cephalozia_leucantha1.jpg from: https://luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/sammalet/hapsipihtisammal.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Cephalozia leucantha Spruce moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Cephaloziaceae family. This unassuming yet intriguing moss, commonly referred to as Cephalozia, has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the details of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Cephalozia leucantha Spruce belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. These bryophytes play crucial roles in various ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling, soil formation, and providing microhabitats for other organisms.

spruce-fir-moss-spider.jpg from: https://fws.gov/species/spruce-fir-moss-spider-microhexura-montivaga
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Cephalozia leucantha Spruce is a small, delicate moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the substrate it inhabits. Its stems are slender and creeping, with leaves arranged in two rows along the stem. These leaves are deeply divided into two or more lobes, giving the moss a distinctive feathery appearance.
One of the key identifying features of Cephalozia leucantha Spruce is its white or pale green coloration, which sets it apart from many other mosses. This unique hue is attributed to the presence of specialized cells that reflect light, providing the moss with a striking appearance.

d6f618db91e93931042f9a9c2bcf4fd8–mountain.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.co.uk/pin/cephalozia-catenulata–308637380693938768/
Global Distribution and Habitat
Cephalozia leucantha Spruce is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as coniferous forests, bogs, and stream banks. This moss prefers acidic soils and is often found growing on decaying logs, stumps, or the base of trees.

growing-salvia-leucantha-5076973-05-88e217710f5446c6b21c18b963ac73ea.jpg from: https://www.thespruce.com/growing-salvia-leucantha-5076973
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Cephalozia leucantha Spruce plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to the formation of soil and the establishment of other plant communities. Its dense mats help retain moisture and provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Cephalozia leucantha Spruce is its ability to survive desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a dormant state, curling up its leaves and reducing metabolic activity. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience in challenging environmental conditions.
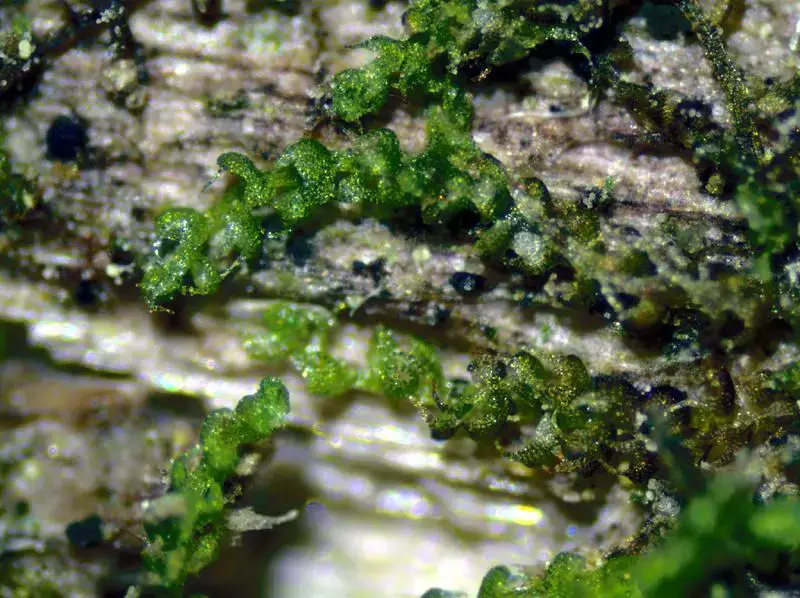

C.-bicuspidata-AH-315-l.jpg from: https://sites.cortland.edu/bryophytes/field-guide/liverworts/cephalozia-bicuspidata-l-dumort/
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Cephalozia leucantha Spruce played a crucial role in facilitating the growth and establishment of certain coniferous tree seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microclimate and retained moisture, creating favorable conditions for the seedlings to thrive.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Cephaloziaceae |
| Genus | Cephalozia |
| Species | leucantha |
| Common Name | Cephalozia |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows along the stem |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided into lobes |
| Color | White or pale green |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia |
Conclusion
The Cephalozia leucantha Spruce moss, a member of the Cephaloziaceae family, is a remarkable bryophyte that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its unique morphology, ecological roles, and adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore the intricate world of mosses, we are reminded of the incredible diversity and resilience of these often overlooked organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a dense mat of Cephalozia leucantha Spruce, you’ll pause and reflect on the remarkable journey of this unassuming yet extraordinary moss.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the smallest wonders, what other hidden marvels might we be missing, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?