Figs-A-K-Barbella-rufifolia-Thwait-Mitt-Broth-A-dry-plant-667-B-wet.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figs-A-K-Barbella-rufifolia-Thwait-Mitt-Broth-A-dry-plant-667-B-wet_fig1_239589720
Barbella rufifolioides: The Fascinating Moss of the Meteoriaceae Family
Introduction
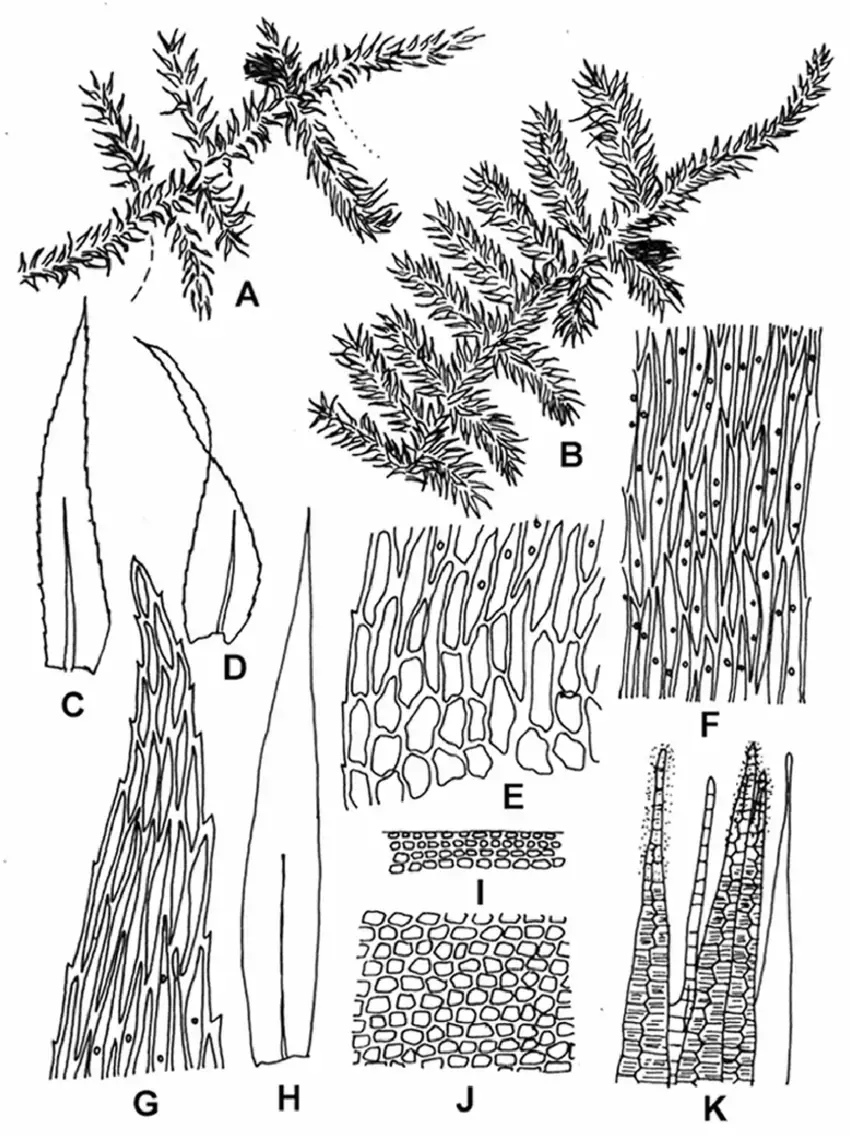
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting moss is Barbella rufifolioides (Broth.) Broth.

Brothera-leana-700×467.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/aaa-bryology5-asexua/
, also known simply as

lbb.jpg from: https://thealevelbiologist.co.uk/culturing-media/
Barbella. This unique moss belongs to the Meteoriaceae family and has some fascinating characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Barbella and explore what makes it so special.
Background
Barbella rufifolioides is classified under the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. The Meteoriaceae family to which it belongs contains over 300 species of mosses found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. Barbella was first described by

