
2034.jpeg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=8834
Exploring the Fascinating World of Pohlia tundrae A.J.Shaw Moss

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/167149-Pohlia-tundrae

007864664_2-6c7b0a5562a3672c58a92a6be7089b02-768×994.png from: https://studylib.net/doc/7864664/pohlia-tundrae
Introduction
The world of mosses is full of incredible diversity and fascinating species. One particularly interesting moss is Pohlia tundrae A.J.Shaw

il_fullxfull.2752110227_j7u7.jpg from: https://www.thebryophytanursery.com/listing/901886028/terrarium-moss-pohlia-nutans-perfect
, a member of the Mniaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into this unique species, exploring its morphology, habitat, ecological roles, and more. Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of Pohlia moss!
Background on Mosses
Before we jump into the specifics of Pohlia tundrae, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses are small, non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses play important roles in many ecosystems as pioneer species, assisting with soil formation, water retention, and providing habitat for tiny organisms.
Morphology and Identification
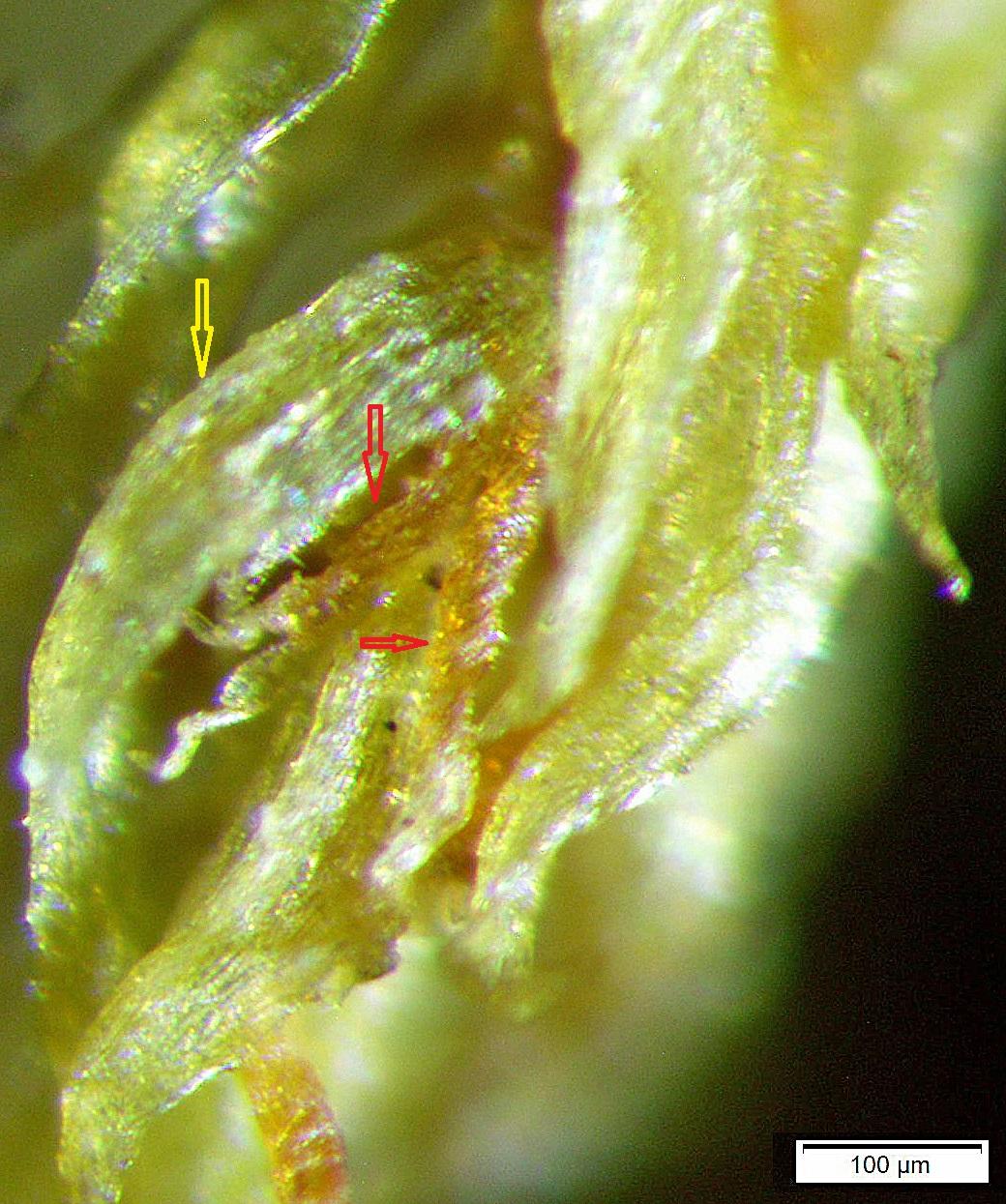
