Repartition-de-Phascum-cuspidatum-Schreb-ex-Hedw-a-Porquerolles.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Repartition-de-Phascum-cuspidatum-Schreb-ex-Hedw-a-Porquerolles_fig74_328841440
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Phascum cuspidatum Schreb. ex Hedw. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Phascum, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Phascum cuspidatum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content

46194077.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/233232045?_popup=1
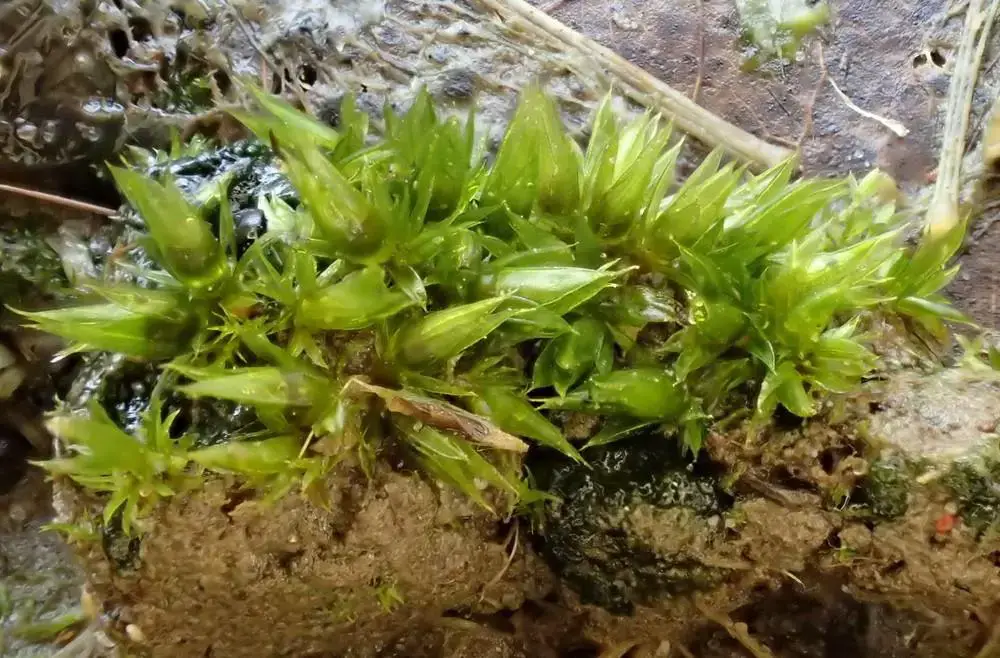
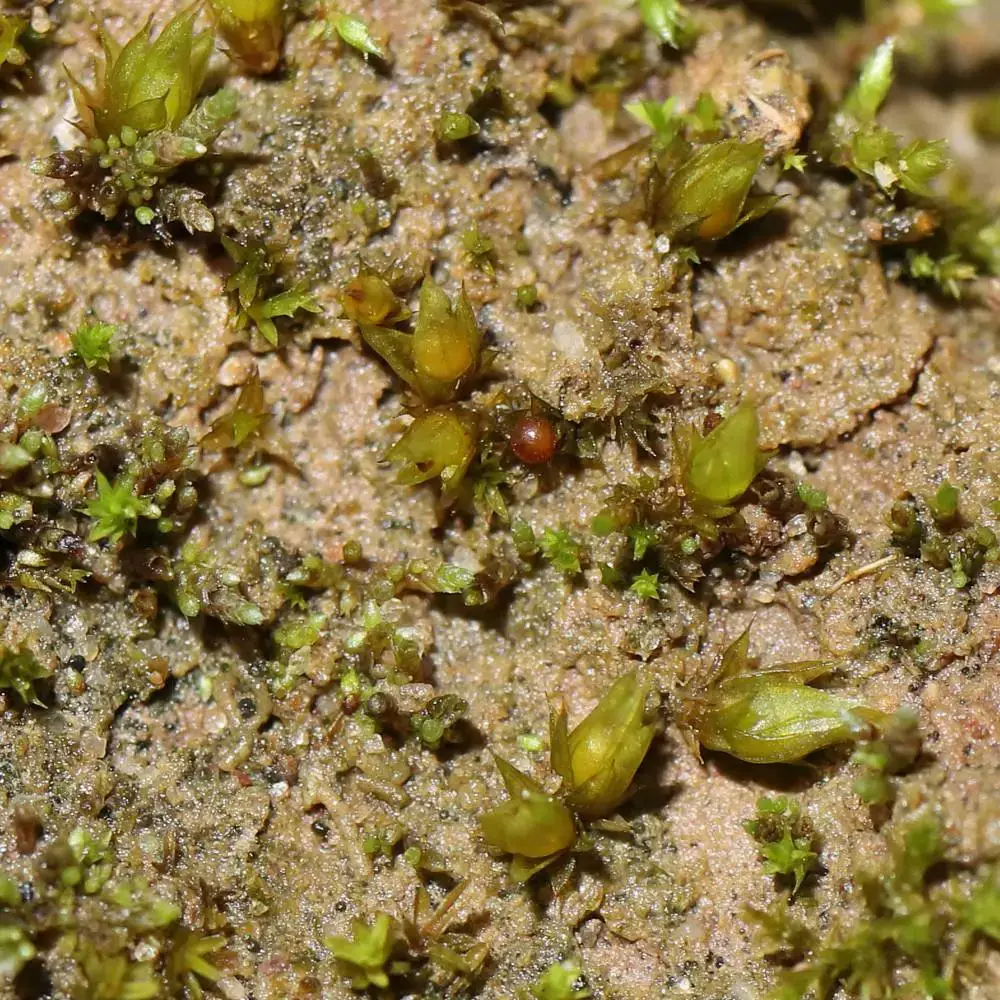
Morphology and Identification
Phascum cuspidatum is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts. Its leaves are ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive cuspidate (gradually tapering to a fine point) apex. The leaf margins are entire, and the costa (midrib) extends to the leaf apex or slightly beyond. The sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) are relatively large compared to the size of the plant, with a pyriform (pear-shaped) capsule that becomes reddish-brown when mature.
