
image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Ulota intermedia Schimp. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Ulota intermedia Schimp., a moss belonging to the Orthotrichaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the captivating world of this tiny but mighty plant.
Background
Ulota intermedia Schimp., also known simply as Ulota, is a type of moss classified under the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. Mosses are non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids that absorb water and nutrients directly from their surroundings.
Morphology and Identification
U. intermedia forms small, dense cushions or tufts on tree bark or rocks. Its phyllids are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and have a distinct midrib. The capsules, which contain spores, are cylindrical and have 8 furrows when dry. A key identifying feature is the presence of multicellular gemmae, asexual reproductive structures, on the phyllid tips.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide distribution, found in Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of Africa. It typically grows in

image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
temperate and boreal forests, favoring habitats with high humidity. U. intermedia is epiphytic, meaning it grows on other plants (usually trees) without harming them.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, U. intermedia plays important ecological roles:
Moisture retention: Its dense growth form helps trap and retain moisture, preventing soil erosion and maintaining humidity in the microenvironment.
Nutrient cycling: As mosses decompose, they release nutrients back into the ecosystem, supporting the growth of other plants.
Habitat provision: Many small invertebrates, such as tardigrades and springtails, live among moss cushions.
image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
U. intermedia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
Desiccation tolerance: It can survive periods of drought by going dormant and quickly reviving when moisture returns.

image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
Asexual reproduction: The gemmae allow for rapid colonization of new substrates without the need for sexual reproduction.
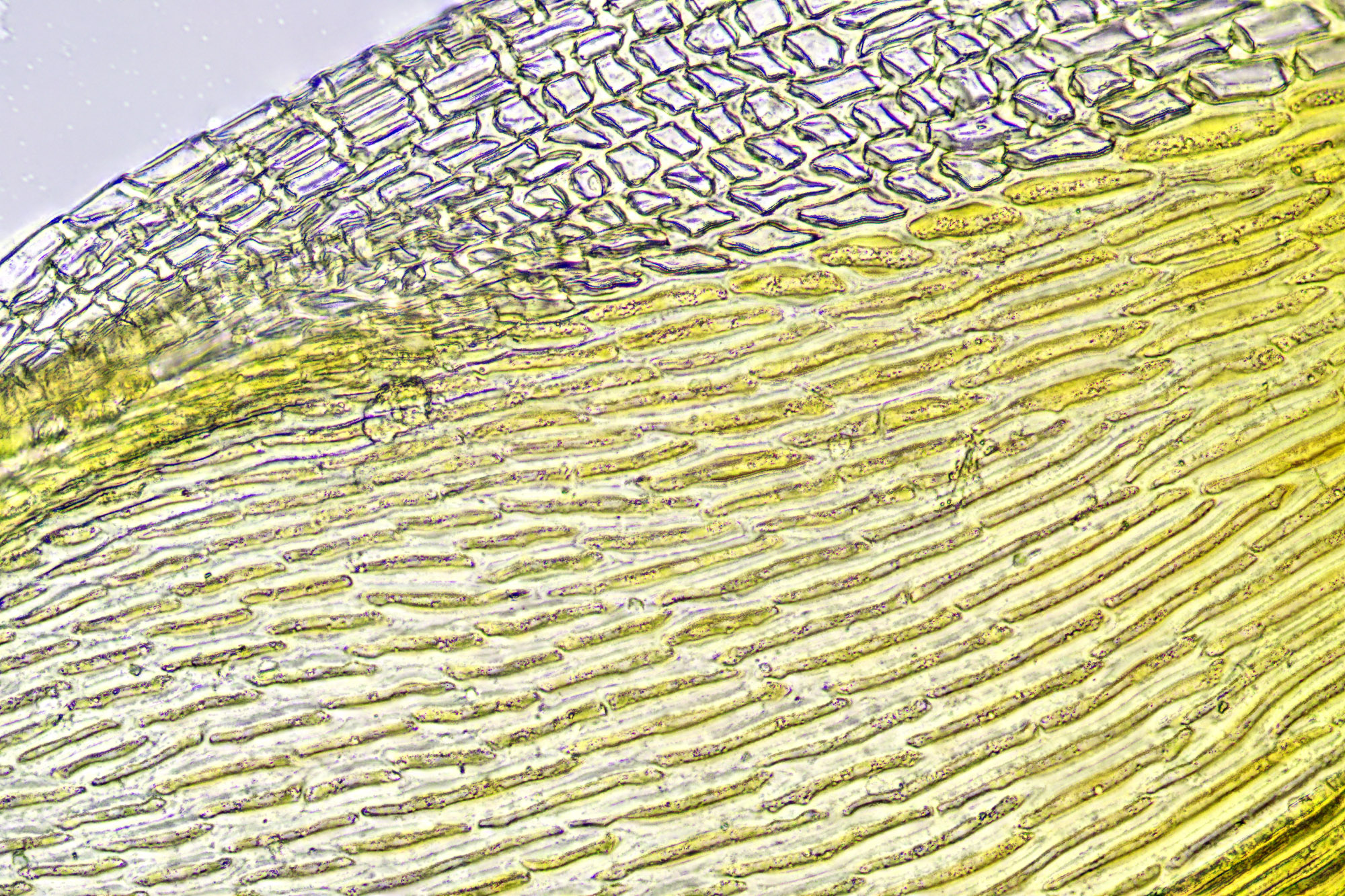
image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
Efficient nutrient uptake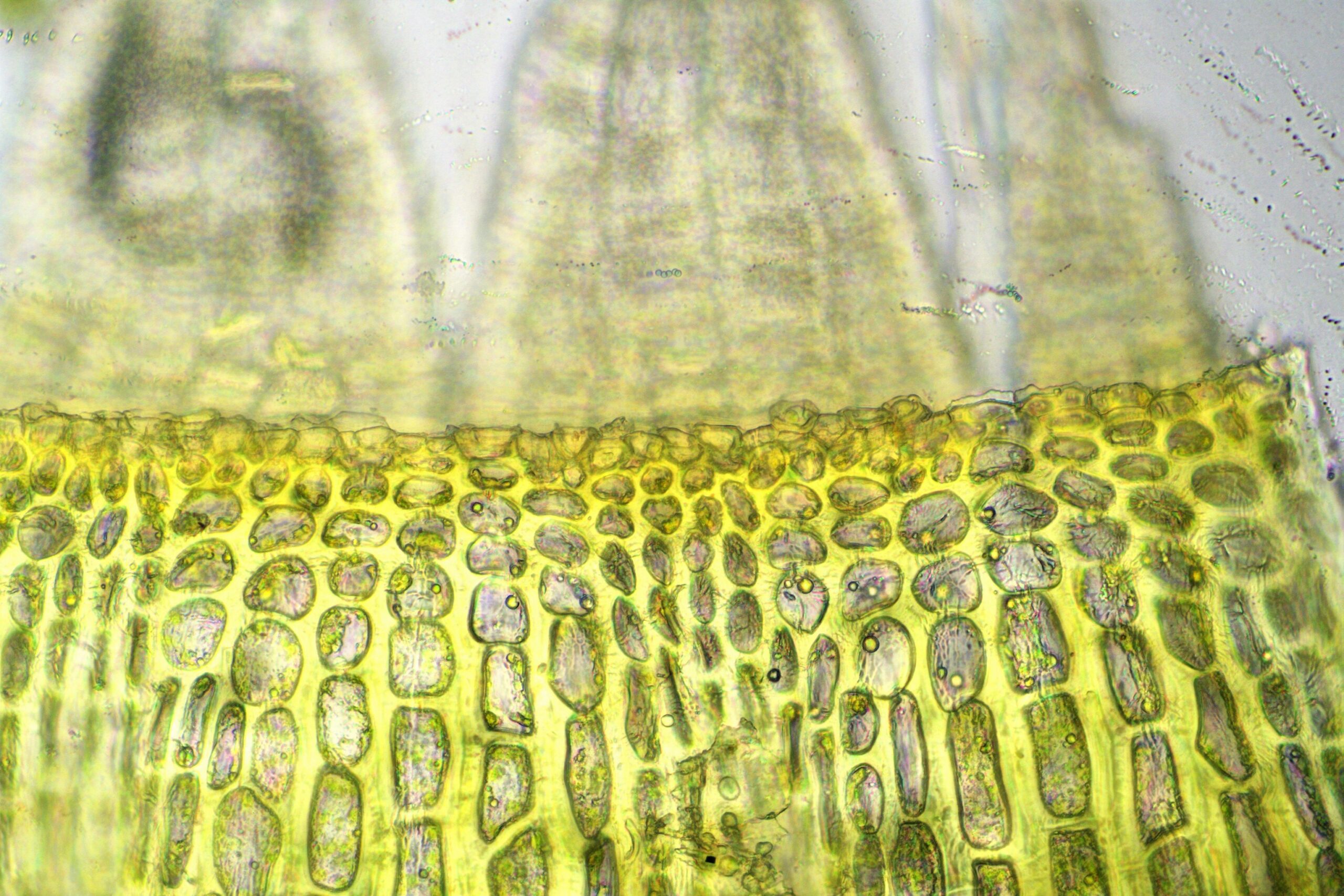
image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
: Lacking true roots, this moss absorbs nutrients directly through its phyllids.
