
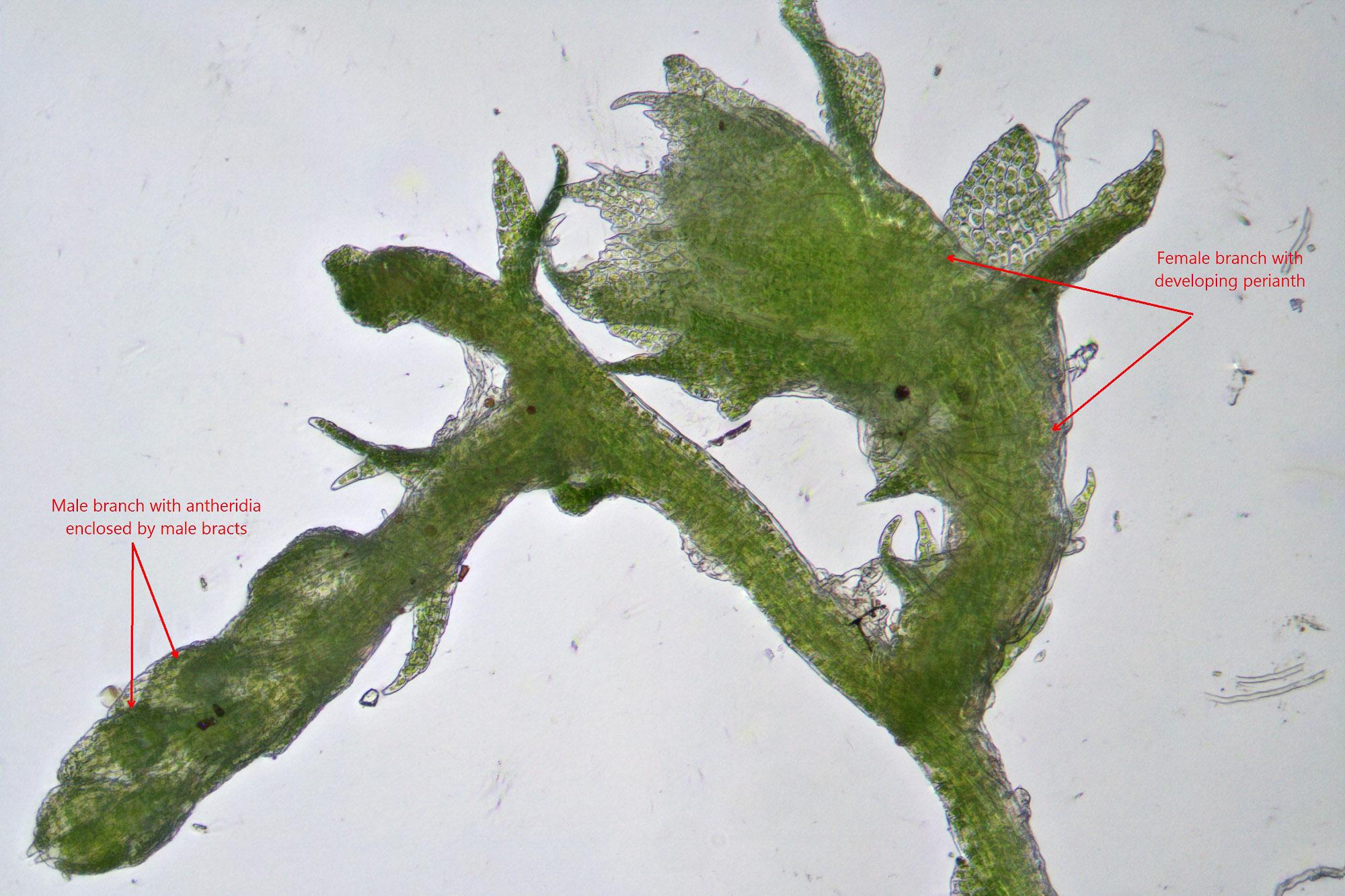
Cephaloziella-stellulifera_VC7023-04-03-15-26-49-scaled.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/cephaloziella-stellulifera/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Cephaloziella stellulifera var. limprichtii Moss
Introduction
The world of mosses is full of incredible diversity and fascinating species. One particularly interesting moss is Cephaloziella stellulifera var. limprichtii (Warnst.) Macvicar, a tiny but mighty plant in the Cephaloziellaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this unique moss, exploring its morphology, global distribution, ecological roles, and more. Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of
2021-11-09-16-55-07.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/cephaloziella-hampeana/
Cephaloziella!
