image from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/03/hepaticas-lepidoziaceae-arachniopsis.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Arachniopsis diacantha (Mont.) M.Howe moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Lepidoziaceae family. Often referred to simply as Arachniopsis, this unassuming yet intriguing moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Arachniopsis diacantha belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, class Jungermanniopsida

image from: https://grasslands.ecolinc.vic.edu.au/fieldguide/flora/grey-copper-burr
, order Jungermanniales, and family Lepidoziaceae
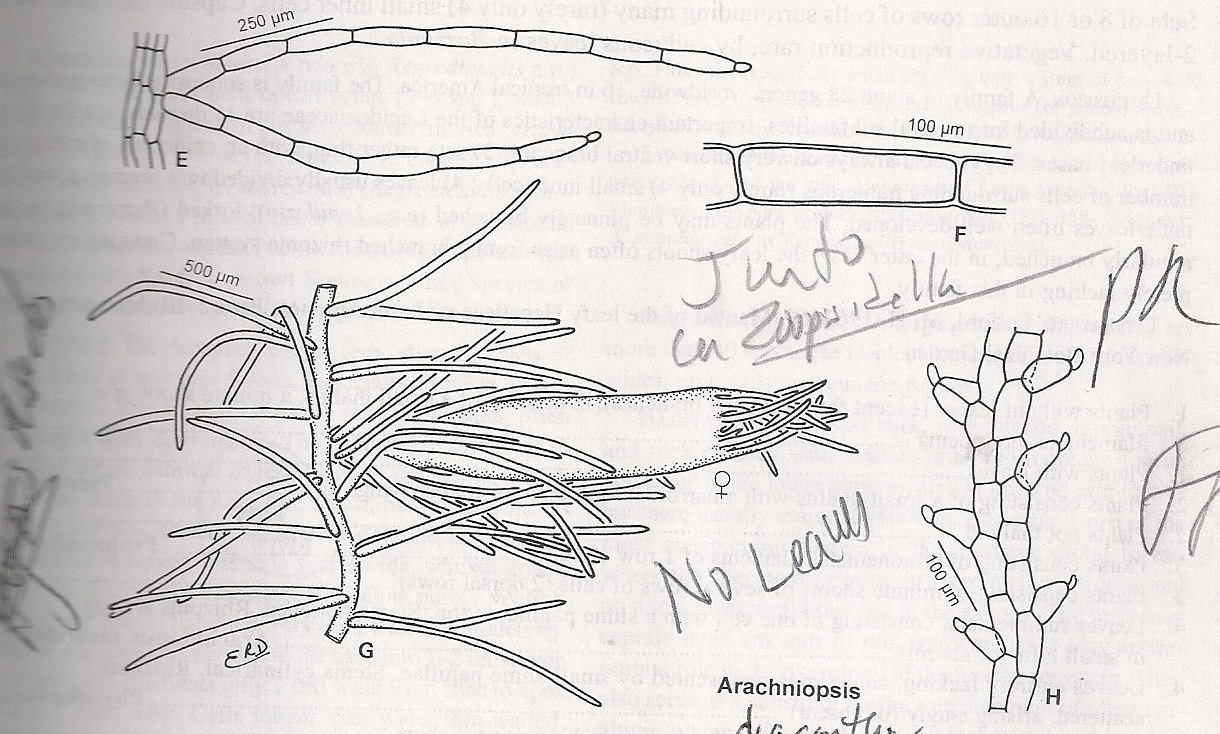
![https://bioone.org/journals/fieldiana-botany/volume-2004/issue-44/0015-0746(2004)44[1:AHATAP]2.0.CO;2/Austral-Hepaticae-35-A-Taxonomic-and-Phylogenetic-Study-of-span/10.3158/0015-0746(2004)44[1:AHATAP]2.0.CO;2.full](https://bioone.org/ContentImages/Journals/fbot/2004/44/0015-0746_2004_44_1_AHATAP_2.0.CO_2/graphic/i0015-0746-44-1-1-f45.gif)
image from: https://bioone.org/journals/fieldiana-botany/volume-2004/issue-44/0015-0746(2004)44[1:AHATAP]2.0.CO;2/Austral-Hepaticae-35-A-Taxonomic-and-Phylogenetic-Study-of-span/10.3158/0015-0746(2004)44[1:AHATAP]2.0.CO;2.full
. This tiny, unassuming plant plays a crucial role in various ecosystems, serving as a vital component of the intricate web of life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

image from: https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/26660
Arachniopsis diacantha is a delicate and intricate moss, with a unique appearance that sets it apart from its counterparts. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with overlapping leaves

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271814742_Taxonomic_Notes_on_Gracilaria_mammillaris_Mont_Howe_and_Gracilaria_Veleroae_Dawson_Rhodophyta_Gigartinales
that form a

image from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/435441857719830308/
feathery pattern. These leaves are deeply divided, giving the moss a fern-like appearance. The leaf cells are elongated and thick-walled, contributing to the plant’s resilience in harsh environments.
One of the most distinctive features of

image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/tony_rodd/10922980806/
Arachniopsis diacantha is its reproductive structures. The archegoniophores (female reproductive structures) are elongated and slender, resembling delicate stalks topped with spherical capsules. The antheridiophores (male reproductive structures) are clustered and sessile, adding to the moss’s intricate beauty.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Arachniopsis diacantha is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australasia. This moss thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and stream banks. It often forms dense mats or cushions, creating a vibrant and verdant carpet on the forest floor or clinging to the bark of trees.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Arachniopsis diacantha plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance for these tiny creatures.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Arachniopsis diacantha is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture and reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Arachniopsis diacantha is a common sight in old-growth forests. These ancient ecosystems provide the perfect conditions for the moss to flourish, forming lush carpets that contribute to the overall biodiversity of the area. Researchers have documented the moss’s ability to facilitate the establishment of other plant species, further emphasizing its ecological importance.

image from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/127789708151545070/

image from: https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/2609

image from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=8939
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Overlapping, deeply divided |
| Reproductive Structures | Elongated archegoniophores, clustered antheridiophores |