
19421751500_394c1ef6e0_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/19421751500/
Introduction
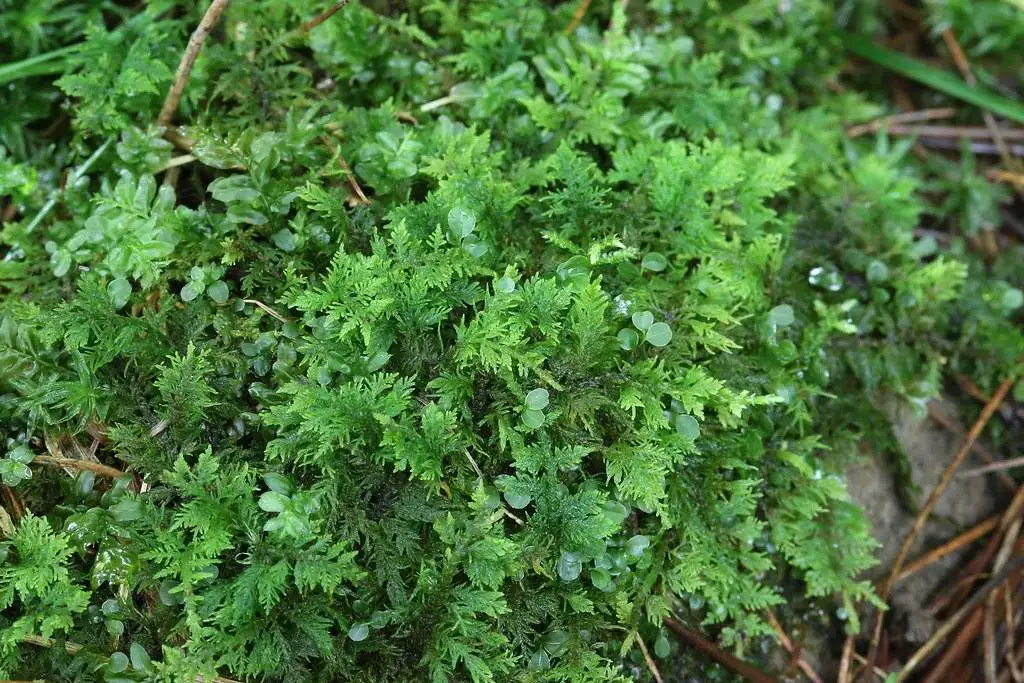
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Thuidium recognitum (Hedw.) Lindb. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Thuidiaceae

17318599084_34c88d3490_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/17318599084/
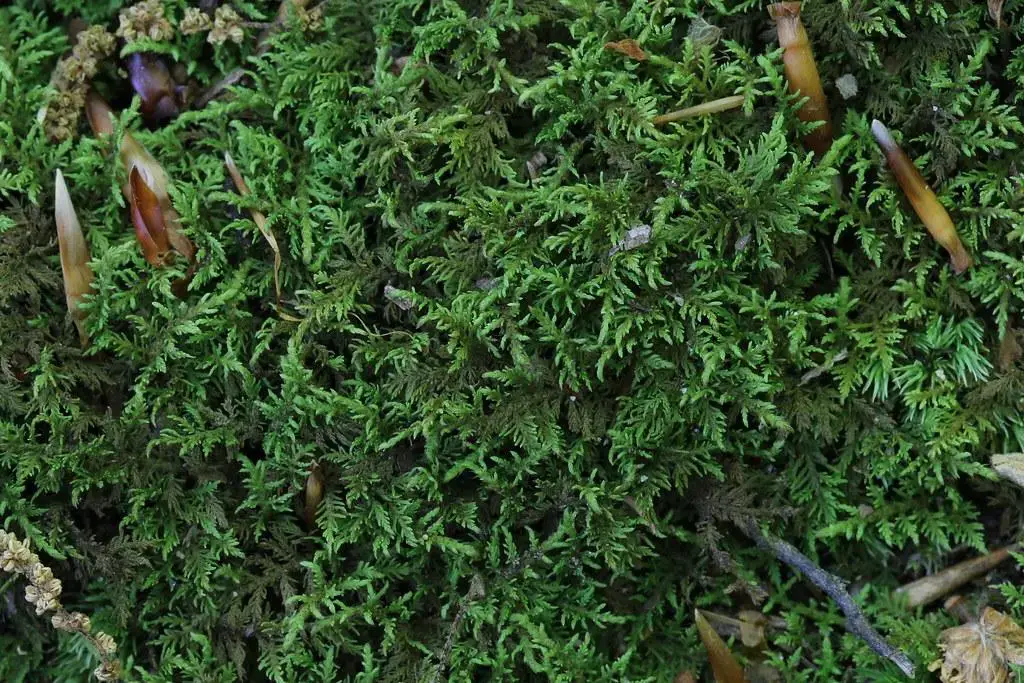
family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its intricate beauty and ecological significance.