Background on Mosses
Before we jump into specifics about C. stellulifera var. limprichtii, let’s cover some moss basics. Mosses are small, non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta. Unlike other land plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids and thread-like rhizoids that anchor them to substrates. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in diverse habitats worldwide, from arctic tundra to tropical rainforests.

3327-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19936

3327-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19934
Morphology and Identification
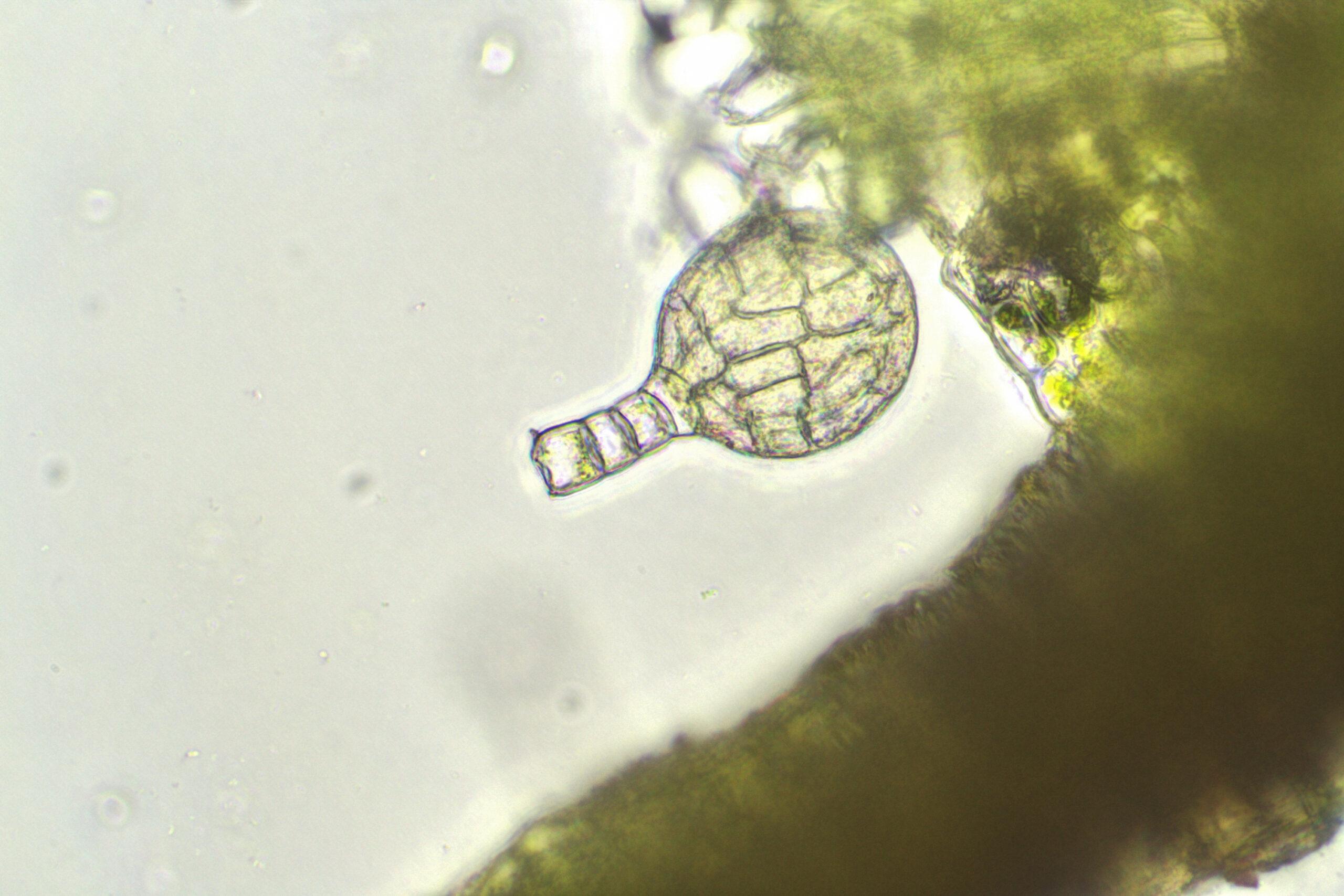
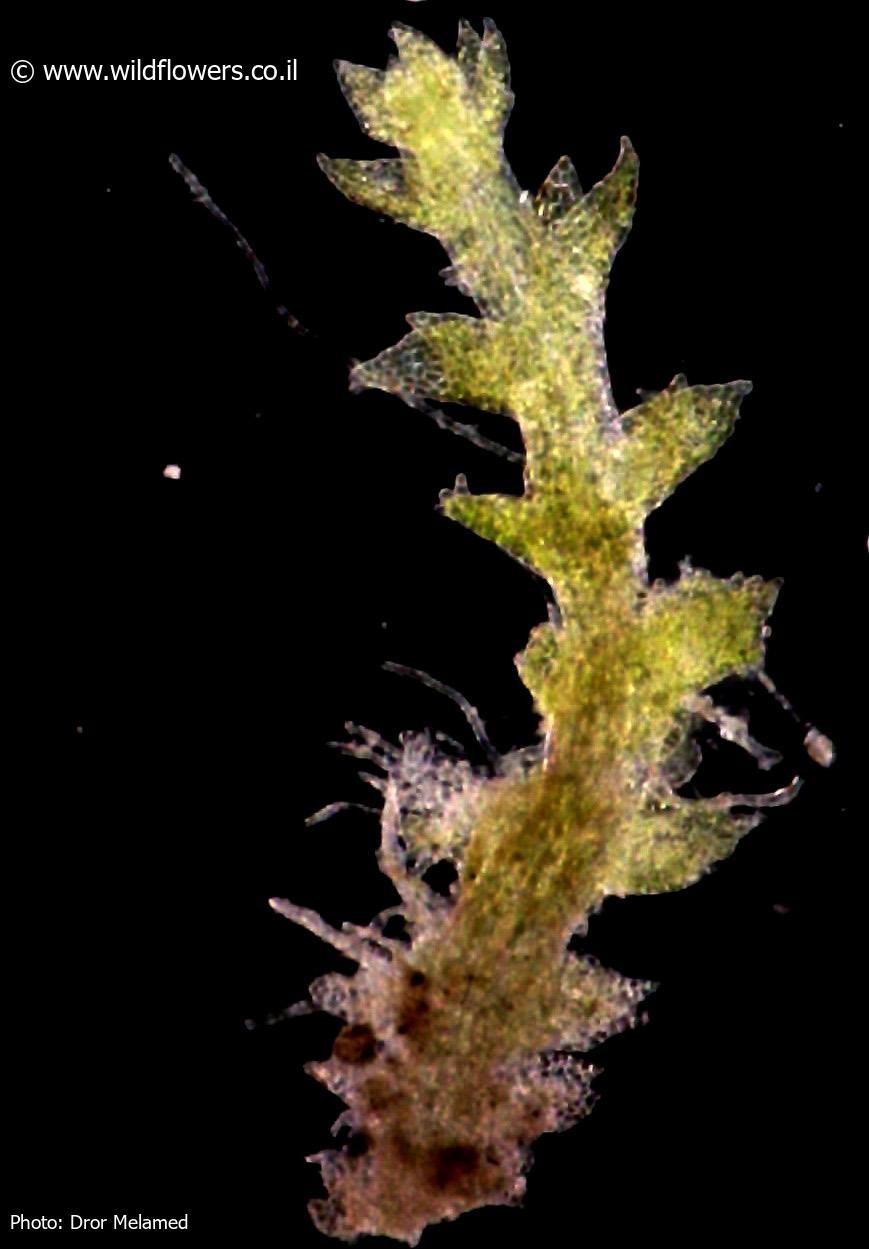
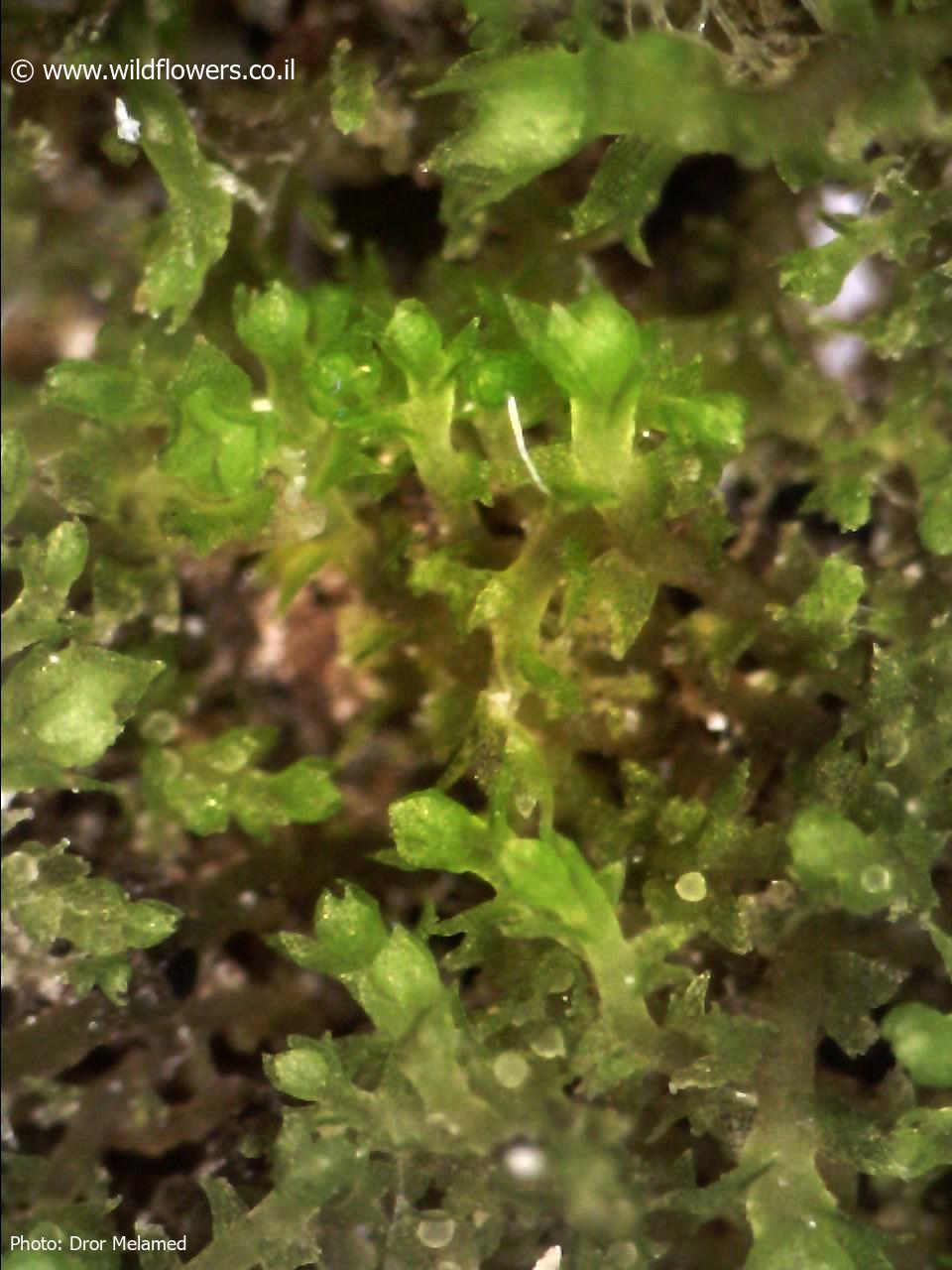
Cephaloziella stellulifera var. limprichtii is a diminutive moss, typically growing in dense mats or patches. Its phyllids are minute, only 0.2-0.4 mm long, and are arranged in two rows along the stem. The phyllids have a characteristic stellate (star-shaped) appearance due to their deeply divided lobes. This stellate shape is a key identification feature and is referenced in the species epithet “stellulifera“, meaning “star-bearing”.