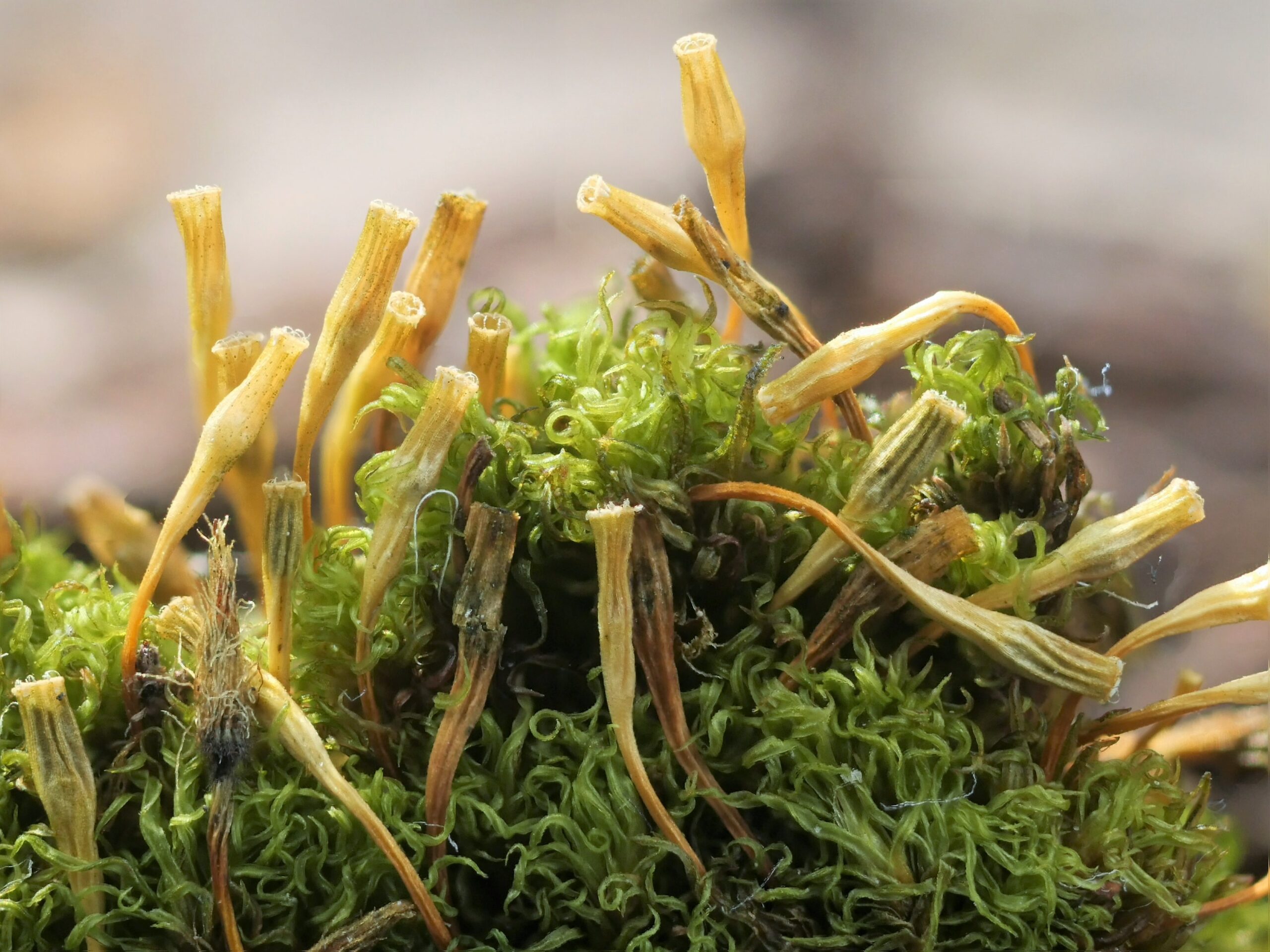

image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
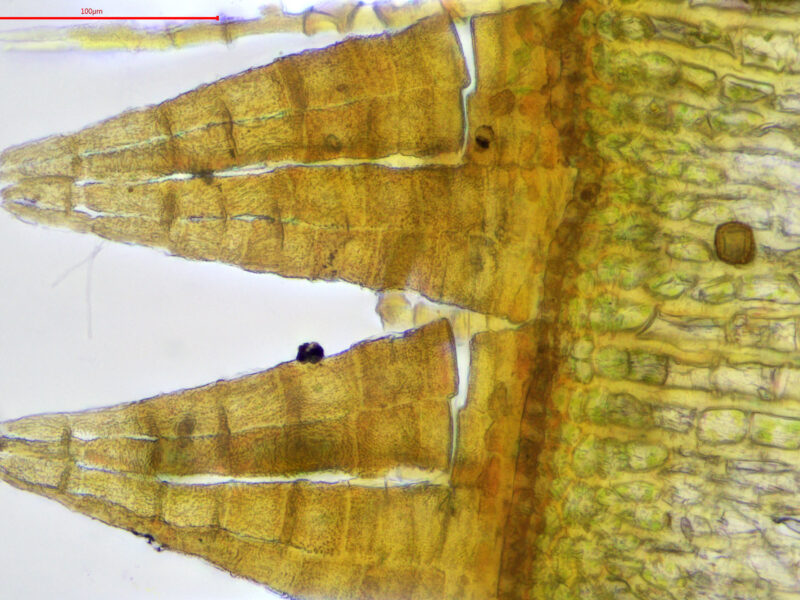

image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/

image from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ulota-intermedia/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae |
| Genus | Ulota |
| Species | U. intermedia |
| Growth form | Cushions or tufts |
| Substrate | Epiphytic (on trees) or saxicolous (on rocks) |
| Phyllids | Lanceolate with distinct midrib |
| Capsules | Cylindrical with 8 furrows when dry |
