image from: https://www.baike.com/wikiid/4355543150966325721
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Sematophyllaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background

image from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/Sematophyllaceae/6536687
Before delving into the intricacies of

image from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/01_Semat.html
Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, collectively known as Bryophyta, encompass mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and play crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt., commonly referred to as Acroporium, is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate fronds form dense mats or cushions, adorned with tiny, intricate leaves that exhibit a distinctive lanceolate shape. The leaves are typically
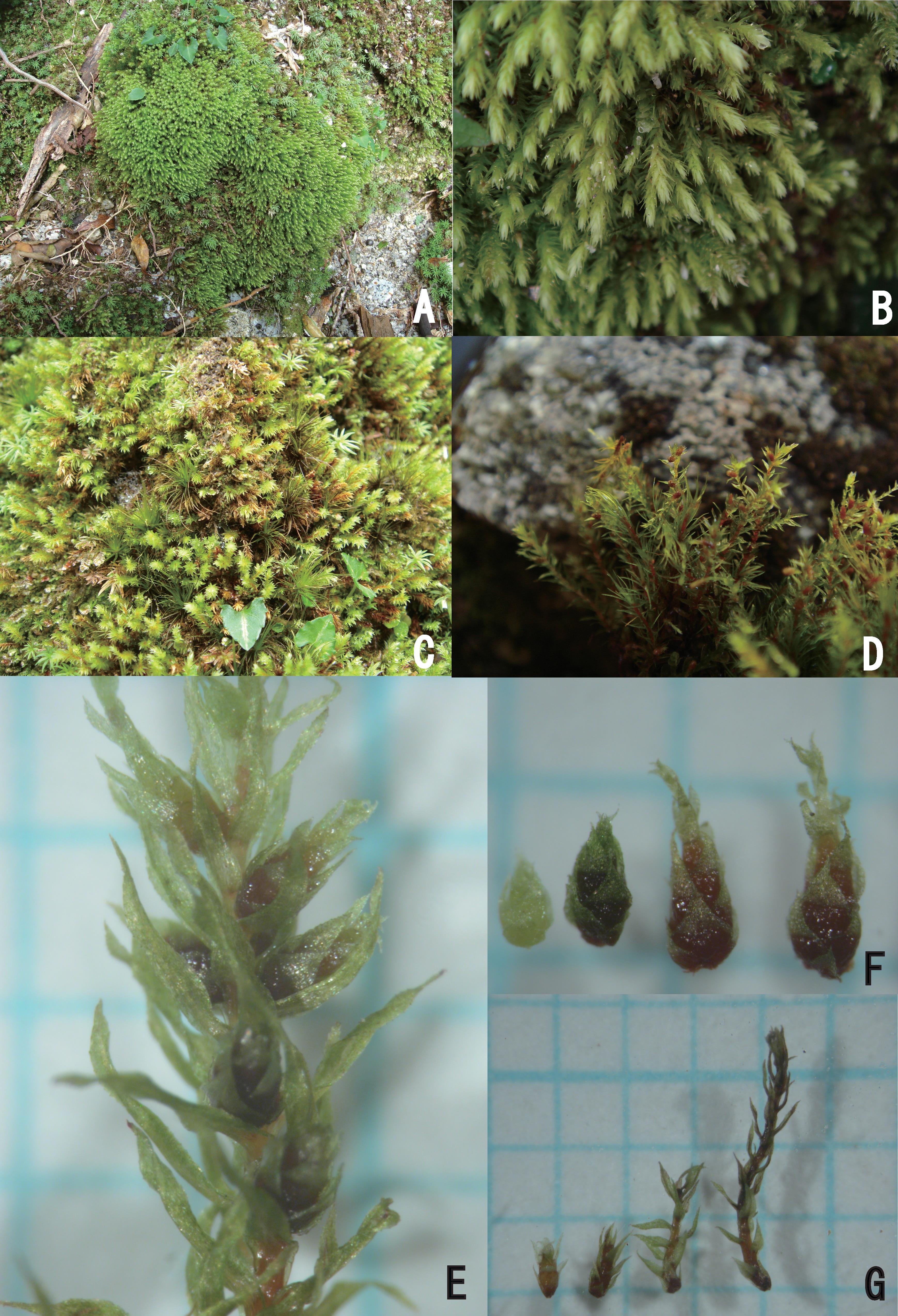
image from: https://bioone.org/journals/the-bryologist/volume-112/issue-4/0007-2745-112.4.749/Habitat-and-morphological-differentiation-between-span-classgenus-speciesPohlia-annotina-span/10.1639/0007-2745-112.4.749.full
1-2 mm long and feature a short, abruptly pointed tip, lending the species its specific epithet, “brevicuspidatum.”
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species boasts a widespread distribution, thriving across various regions of the world. It can be found in
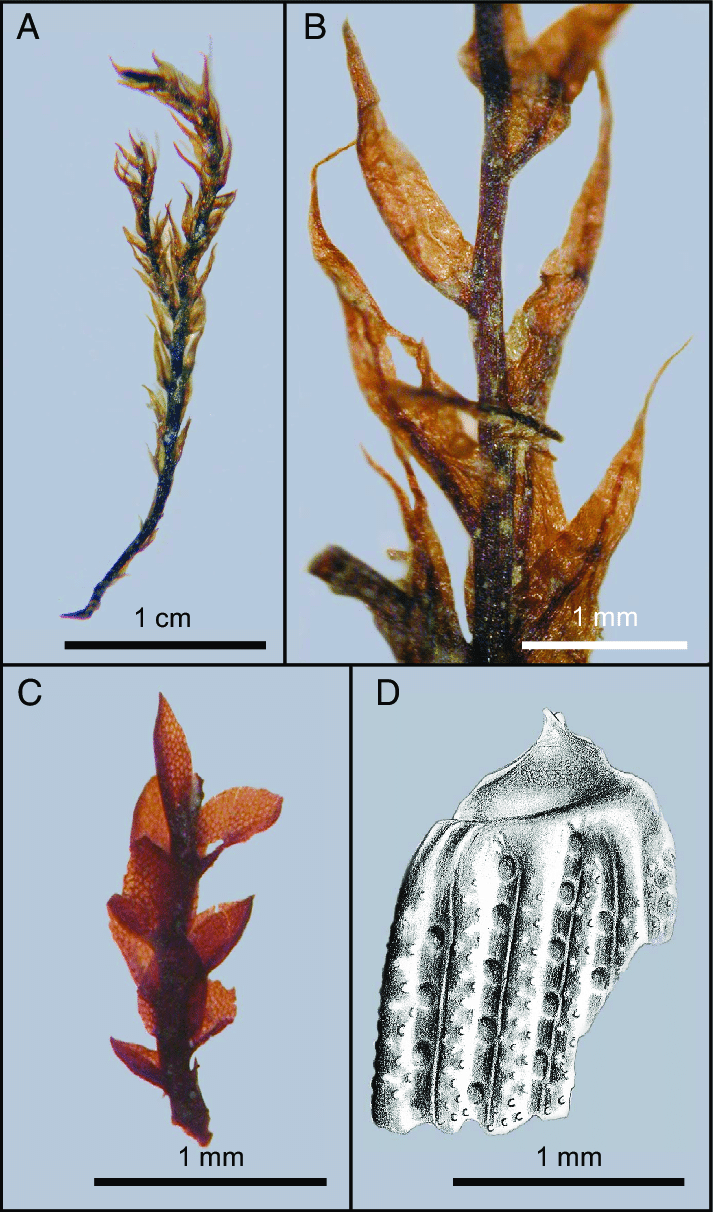
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
Asia, Africa, Europe, North and South America, and Oceania. Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt. favors moist, shaded environments, often inhabiting the bark of trees, rotting logs, and damp soil in forests and woodlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

image from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8795
Despite their diminutive size, mosses like Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt. play vital roles in their ecosystems. They act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Additionally, they contribute to soil formation, water retention, and nutrient cycling, creating microhabitats for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt. is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples

image from: https://www.naturalista.mx/taxa/155590-Acroporium
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Acroporium-hyalinum-var-turgidum-A-Habit-of-stem-B-Sporophyte-C-D-Leaves-E-Leaf_fig4_329961872
Acroporium brevicuspidatum Mitt. played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture levels and microclimate within old-growth forests. The moss’s ability to retain water and create a humid microenvironment supported the growth and diversity of other bryophyte species, as well as various fungi and invertebrates.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
 image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/20719304532/ |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Genus | Acroporium |
Species
 image from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55 |
brevicuspidatum Mitt. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm long |
| Habitat | Bark, rotting logs, damp soil |