Pohlia tundrae is a small to medium-sized moss, typically growing in loose tufts or mats. Its stems are reddish-brown in color and can reach lengths of 2-4 cm. The leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and have a glossy, translucent appearance. Under a microscope, you can see that the leaf cells are elongated and the margins are serrated.
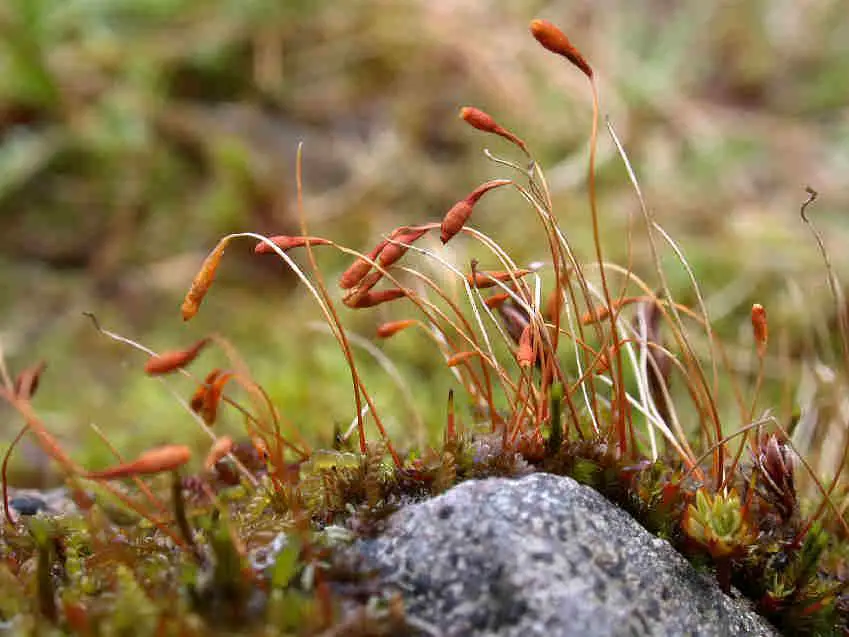
One key identifying feature of P. tundrae is its distinctive capsule shape. The capsules are cylindrical and slightly curved, with a long neck

po_tundrae7.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/pohlia_tundrae.html
. They are borne on tall, reddish setae (stalks) that can reach 2-4 cm in height. The capsules mature in summer and release spores through a ring of teeth called the peristome.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Pohlia tundrae has a circumpolar distribution, meaning it is found in arctic and subarctic regions around the world. Its range includes northern Europe, Asia, and North America. In North America, it occurs in Alaska, Canada, and the northern contiguous United States.
fpls-13-920138-g001.jpg from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2022.920138/full
This moss is well-adapted to the harsh conditions of tundra environments. It commonly grows on disturbed soils, rocky slopes, and frost-heaved ground

COLO-B-0043261_lg.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/5711017
in open tundra and alpine habitats.