| Asexual reproduction | Multicellular gemmae on phyllid tips |
Conclusion
Ulota intermedia Schimp. may be small, but it is a fascinating and ecologically important moss species. Its unique adaptations and wide distribution make it a valuable component of many forest ecosystems. Next time you’re out for a walk in the woods, take a closer look at the tree bark and rocks – you might just spot this tiny but remarkable plant! What other secrets of the moss world are waiting to be discovered?
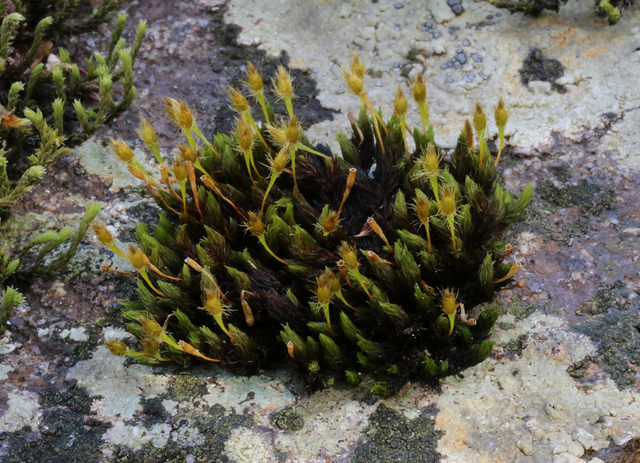

image from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/view/10821