209924.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5425
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Thuidium recognitum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

thuidium-recognitum-known-as-lesser-tamarisk-moss-or-thuidium-moss-2E3YR5C.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/thuidium-recognitum-known-as-lesser-tamarisk-moss-or-thuidium-moss-image398293320.html
Thuidium recognitum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its vibrant green hue and delicate, feathery appearance make it a true delight to behold. The stems are irregularly branched, and the leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern, giving the plant a distinct, almost lacy texture.

17318598984_7737bf582d_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/17318598984/
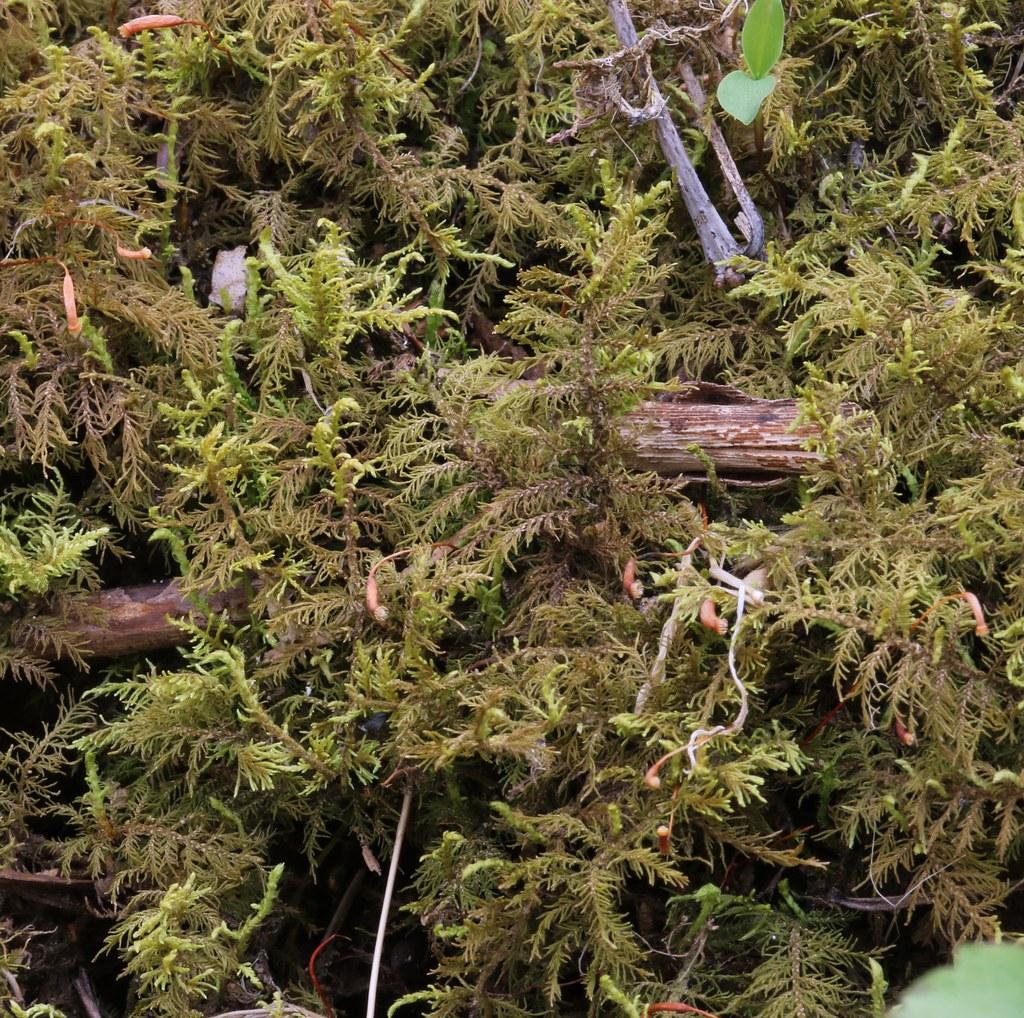
One of the most striking features of Thuidium recognitum is its paraphyllia, which are small, leaf-like structures found on the stems. These paraphyllia are often used as a key identifying characteristic for this species within the Thuidiaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Thuidium recognitum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as forests, woodlands, and even urban areas with suitable microclimates.