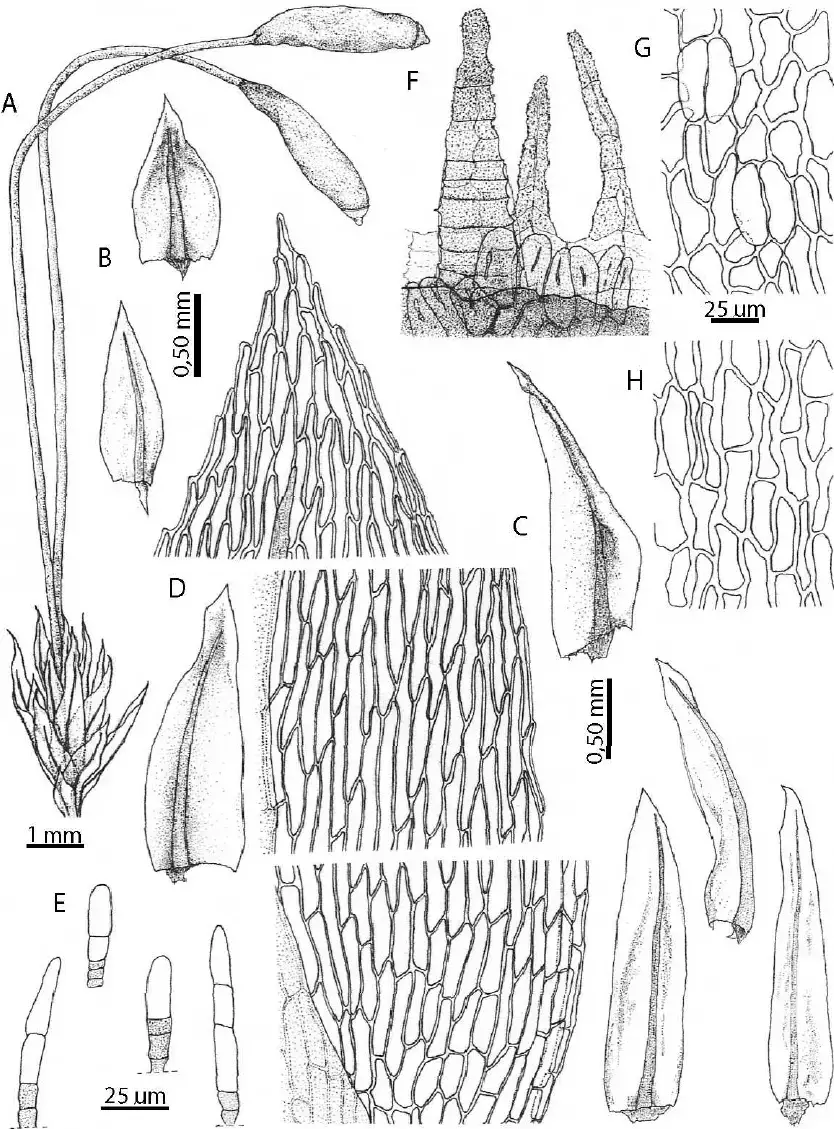
Pohlia-chilensis-A-Habit-B-Basal-leaves-C-Apical-leaves-D-Laminal-cells-apical.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pohlia-chilensis-A-Habit-B-Basal-leaves-C-Apical-leaves-D-Laminal-cells-apical_fig1_232665466
P. tundrae is often found in areas with late-lying snow beds that provide moisture during the growing season.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Pohlia tundrae plays a vital role in tundra ecosystems as a pioneer species. It is one of the first plants to colonize bare, disturbed soils, helping to stabilize the substrate and pave the way for other vegetation to establish. As it grows,
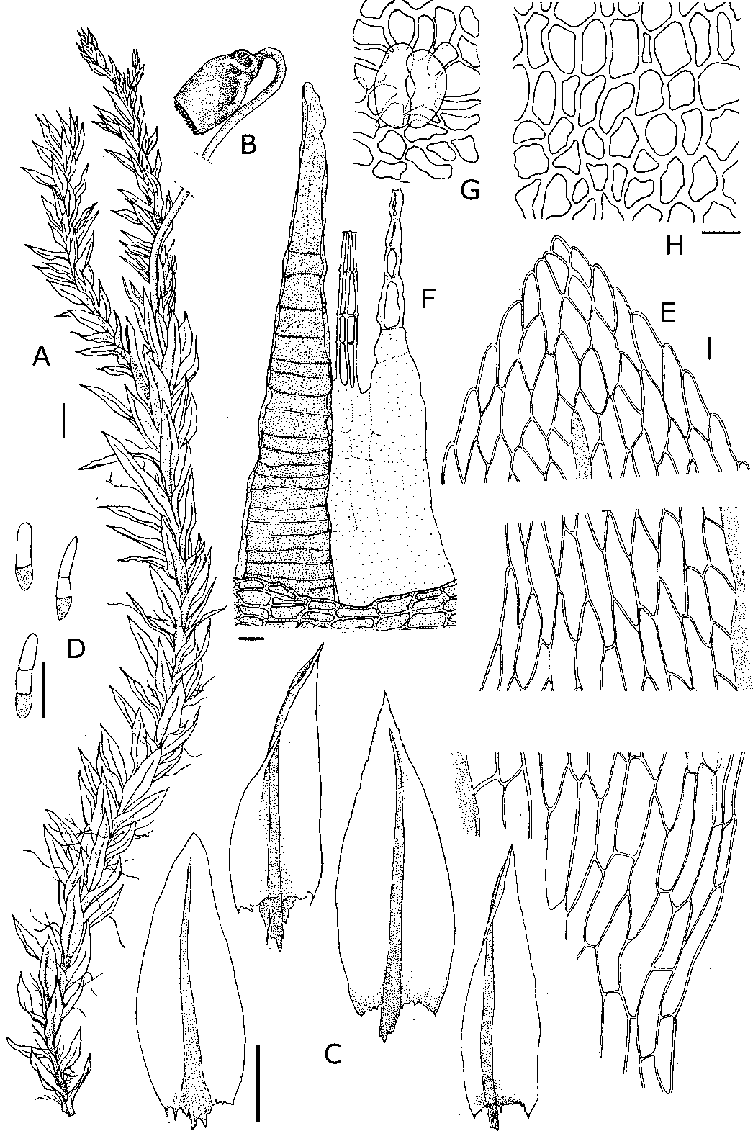
Pohlia-wahlenbergii-A-Habit-wet-B-Seta-and-capsule-C-Leaves-D-Axillary-hairs-E.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pohlia-wahlenbergii-A-Habit-wet-B-Seta-and-capsule-C-Leaves-D-Axillary-hairs-E_fig4_233627490
P. tundrae contributes to the buildup of organic matter in the soil, aiding in the development of tundra soil profiles.
The dense mats formed by P. tundrae also help to insulate the soil, protecting permafrost and moderating temperature fluctuations. This is crucial in tundra environments where freeze-thaw cycles can cause significant disturbance. Additionally, the mats retain moisture, reducing erosion and providing a consistent water supply for itself and other organisms.
Pohlia tundrae has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in the tundra. Its small size and compact growth form help to minimize water loss and exposure to drying winds. The

Pohlia_elongata-elon_009.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Pohlia_elongata_var_elongata.html
reddish pigments in its stems and setae may offer protection against UV radiation, which can be intense at high latitudes and elevations. Furthermore, P. tundrae can tolerate long periods of dormancy beneath the snow, resuming growth quickly when conditions become favorable.
Conclusion
Pohlia tundrae A.J.Shaw is a remarkable moss with a fascinating ecology. From its distinctive morphology to its crucial roles in tundra ecosystems, this small but mighty plant is a true wonder of the natural world. Next time you find yourself in the far north, take a moment to appreciate the intricate beauty and resilience of Pohlia moss. Who knows what other secrets these ancient plants hold?