
00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Acroporium convolutum (Sande Lac.) M.Fleisch., commonly known as Acroporium. This unassuming yet fascinating plant belongs to the Sematophyllaceae family and has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, let’s set the stage with a brief background. Bryophytes, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These resilient organisms have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the dinosaurs!

66b6cf8c6ef56719b3b53d4e0f953ea1.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8795
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
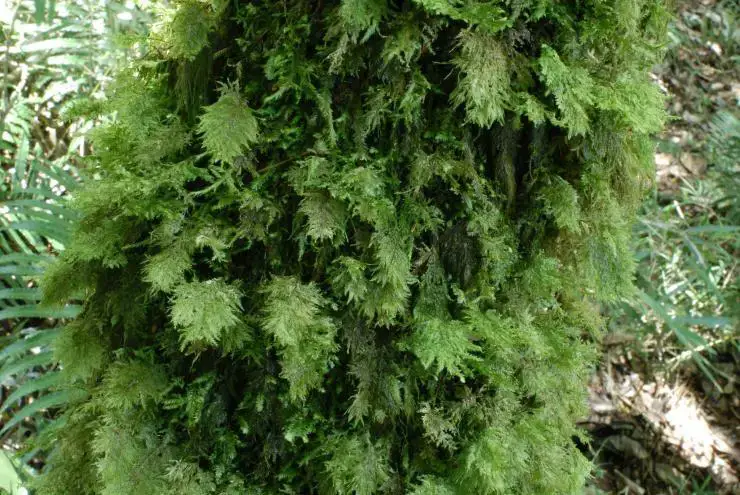
Acroporium convolutum is a true masterpiece of nature, with its delicate fronds and intricate branching patterns. This moss is characterized by its slender, creeping stems that form dense mats or cushions. The leaves

5622e6df2ce9f1051a576c6c516b9db2.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/d3c69fc27fdd03291ec8fc9aa7341fc5
are small, ovate to lanceolate in shape, and spirally arranged around the stem, creating a feathery appearance.
One of the most distinctive features of Acroporium convolutum is its leaf margins, which are strongly revolute (rolled inward). This unique characteristic, combined with the spirally twisted leaves, gives the moss a convoluted or twisted appearance, hence its specific epithet “convolutum.”
Global Distribution and Habitat
Acroporium convolutum is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found in various regions across the globe. It thrives in