This moss prefers acidic soils and is commonly found growing on decaying logs, stumps, and the base of trees. Its ability to colonize these substrates highlights its role in the decomposition process and nutrient cycling within ecosystems.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Thuidium recognitum plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of its habitat. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves.
Moreover,
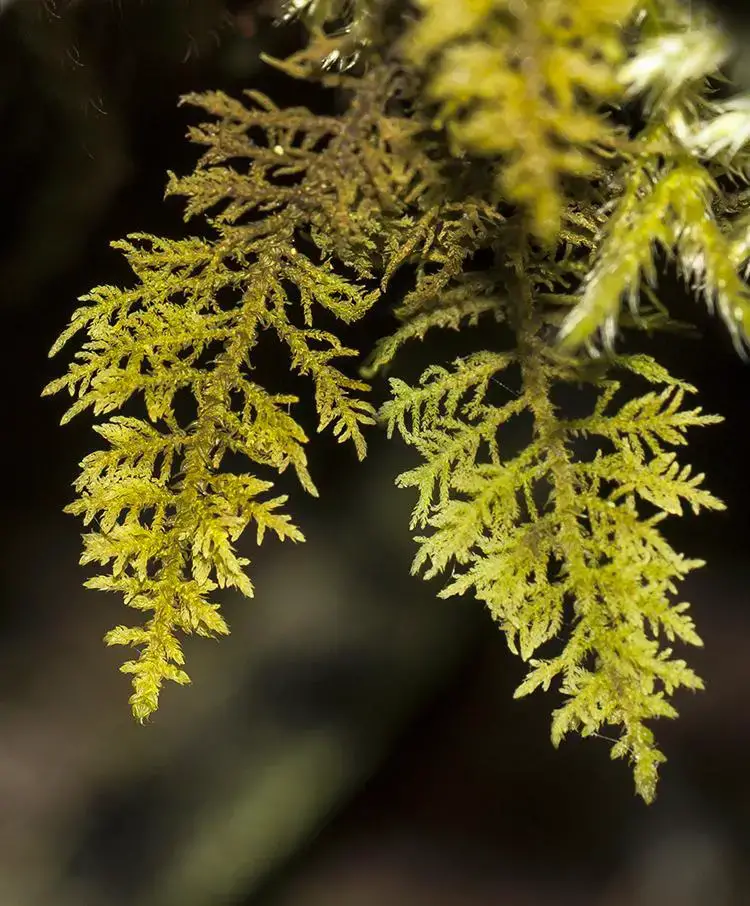

595275_a576389f.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/595275.html
Thuidium recognitum is highly efficient at absorbing and retaining moisture, acting as a natural sponge in its environment. This trait not only benefits the moss itself but also provides a moist microhabitat for various invertebrates, such as insects and soil-dwelling organisms.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Thuidium recognitum played a crucial role in facilitating the growth and establishment of coniferous tree seedlings. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and create a favorable microclimate contributed to the successful regeneration of these forests.
