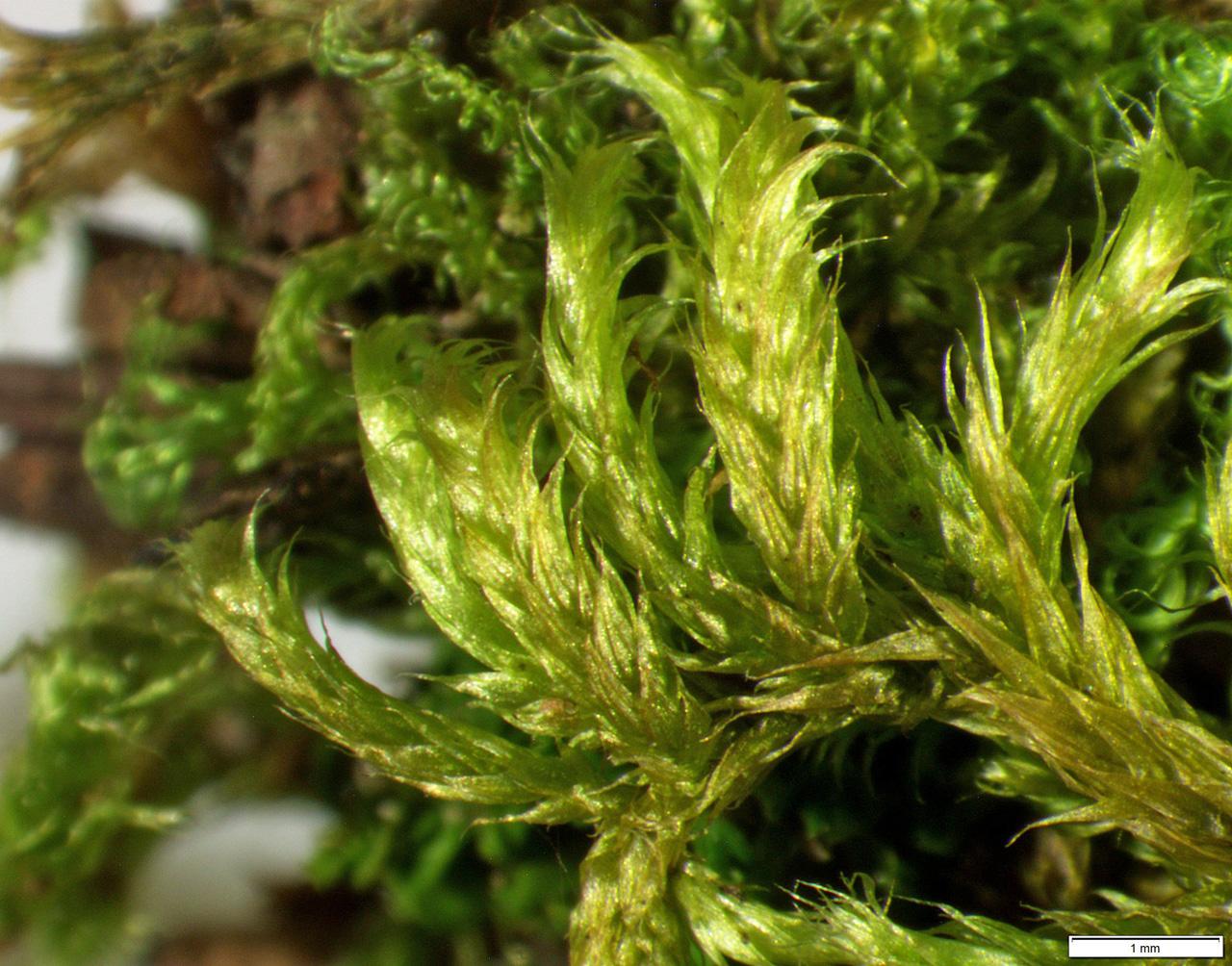

brachythecium_erythrorrhizon.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/brachythecium_erythrorrhizon.html
Introduction
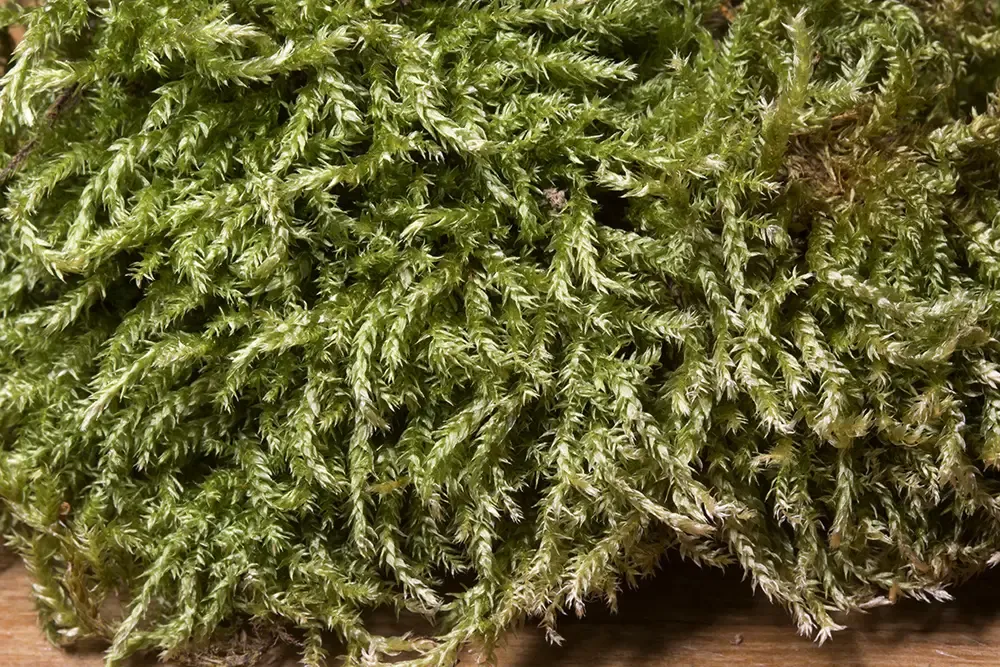

b361e6d28492f0ba03b1f18a3e4da86e.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/genero/brachythecium
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the
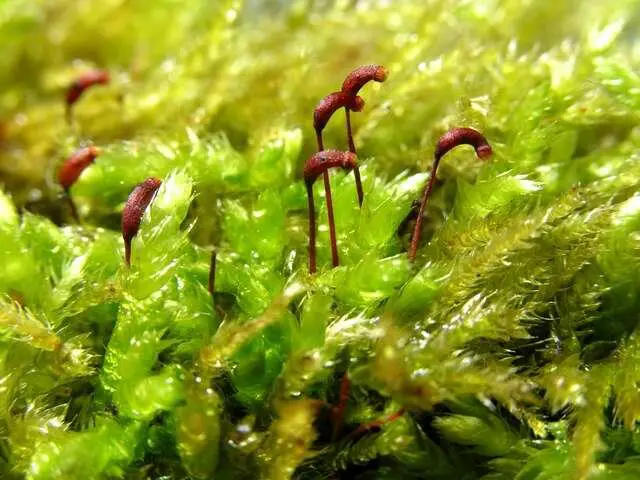

913.32424.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/853273/media
Brachythecium erythrorrhizon Schimp. moss. Belonging to the family Brachytheciaceae, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Background