Global Distribution and Habitat

45594192.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/231236729?_popup=1
This moss has a cosmopolitan distribution, meaning it can be found on almost every continent. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, including disturbed areas, bare soil, rock crevices, and even on walls and roofs. Phascum cuspidatum is particularly well-adapted to dry and nutrient-poor environments, making it a pioneer species in colonizing newly exposed substrates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Phascum cuspidatum plays a vital role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its ability to withstand desiccation and rapidly rehydrate makes it an excellent indicator of environmental conditions.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Phascum cuspidatum is its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, effectively shutting down its metabolic processes until moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows it to survive in harsh, arid environments where other plants would perish.
Case Studies/Examples
Phascum cuspidatum has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, particularly in the fields of bryology and ecology. For instance, researchers have investigated its role in soil stabilization and revegetation efforts in areas affected by mining or other disturbances. Additionally, its desiccation tolerance has been studied extensively, providing insights into the mechanisms that allow plants to survive extreme drought conditions.
Technical Table
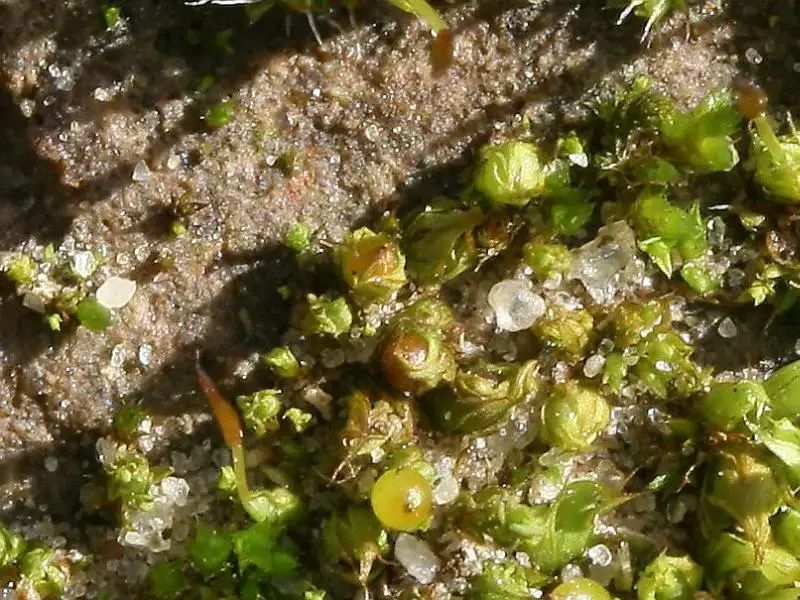

Phascum_cuspidatum.jpeg from: https://de-academic.com/dic.nsf/dewiki/1102609
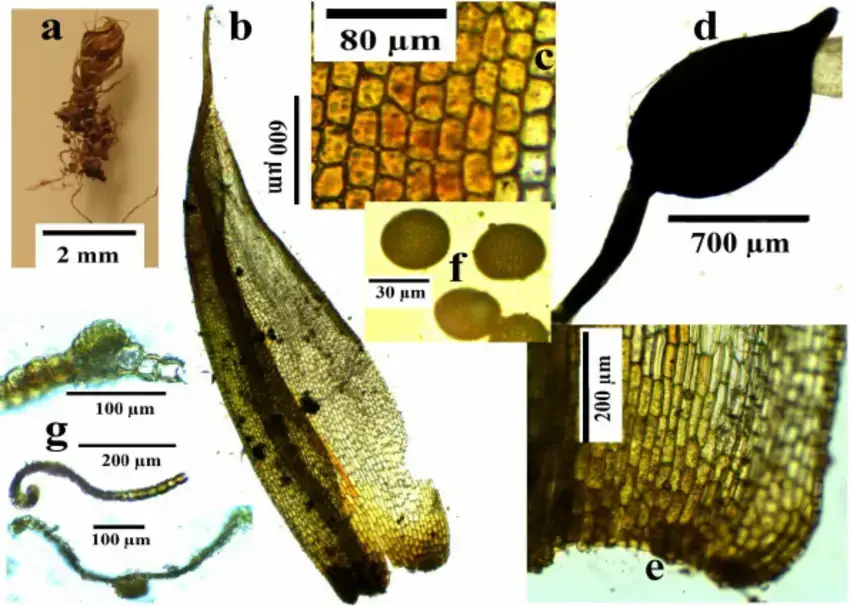
Characteristic-features-of-Phascum-cuspidatum-Image-by-Serhat-URSAVAS-a-Plant-b.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Characteristic-features-of-Phascum-cuspidatum-Image-by-Serhat-URSAVAS-a-Plant-b_fig9_268502605
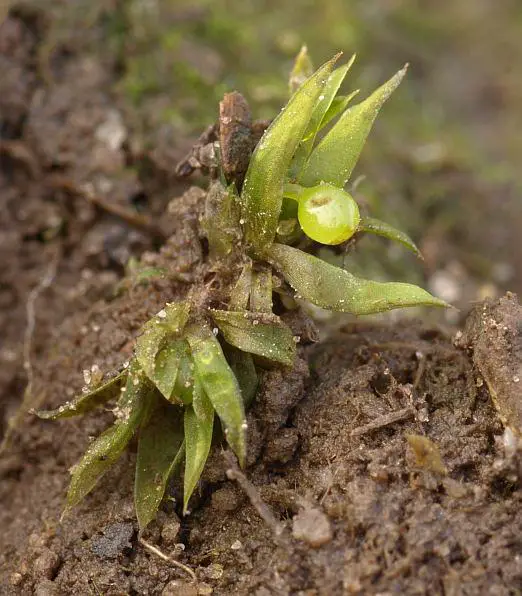

fa443408.jpg from: https://www.naturbasen.dk/forum-arkiv/traad?id=443408
