
large.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/1880025
Introduction
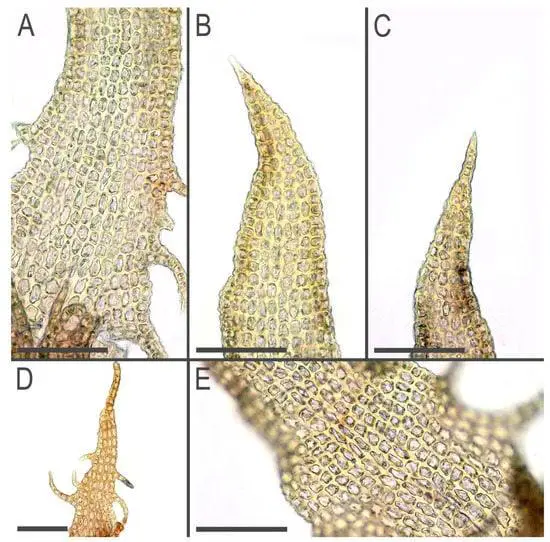
plants-11-03121-g009-550.jpg from: https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/11/22/3121
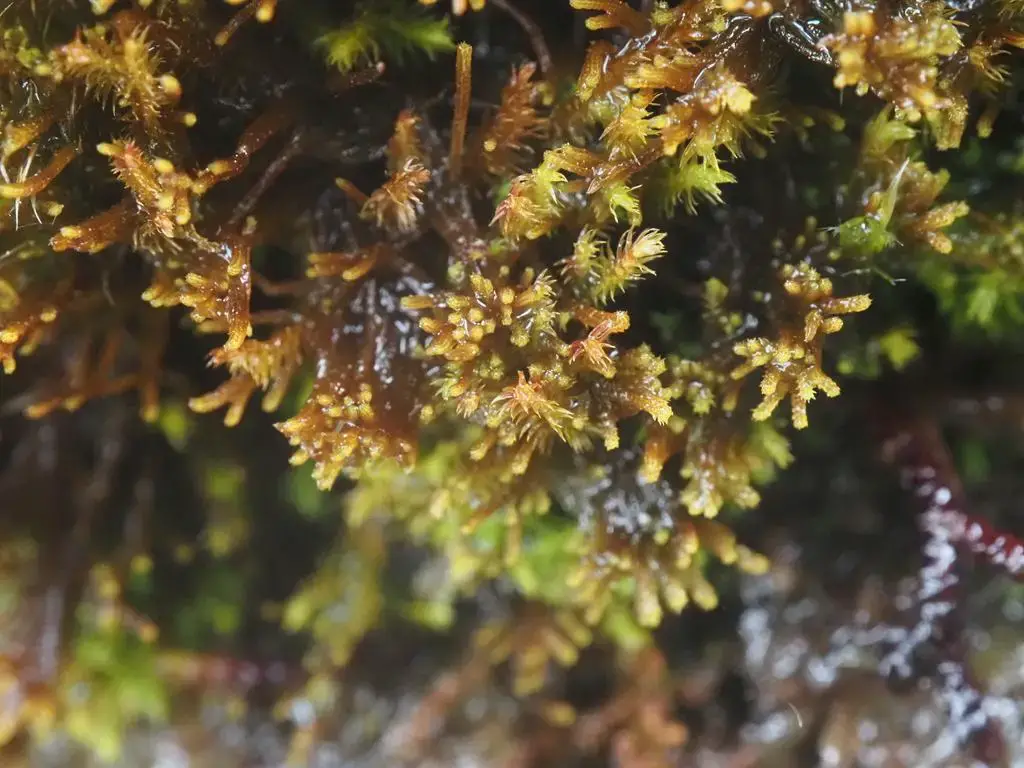
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one tiny moss stands out with its delicate beauty and resilience:

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365436760_Hidden_Diversity_within_Tetralophozia_filiformis_Marchantiophyta_Anastrophyllaceae_in_East_Asia
Tetralophozia filiformis (Steph.) Urmi. Belonging to the Anastrophyllaceae family, this
Tetralophozia-sibirica-Vilnet-et-Bakalin-1-plant-habit-dorsal-view-2-plant-habit.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Tetralophozia-sibirica-Vilnet-et-Bakalin-1-plant-habit-dorsal-view-2-plant-habit_fig3_365436760
moss is also commonly known as Tetralophozia. Despite its diminutive size, this fascinating plant plays a crucial role in various ecosystems, making it a subject of great interest for enthusiasts and researchers alike.