2022-03-29-09-28-13.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/tortella-flavovirens/
Viktor Ferdinand Brotherus in the early 20th century.
Morphology and Identification
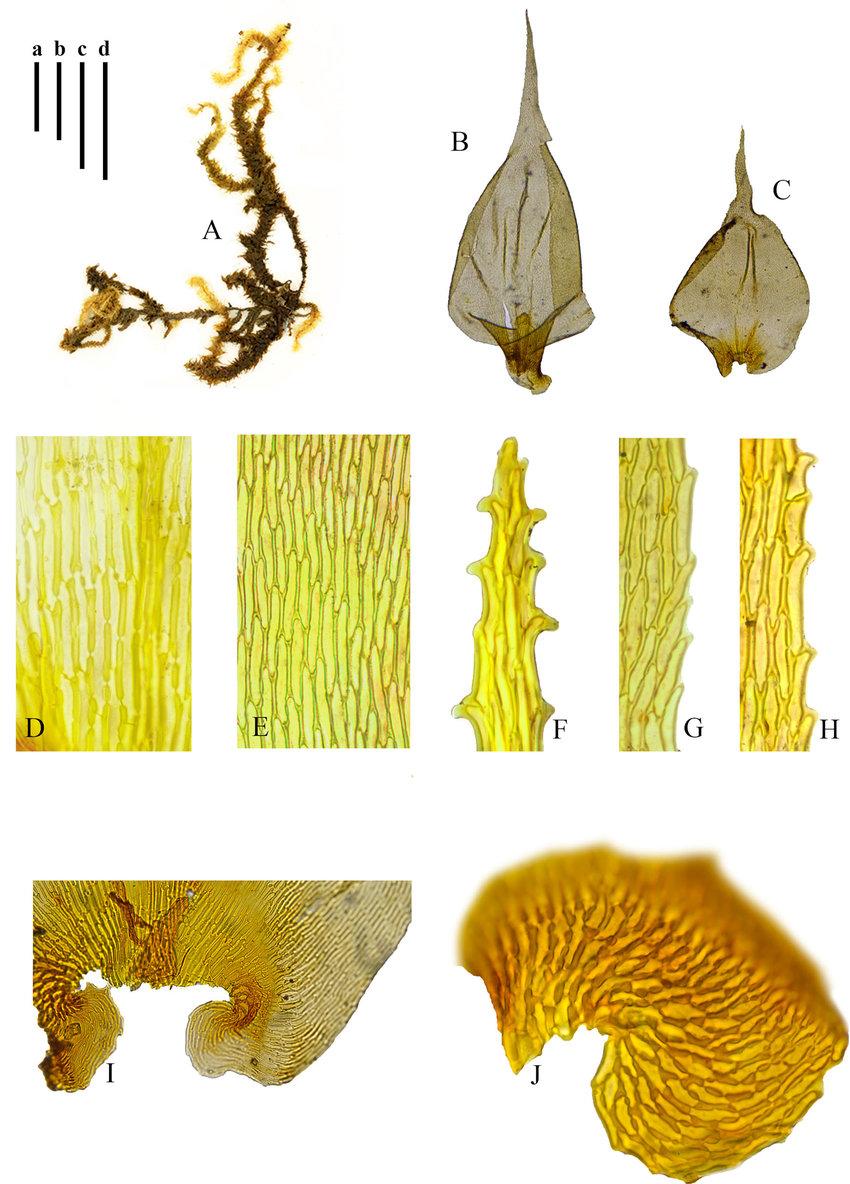
Barbella has a distinctive appearance that helps with identification. Its stems are pinnately branched and can grow up to 10 cm long. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape and have a

five-big-orange-cap-boletus-mushrooms-white-background-143445096.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/five-big-orange-cap-boletus-mushrooms-white-background-image143445096
reddish color, especially when dry (hence the species name rufifolioides meaning “red leaves”). Barbella is dioicous, meaning male and female reproductive structures are on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Barbella has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions of Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It typically grows at low to middle elevations in humid forests. Barbella is an epiphytic moss, meaning it grows on other plants like tree trunks and branches without harming the host. It prefers shaded habitats with high moisture

Meteoriella-soluta-Mitt-SOkamur-A-Plant-B-Branch-leaf-C-Stem-leaf-D-Basal.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Meteoriella-soluta-Mitt-SOkamur-A-Plant-B-Branch-leaf-C-Stem-leaf-D-Basal_fig4_348089946
.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

image_5dfca7095c286.png from: https://subscriptionboxramblings.com/2019/12/barbella-box-january-2020-spoiler-1/
Like other mosses, Barbella plays important ecological roles:
- Moisture retention: Barbella’s mat-like growth traps and retains moisture
- Nutrient cycling: It helps capture nutrients from the air and rain
- Microhabitats: Barbella provides shelter for small invertebrates
- Indicator species: Its presence or absence can indicate environmental conditions
Barbella has adaptations that help it thrive in its habitat:
- Pinnate branching maximizes surface area for moisture and nutrient uptake
- Reddish pigments may protect against UV radiation and help with photosynthesis in low light
- Rhizoids anchor the moss to its substrate
- Desiccation tolerance allows it to survive periodic drying

barbella-reviews-featured-1.jpg from: https://theunbox.com/barbella-box-review/

Barbella.png from: https://www.gonintendo.com/archives/246574-skylanders-imaginators-barbella-footage
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Meteoriaceae |
| Genus | Barbella |
| Species | B. rufifolioides |
| Plant type | Moss |
| Substrate | Epiphytic |
| Elevation range | Low to middle |
| Habitat | Humid forests |
| Distribution | Pantropical |
Conclusion
Barbella rufifolioides is a prime example of how even the smallest organisms can have fascinating features and important ecological roles. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and habitat preferences make it an interesting subject of study for botanists and moss enthusiasts alike. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, keep an eye out for this reddish moss on the trees around you. What other secrets might it hold?

ef593084b8f0cd746bd5de2a71ae497c.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/310466968048704251/