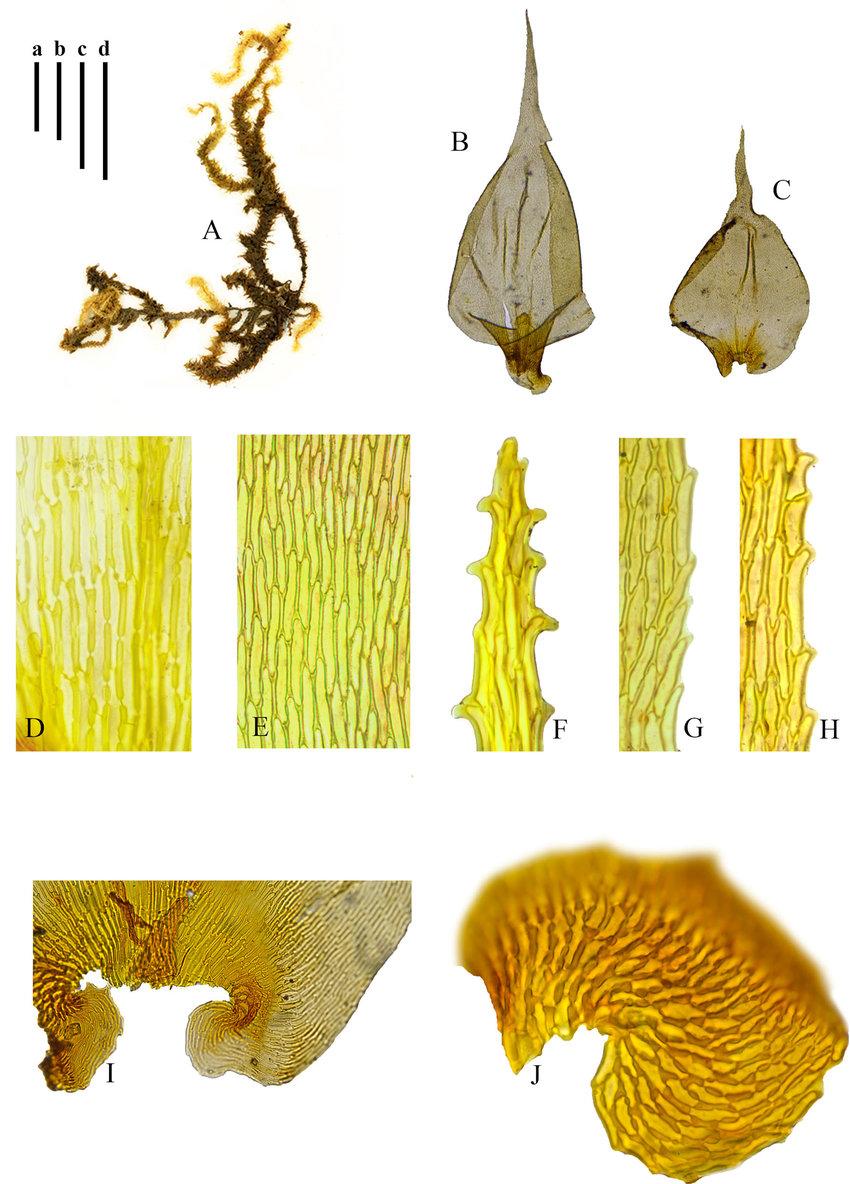

Meteoriella-soluta-Mitt-SOkamur-A-Plant-B-Branch-leaf-C-Stem-leaf-D-Basal.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Meteoriella-soluta-Mitt-SOkamur-A-Plant-B-Branch-leaf-C-Stem-leaf-D-Basal_fig4_348089946
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Meteoriella soluta (Mitt.) S.Okamura. Belonging to the Hylocomiaceae family, this delicate yet resilient moss is commonly referred to as