Under a microscope, additional distinctive traits of C. stellulifera var. limprichtii can be observed. Its phyllid cells are small with evenly thickened walls. Specialized oil bodies are present in each leaf cell, appearing as grayish, granular structures. The underleaves (modified leaves on the underside of the stem) are small or absent.
Global Distribution and Habitat
C. stellulifera var. limprichtii has a scattered global distribution, with records from Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It is found in a variety of habitats, including:
- Soil banks
- Rotting logs and stumps
- Tree bases
- Damp rocks
- Peaty substrates
This adaptable moss often grows in association with other bryophytes and can tolerate moderate shade to partial sun exposure. In some regions, it is considered an indicator of ancient woodland habitats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, C. stellulifera var. limprichtii plays important ecological roles:
Nutrient cycling: Mosses trap and store nutrients, releasing them slowly over time. This helps regulate nutrient availability in ecosystems.
Moisture retention: The dense growth form of mosses helps retain moisture in the environment, reducing evaporation and buffering against drought.
Microhabitats: Moss mats provide shelter and microhabitats for diverse invertebrates and microorganisms.
Erosion control: By stabilizing soil surfaces, mosses help prevent erosion.
C. stellulifera var. limprichtii has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its preferred habitats. Its small size and dense growth form help it retain moisture and protect against desiccation. The stellate shape of its phyllids increases surface area for photosynthesis and gas exchange. Its ability to tolerate a range of light levels and substrates makes it adaptable to various microenvironments.
Conclusion
Cephaloziella stellulifera var. limprichtii may be a tiny moss, but it is a fascinating and ecologically important species. From its star-shaped phyllids to its global distribution, this mighty moss showcases the incredible diversity within the Marchantiophyta. Next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot a patch of Cephaloziella starring back at you! What other small wonders of the plant world have you discovered?