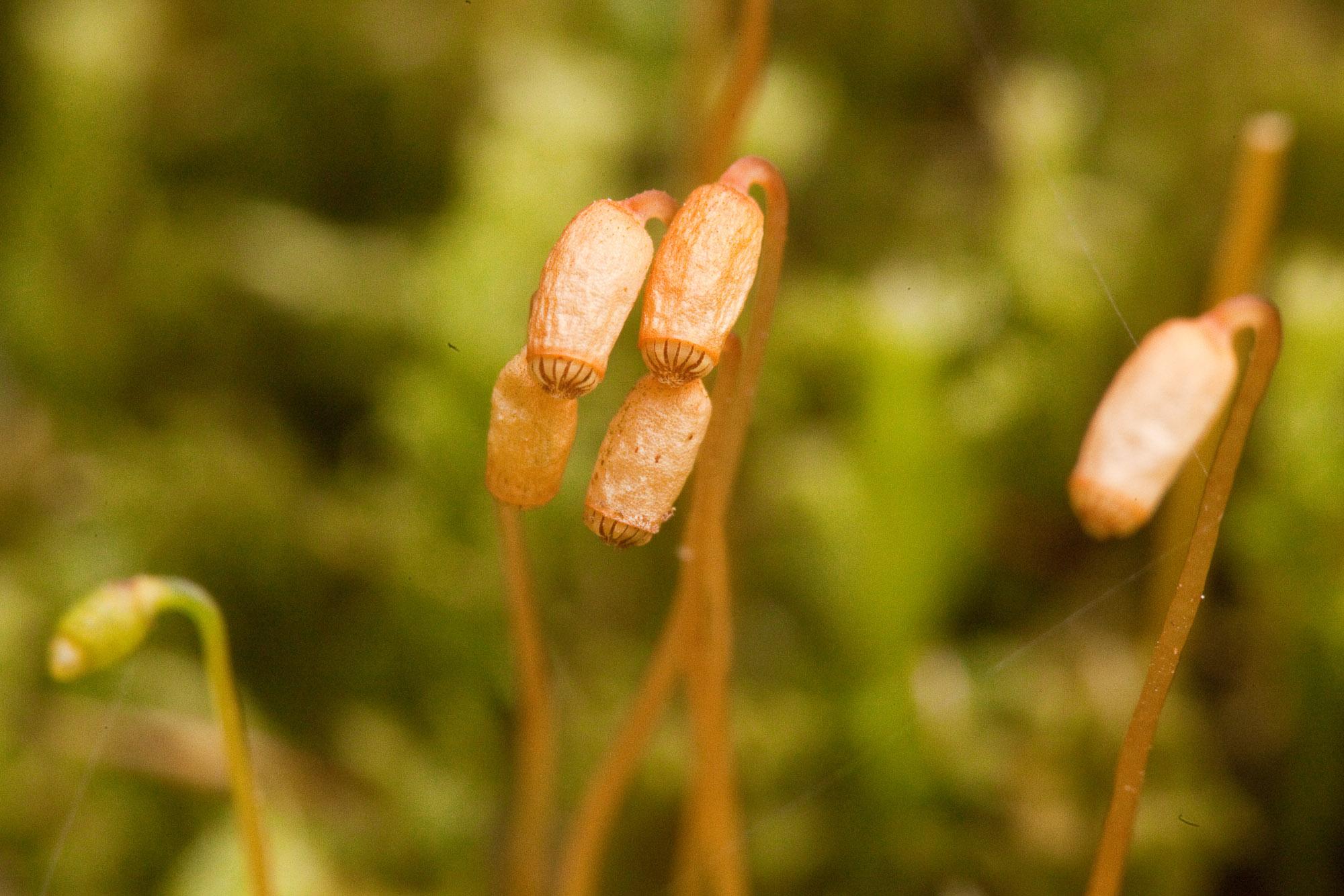

Plagiomnium-cuspidatum-8.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-plagiomnium-cuspidatum/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Phascum |
| Species | Phascum cuspidatum Schreb. ex Hedw. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense cushions |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate, cuspidate apex |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Costa | Extending to leaf apex or slightly beyond |
| Sporophyte | Pyriform capsule, reddish-brown when mature |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
| Habitat | Disturbed areas, bare soil, rock crevices, walls, roofs |
| Ecological Role | Pioneer species, soil stabilization, moisture retention |
| Adaptation | Desiccation tolerance |
Conclusion
Phascum cuspidatum Schreb. ex Hedw., a member of the Pottiaceae family and commonly known as Phascum, is a remarkable moss that has captured the attention of enthusiasts and scientists alike. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study. Moreover, its ability to withstand extreme desiccation and rapidly rehydrate serves as a testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes.