rough-stalked-feather-moss-brachythecium-rutabulum-growing-on-wood-BAYND1.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-rough-stalked-feather-moss-brachythecium-rutabulum-growing-on-wood-23966461.html
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, let’s set the stage with some essential background information. Bryophytes, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These resilient organisms have played a crucial role in the colonization of terrestrial environments, paving the way for more complex plant life to thrive.
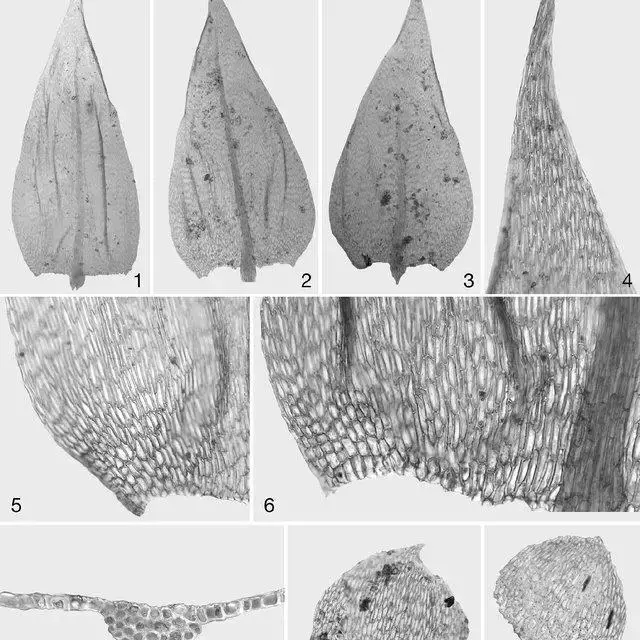
Brachythecium-mildeanum-1-9-VIT-32653-1-2-3-stem-leaves-4-stem-leaf-apex-5_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/48166175_New_data_on_distribution_morphology_and_habitat_of_brachythecium_Schimp_Schimp_Brachytheciaceae_Bryophyta_in_the_Iberian_Peninsula
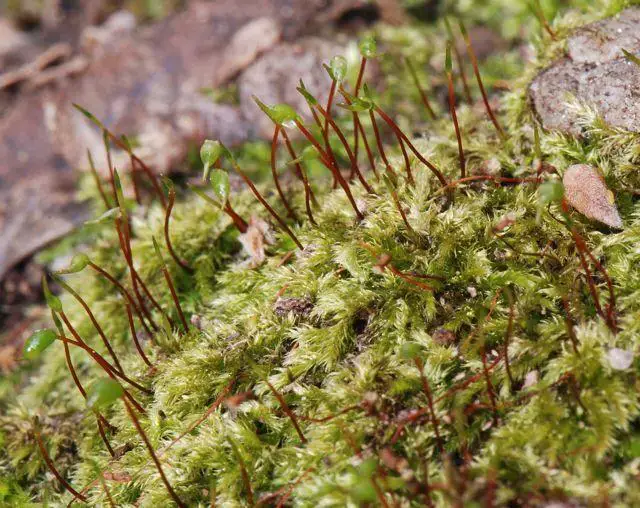

0251.jpeg from: https://ucjeps.berkeley.edu/CA_moss_eflora/genus_display.php?genus=Brachythecium
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
The Brachythecium erythrorrhizon Schimp. moss is a true marvel of nature, with its delicate yet intricate structure. This acrocarpous moss forms dense, glossy green to reddish-brown tufts or mats, often adorned with a striking reddish tinge – a characteristic that lends it its specific epithet, “erythrorrhizon” (meaning “red-rooted”).
One of the key identifying features of this moss is its curved, cylindrical capsules that emerge from the tips of the stems. These capsules, which contain the reproductive spores, are a testament to the incredible adaptations that have allowed bryophytes to thrive in diverse environments.
Global Distribution and Habitat
The Brachythecium erythrorrhizon Schimp. moss is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even urban environments, where it can be found growing on walls, pavements, and tree bases.
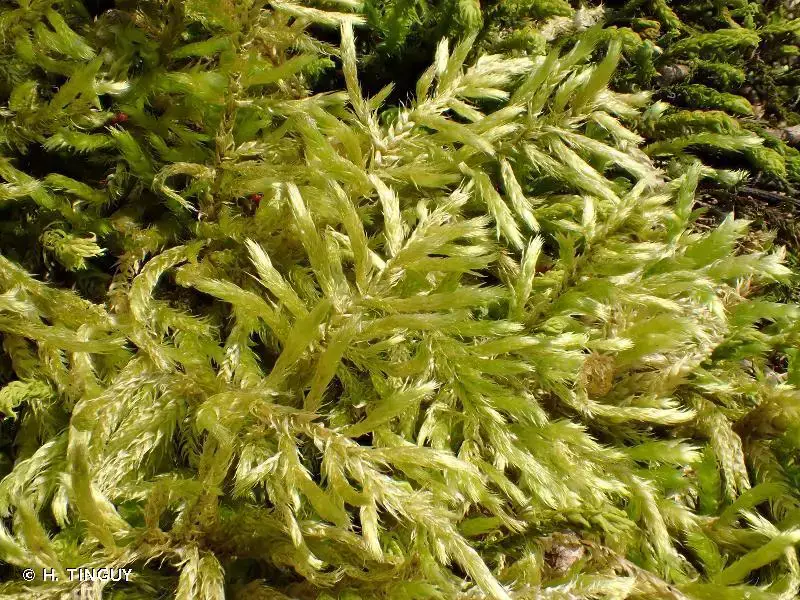

