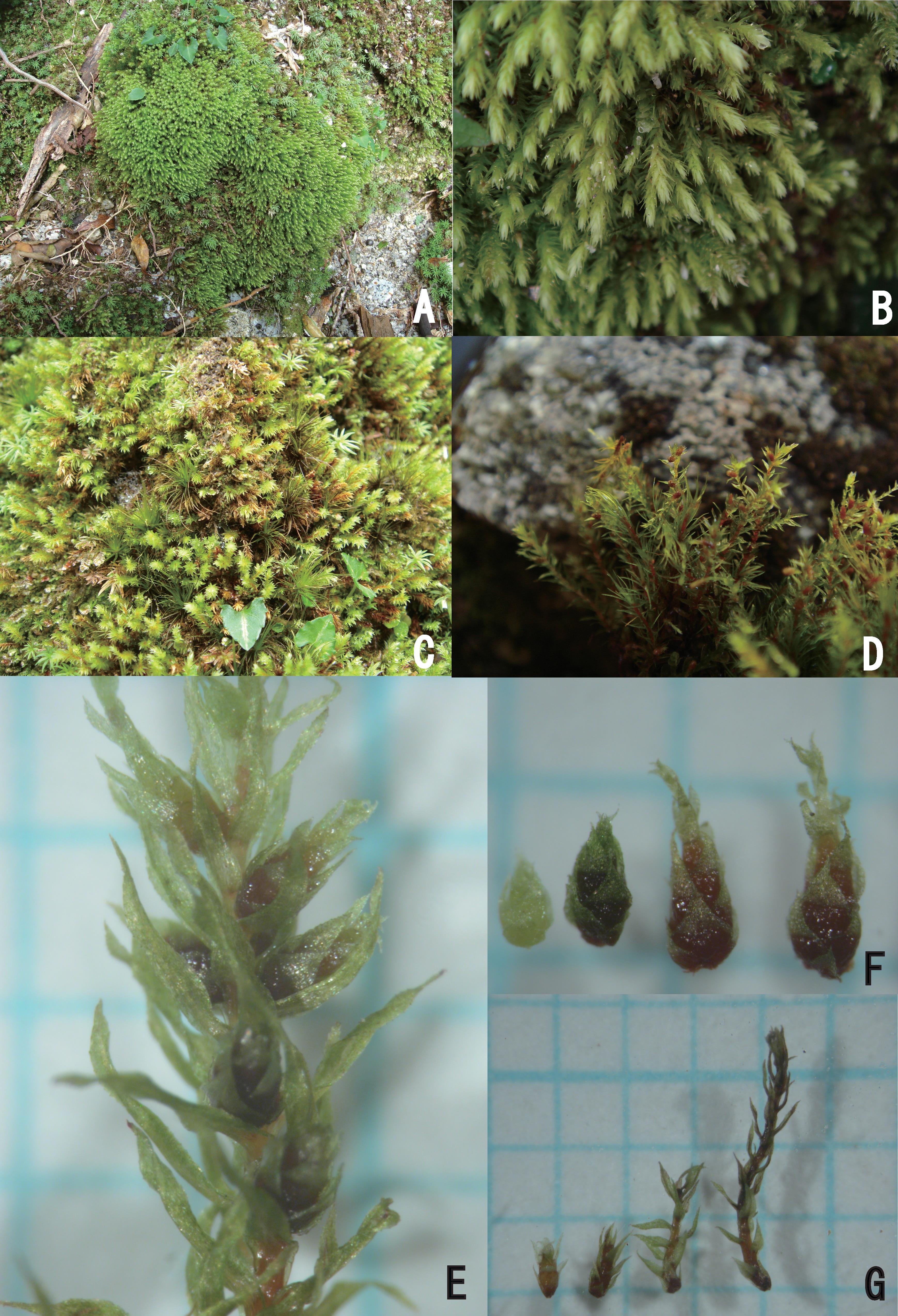
image from: https://bioone.org/journals/the-bryologist/volume-112/issue-4/0007-2745-112.4.749/Habitat-and-morphological-differentiation-between-span-classgenus-speciesPohlia-annotina-span/10.1639/0007-2745-112.4.749.full
for a diverse array of microscopic organisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of their environment.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acroporium is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, these mosses can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth when moisture becomes available again. This resilience is a testament to the incredible survival strategies employed by these tiny yet tenacious plants.
Case Studies/Examples
To illustrate the significance of Acroporium macroturgidum Dixon, let’s consider a case study from a temperate rainforest in the Pacific Northwest. In this lush ecosystem, Acroporium plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the forest floor. Its dense mats help retain moisture, creating a microclimate that supports the growth of other plant species and provides shelter for a myriad of invertebrates.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphological-structures-connected-to-ectohydric-water-transport-A-Alar-groups-in_fig2_327550942

image from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-family-Sematophyllaceae-(Bryopsida)-in-Part-2.-Schofield-Ramsay/6e2613a7e066bc0d295ff5aa59e38485f71ff2bd/figure/7

image from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-family-Sematophyllaceae-(Bryopsida)-in-Part-2.-Schofield-Ramsay/6e2613a7e066bc0d295ff5aa59e38485f71ff2bd/figure/3
| Technical Data | Value |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Genus | Acroporium |
| Species | macroturgidum Dixon |