LAUR_cass_fili_1717105.jpg from: https://plantidtools.fieldmuseum.org/pt/rrc/catalogue/395500
Background
Tetralophozia filiformis is a member of the Marchantiophyta division, which encompasses liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. These ancient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. As part of the Jungermanniopsida class, Tetralophozia belongs to a group of leafy liverworts that exhibit intricate and captivating morphological features.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
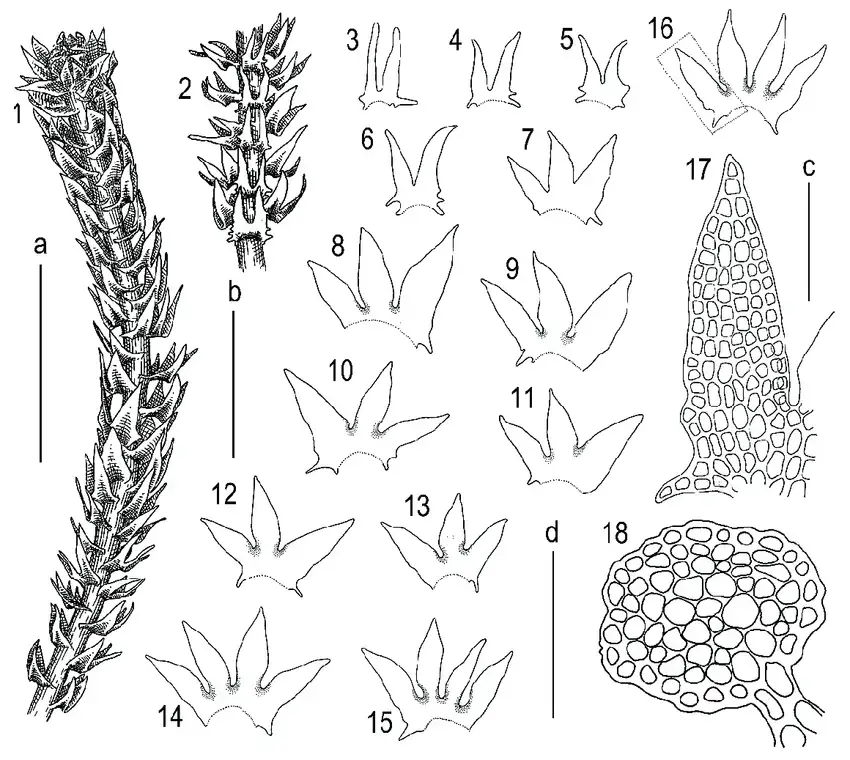
Tetralophozia filiformis is a tiny, thread-like moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its delicate stems are filiform (thread-like) and can reach up to 5 centimeters in length. The leaves are deeply divided into four lobes, giving the plant its distinctive appearance. These lobes are often curved or twisted, adding to the moss’s intricate beauty.
Global Distribution and Habitat

26549262050_5153c5f584_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/mercadanteweb/26549262050/
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe. It can be found in temperate and boreal regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. Tetralophozia filiformis thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as coniferous forests, bogs, and rock crevices. Its ability to colonize a wide range of habitats is a testament to its adaptability and resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Tetralophozia filiformis plays a vital role in its ecosystems. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. They also contribute to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other organisms to thrive.

plants-11-02590-g001-550.jpg from: https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/11/19/2590
One of the remarkable adaptations of Tetralophozia filiformis is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up and appearing lifeless. However, when moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its incredible resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found Tetralophozia filiformis to be a crucial component of old-growth forest ecosystems. These mosses formed intricate carpets on decaying logs and tree trunks, providing microhabitats for a diverse array of invertebrates and fungi.