443b67ab9823f32147237ade9965365a.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/34597
temperate and tropical regions, preferring moist and shaded environments such as forests, rock crevices, and decaying logs. This moss is particularly abundant in Central and South America,
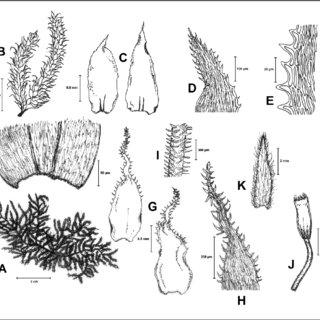
Chaetomitrium-horridulum-Bosch-Sande-Lac-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-shoot-C-Branch_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Chaetomitrium-horridulum-Bosch-Sande-Lac-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-shoot-C-Branch_fig2_356611709
Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Acroporium convolutum plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as
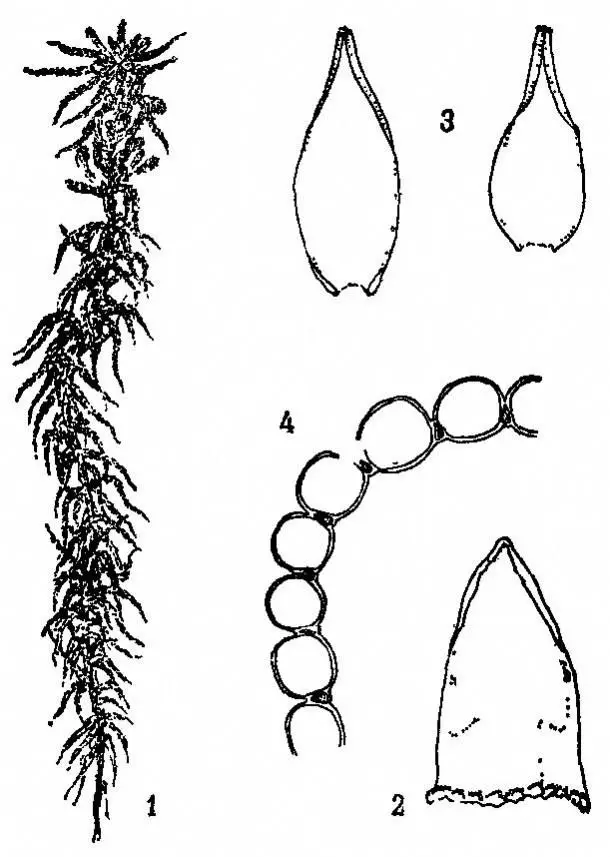
t01b1aab2930c3f3e4f.jpg from: https://baike.so.com/doc/4525174-4735252.html
pioneers, colonizing bare surfaces and facilitating the growth of other plants by retaining moisture and providing a suitable substrate. They also serve as microhabitats for various invertebrates, fungi, and microorganisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of their environment.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acroporium convolutum is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture and reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in a wide range of habitats, from humid forests to arid regions.
Case Studies/Examples
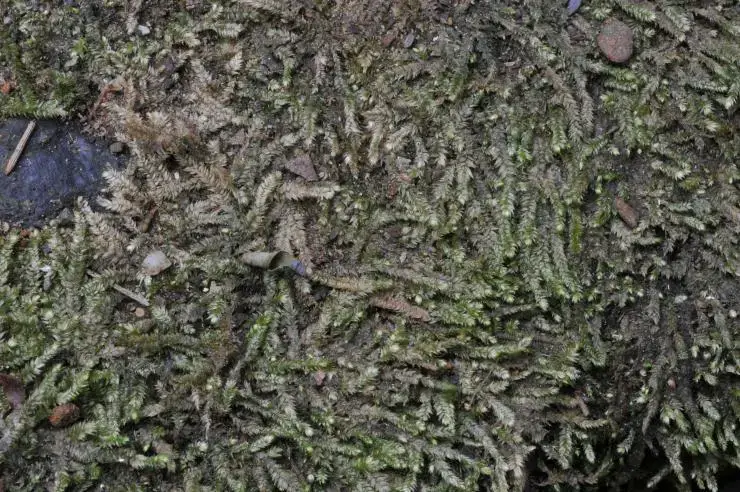

062fe76a3d99abeabe1f00689b0f6142.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/941620afcf4d576ff03d5d1e1c09f139
In the Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve in Costa Rica, Acroporium convolutum is a prominent component of the epiphytic moss community, growing abundantly on tree trunks and branches. Researchers have studied the role of this moss in nutrient cycling and water retention, highlighting its importance in maintaining the delicate balance of this unique ecosystem.
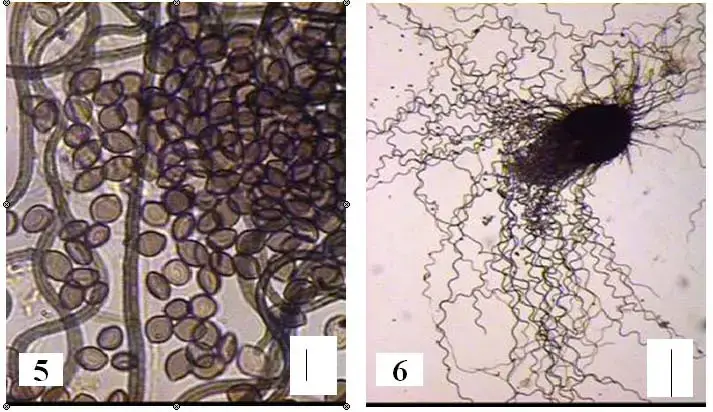

Figures-5-and-6-Chaetomium-convolutum-5-ascospores-6-ascomata-Bar-510m-Bar-6.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figures-5-and-6-Chaetomium-convolutum-5-ascospores-6-ascomata-Bar-510m-Bar-6_fig3_310494777
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Acroporium convolutum (Sande Lac.) M.Fleisch. |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Common Name | Acroporium |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged |
| Leaf Margins | Strongly revolute (rolled inward) |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan (widespread) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forests, rock crevices, decaying logs) |
Conclusion
Acroporium convolutum, a true gem among mosses, reminds us of the incredible diversity and resilience found in the world of bryophytes. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden marvels await our discovery in the realm of these ancient and remarkable plants?