0ef31dd3ced7b46798954781e7af51d9.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/35059
Meteoriella. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Meteoriella soluta, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Meteoriella soluta is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally or creep along surfaces. Its slender, wiry stems can reach lengths of up to 10 centimeters, adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that spiral around the stem. The leaves are typically 1-2 millimeters
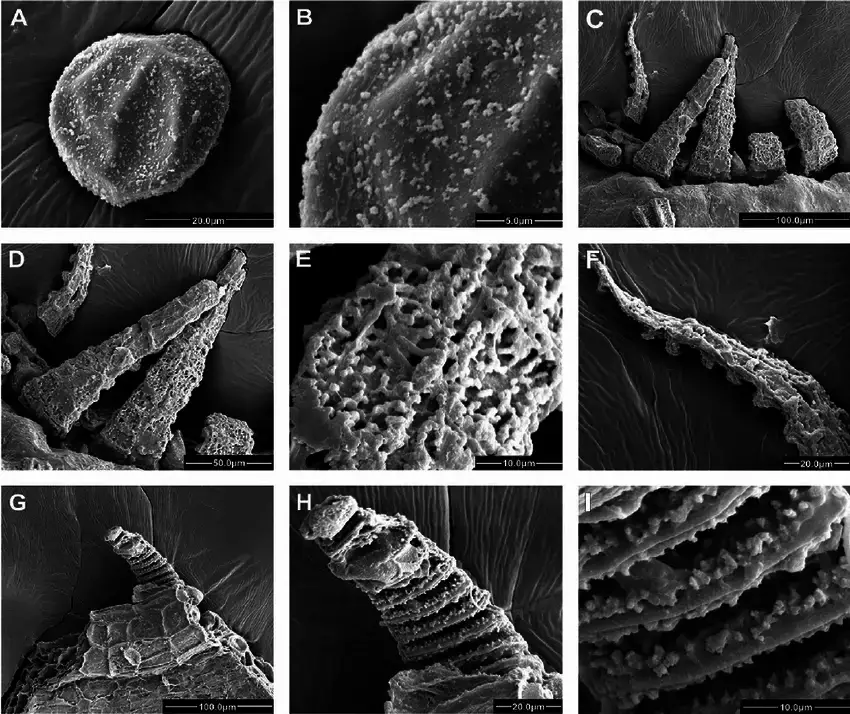
Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Meteoriella-soluta-A-spore-B-surface-ornamentation.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Meteoriella-soluta-A-spore-B-surface-ornamentation_fig1_232815615
long and feature a distinctive midrib that extends nearly to the leaf tip.
One of the most striking features of Meteoriella soluta is its vibrant golden-green hue, which can take on a reddish tinge in certain conditions. This coloration is due to the presence of specialized pigments that help protect the moss from harmful UV radiation.
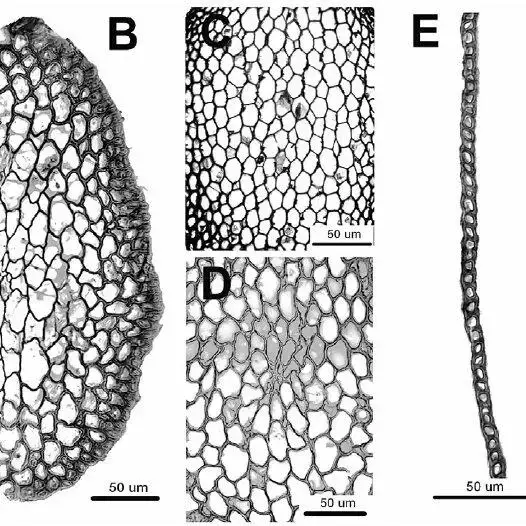
Anatomy-of-Meteoriella-soluta-and-Loeskeobryum-brevirostre-A-B-a-portion-of-the-stem_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Anatomy-of-Meteoriella-soluta-and-Loeskeobryum-brevirostre-A-B-a-portion-of-the-stem_fig2_232815615
Global Distribution and Habitat
Meteoriella soluta is widely distributed across various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from cool, moist forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments. This moss is particularly fond of shaded, humid areas, often found growing on tree trunks, logs, and rocks.

43b1f95b4bcbc53839a61a8041a9a9fe.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/1102
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Meteoriella soluta plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for some bird species.

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232807714_The_systematic_position_of_Meteoriella_S_Okamura_Musci_based_on_molecular_and_morphological_data
One of the remarkable adaptations of Meteoriella soluta is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Physcomitrium-eurystomum-Sendtn-A-habit-B-leaf-displaying-shape-and-apex-C-close-up_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326466455_A_new_country_record_and_additions_to_the_moss_floras_of_Luzon_and_Mindanao_island_Philippines
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Meteoriella soluta

Okamuraea-brachydictyon000L.jpg from: https://digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Okamuraea brachydictyon/Okamuraea_brachydictyon.html
played a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of epiphytic (tree-dwelling) communities. The moss provided a suitable habitat for various invertebrates, lichens, and other bryophytes, contributing to the overall health and complexity of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Scientific Name
 Some-mosses-in-Mt-Kalatungan-Range-Natural-Park-A-Pogonatum-macrophyllum-Dozy-Molk.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Some-mosses-in-Mt-Kalatungan-Range-Natural-Park-A-Pogonatum-macrophyllum-Dozy-Molk_fig6_326770986 |
Meteoriella soluta (Mitt.) S.Okamura |
| Family | Hylocomiaceae |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Stem Length | Up to 10 cm |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped, 1-2 mm long |
| Leaf Midrib | Extends nearly to leaf tip |
Color
 179115170_35cf2c5cbd_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/soluta/179115170 |
Golden-green, sometimes reddish |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Africa |
| Habitat | Cool, moist forests, rocky outcrops, urban areas |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, moisture retention, microhabitats, food source |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
Meteoriella soluta is a remarkable moss species that exemplifies the beauty and resilience of bryophytes. From its delicate yet vibrant appearance to its vital ecological roles, this moss deserves our appreciation and protection. As we continue to explore the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better understand and conserve the often-overlooked wonders of the natural world, like the humble yet extraordinary Meteoriella soluta?