263620.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434456
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their diminutive size, mosses like the Brachythecium erythrorrhizon Schimp. play vital roles in their ecosystems. They act as pioneers, colonizing bare and disturbed areas, stabilizing soil, and creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, these mosses contribute to nutrient cycling, water retention, and even air purification.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation, a trait that has allowed it to thrive in a wide range of environments. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth once moisture returns.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, the Brachythecium erythrorrhizon Schimp. moss has been observed growing on historic buildings and monuments, contributing to their unique character and serving as an indicator of air quality. Researchers have also studied the moss’s ability to accumulate heavy metals, making it a potential biomonitor for environmental pollution.
Technical Table
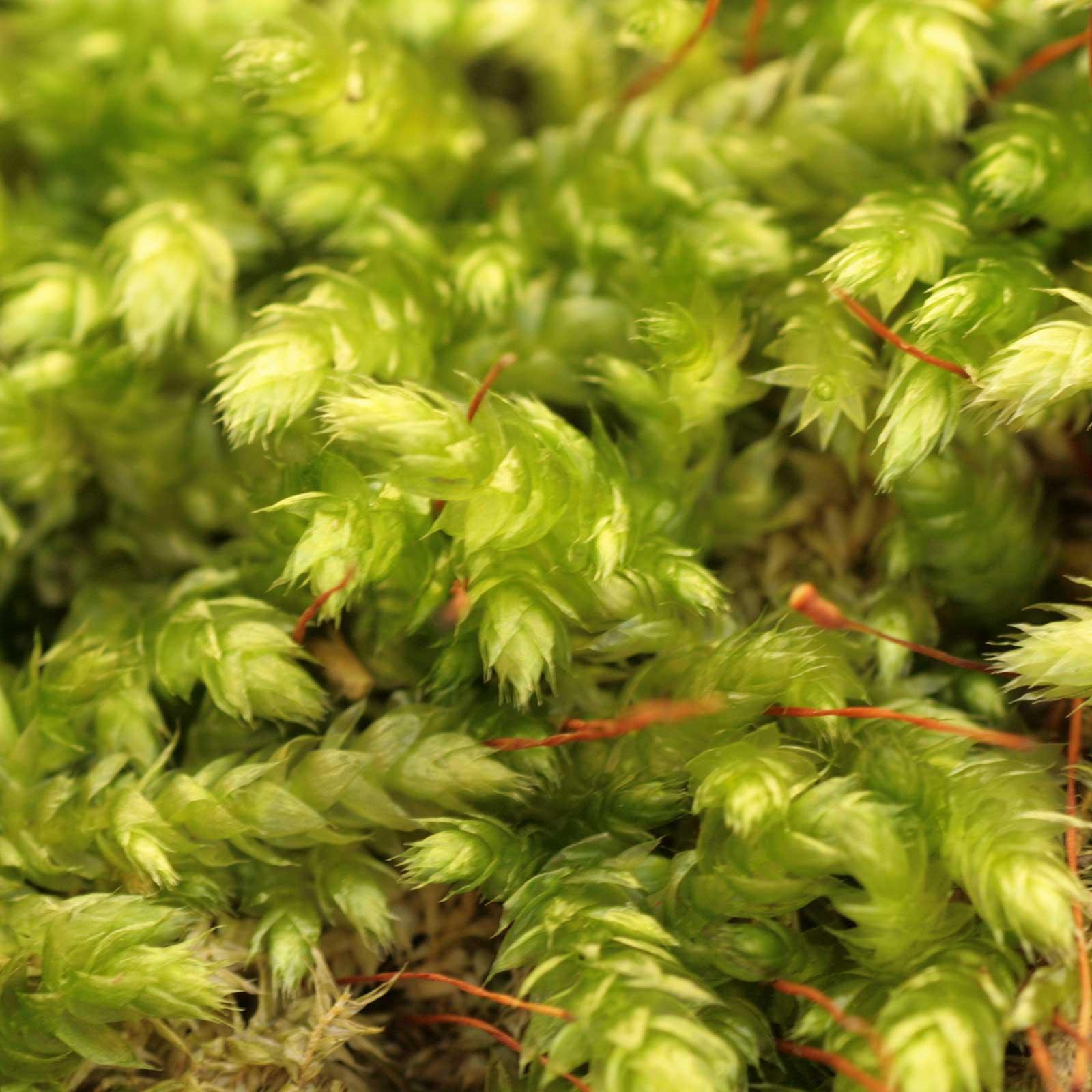

brachythecium-rutabulum-globuli.jpg from: https://www.remedia.at/shop/brachythecium-rutabulum/a9130320
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus | Brachythecium |
| Species | B. erythrorrhizon Schimp. |
| Common Name | Red-stemmed Feather Moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense tufts or mats |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged, overlapping |
| Capsule Shape | Curved, cylindrical |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, rocks, tree bases, urban environments |
| Distribution | Widespread across Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America |
Conclusion