Technical Table
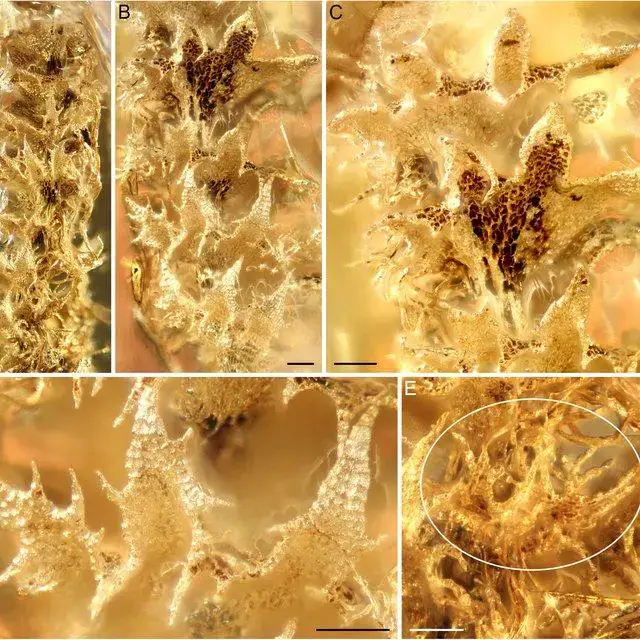
Holotype-of-Tetralophozia-groehnii-sp-nov-GPIH-4575-from-Baltic-amber-The-fossil-was_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Holotype-of-Tetralophozia-groehnii-sp-nov-GPIH-4575-from-Baltic-amber-The-fossil-was_fig1_283496446
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae
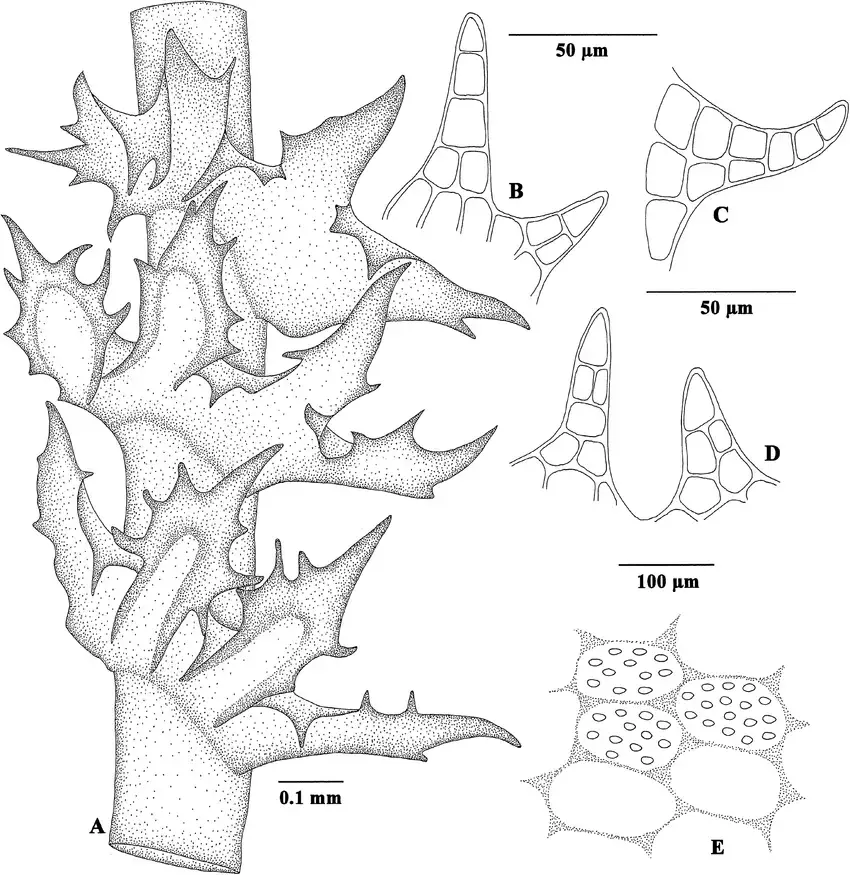 Reconstruction-of-Tetralophozia-groehnii-based-on-the-holotype-A-Portion-of-shoot-with.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Reconstruction-of-Tetralophozia-groehnii-based-on-the-holotype-A-Portion-of-shoot-with_fig6_283496446 |
| Genus | Tetralophozia |
| Species | filiformis |
| Common Name | Tetralophozia |
| Growth Form | Dense mats or cushions |
| Stem Length | Up to 5 cm |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided into four lobes |
Conclusion
Tetralophozia filiformis (Steph.) Urmi, a remarkable moss of the
capitellid-thread-worm-heteromastus-filiformis-EBH955.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/heteromastus-filiformis.html
Anastrophyllaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its delicate beauty, resilience, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these tiny yet vital components of our ecosystems?