
379880.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6460
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Gongylanthus ericetorum (Raddi) Nees, a captivating moss species from the Southbyaceae family, commonly known as Gongylanthus. Prepare to be enchanted by the intricate beauty and resilience of this tiny, yet mighty plant.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Gongylanthus ericetorum belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, also known as liverworts, and the class Jungermanniopsida. These unassuming plants have been around for millions of years, quietly thriving in their own unique way.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
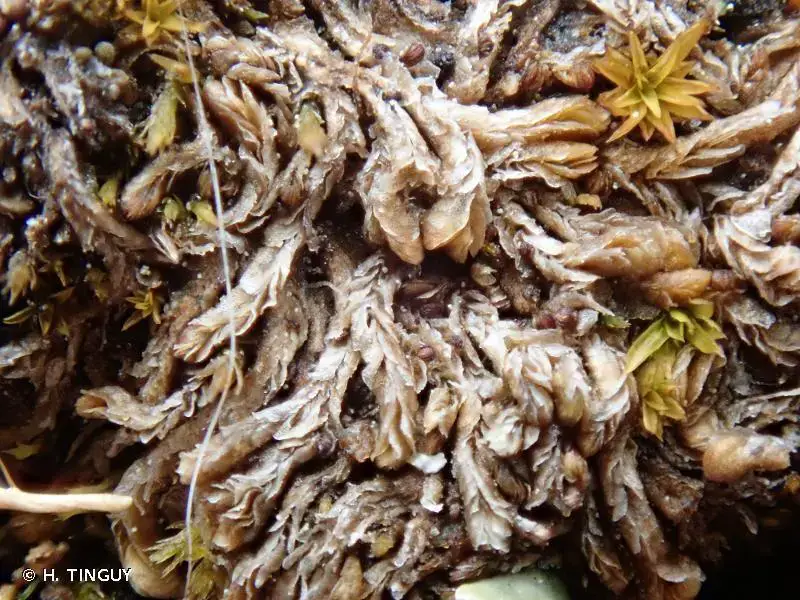
Gongylanthus ericetorum is a true marvel of nature. Its delicate, feathery appearance belies its hardy constitution. This moss forms dense, cushion-like mats, with stems that can reach up to 5 centimeters in length. The leaves are tiny, overlapping, and arranged in a spiral pattern, giving the plant a distinct, almost otherworldly look.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This resilient moss species can be found across various regions of the world, from Europe and Asia to North and South America. Gongylanthus ericetorum thrives in acidic environments, often found growing on rocks, tree bark, and even soil in areas with high humidity and moderate temperatures.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/274858-Gongylanthus-ericetorum
Despite its diminutive size, Gongylanthus ericetorum plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare surfaces and paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. They also provide a microhabitat for various tiny creatures, such as tardigrades (water bears) and springtails.
One of the most remarkable adaptations of
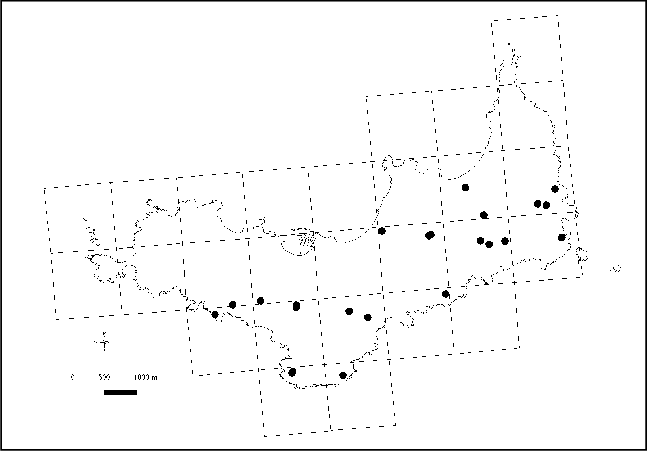
Repartition-de-Gongylanthus-ericetorum-Raddi-Nees-a-Porquerolles.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Repartition-de-Gongylanthus-ericetorum-Raddi-Nees-a-Porquerolles_fig50_328841440
Gongylanthus ericetorum is its ability to survive extreme conditions. These mosses can withstand desiccation (drying out) and quickly revive when moisture becomes available again, a process known as
t_49a387704e0bf0901f7380da0705fe4c.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/genero/gongylanthus

gonglyanthus_ericetorum.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/jungermanniaceae/index.html
poikilohydry.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers discovered a thriving population of Gongylanthus ericetorum growing on the bark of ancient Douglas fir trees. This moss played a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the forest ecosystem, providing a home for countless microscopic organisms and contributing to nutrient cycling.

mvic077.gif from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/brithp/www/gongylan.htm
Technical Table
Morphological-diversity-of-the-Cyperaceae-tribes-A-Sclerieae-Scleria-gaertneri-Raddi.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphological-diversity-of-the-Cyperaceae-tribes-A-Sclerieae-Scleria-gaertneri-Raddi_fig4_351438768

38338945052_8e87723fba_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/wanderflechten/38338945052

e0a1bfcda451532763734d4b76274619.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/icmadophila-ericetorum-from-bhutan–196610339963143716/

c1338e5fcc9f36a77ef17b490baa1fc3.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/icmadophila-ericetorum–139048707223209338/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Southbyaceae |
| Genus | Gongylanthus |
| Species | ericetorum |
| Common Name | Gongylanthus |
| Growth Form | Cushion-like mats |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Habitat | Acidic environments, rocks, tree bark, soil |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North and South America |
| Adaptations | Poikilohydry (desiccation tolerance) |
Conclusion
Gongylanthus ericetorum is a true testament to the resilience and beauty of nature’s smallest wonders. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this moss species never fails to captivate and inspire. As we bid farewell to our mossy friend, let us ponder this thought: In a world where we often overlook the smallest things, what other marvels might we be missing?