mossbrachytheciumrutabulum4067.jpg from: https://www.brickfieldspark.org/data/mossroughstalkedfeather.htm
The Brachythecium erythrorrhizon Schimp. moss is a true testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments, contribute to ecosystem functions, and serve as an indicator of environmental conditions makes it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, we are reminded of the incredible diversity and complexity that exists within the smallest of life forms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a vibrant patch of moss, you’ll pause and ponder the remarkable journey of these ancient and resilient plants.
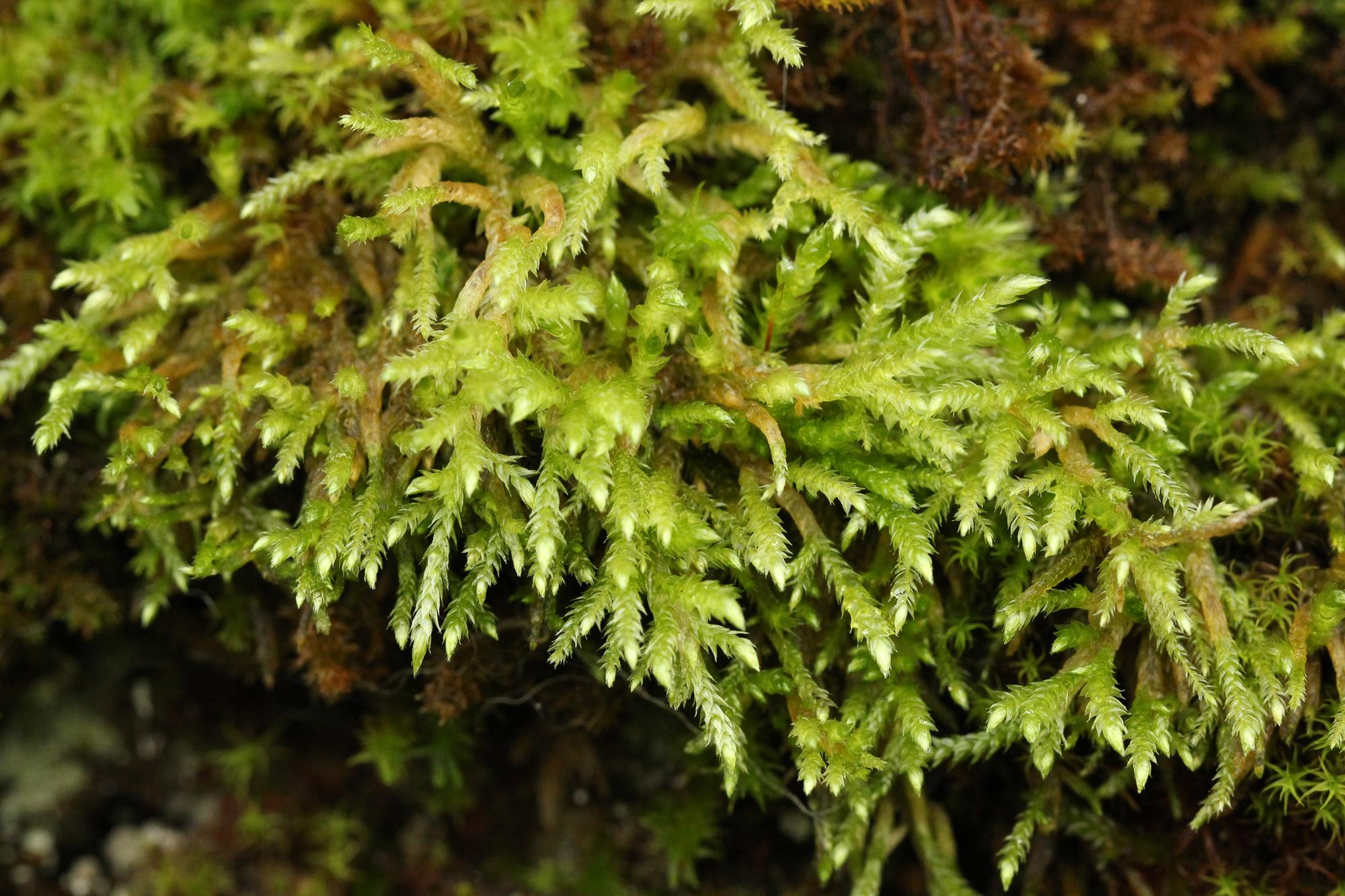

2017-01-14-11-56-46.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/brachythecium-rutabulum/