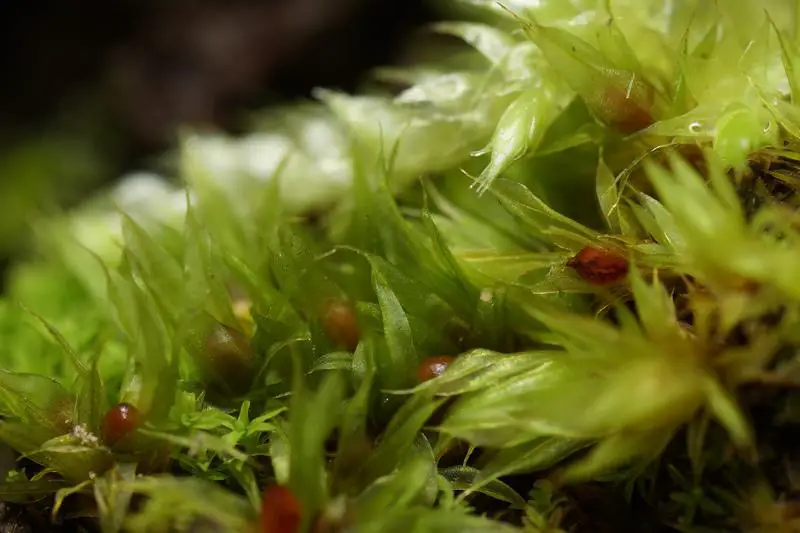

1046795.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/863726.html
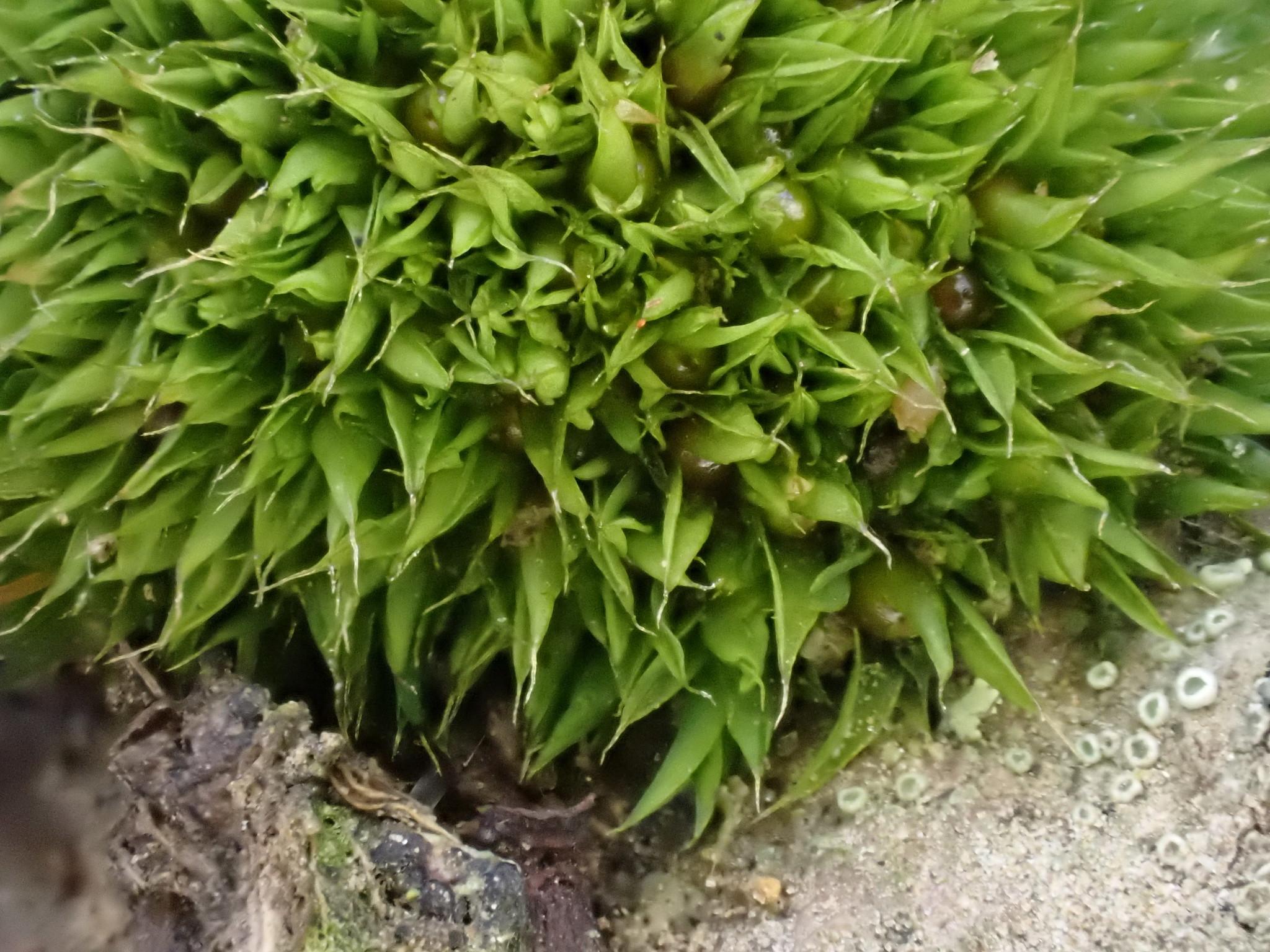

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/8376948

Botanical_Moss_Curtis_William_PhascumSubulatumandPhascumCuspidatum_FloraLondonensis_c1817_470x285mm_p140x175mm_530x@2x.jpg from: https://antiquarianprintshop.com/products/botanical-curtis-william-moss-phascum-subulatum-and-phascum-cuspidatum-flora-londinensis-c1817
As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of the natural world, Phascum cuspidatum stands as a reminder of the intricate beauty and complexity that can be found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter this unassuming moss, you’ll pause and reflect on the incredible journey it has undertaken, from the dawn of land plants to the present day, persevering through countless environmental challenges and playing a vital role in the intricate web of life.