Technical Table
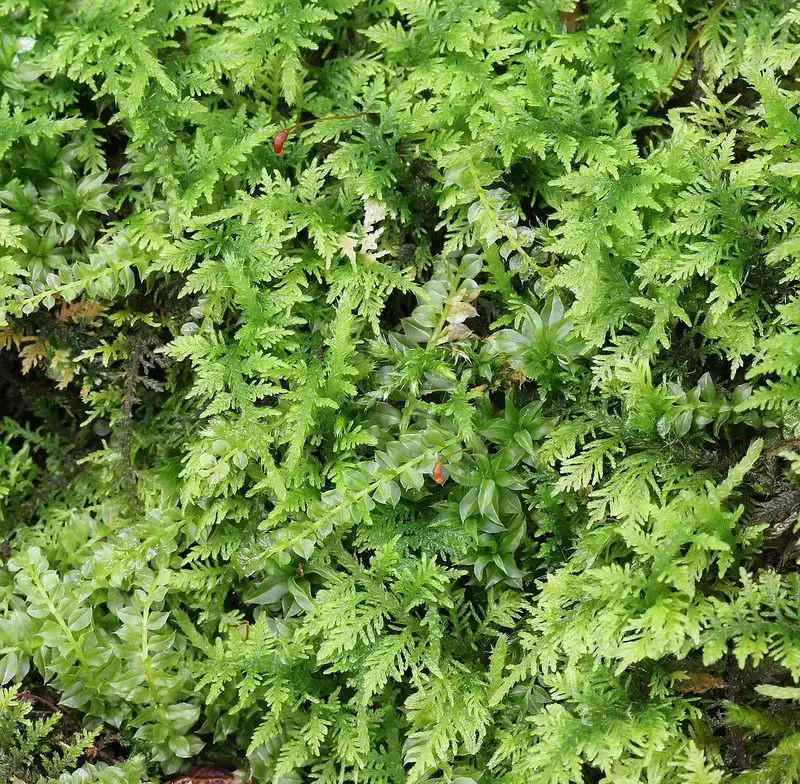

jim__stasz_19614292951_2319562dca_c.jpg from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/viewSpecies.php?species=10809
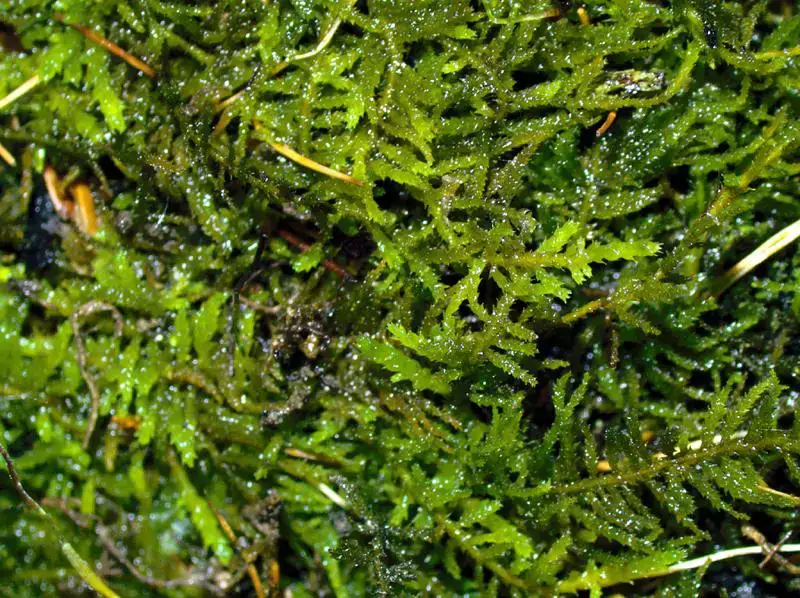

Thuidium-recognitum-AH-259.jpg from: https://sites.cortland.edu/bryophytes/field-guide/mosses/pleurocarp/thuidium-recognitum/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta
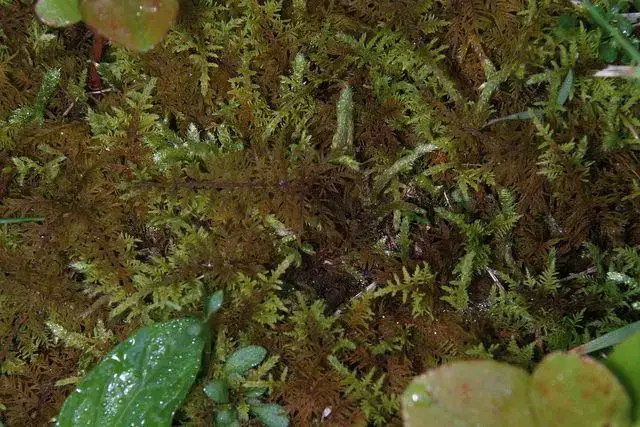 jim__stasz_14547585687_c30b820c9c_z.jpg from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/view/10809 |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Thuidiaceae |
| Genus | Thuidium |
| Species | Thuidium recognitum (Hedw.) Lindb.
 120px-Thuidium_recognitum_(a%2C_141735-474124)_8846.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Thuidium_recognitum |
| Common Name | Thuidium Moss |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forests, woodlands) |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Africa |
Conclusion
The Thuidium recognitum (Hedw.) Lindb. moss, a member of the Thuidiaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate beauty, ecological significance, and adaptations make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?