
549.BI-image-53472.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/36210
Exploring the Fascinating World of Lophozia grandiretis var. proteidea (Arnell) Arnell Moss
Introduction
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Lophozia grandiretis var. proteidea (Arnell) Arnell

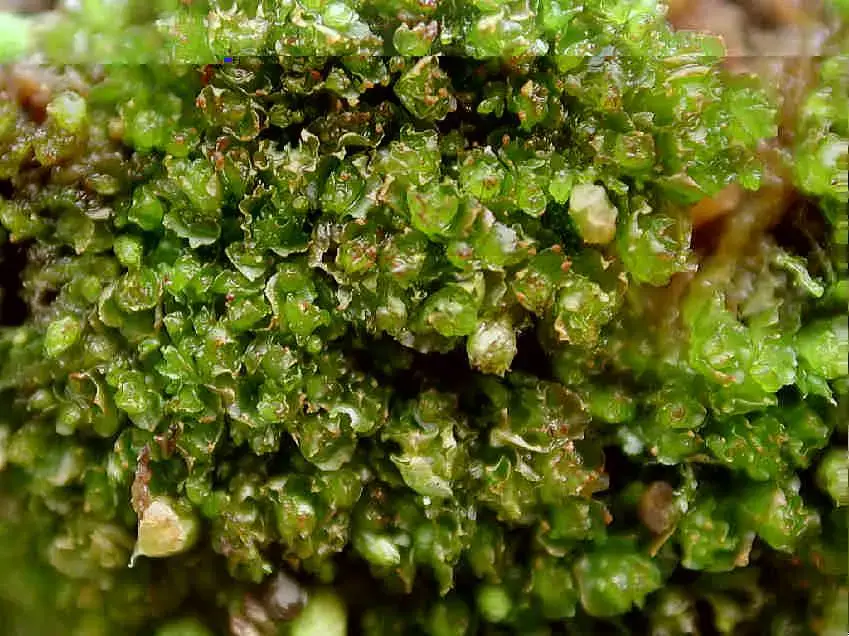
Lophozia-longidens-1119.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/lophozia-longidens/
, a member of the

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/485470-Philonotis-arnellii
Scapaniaceae family. Commonly known simply as Lophozia
H4205353%2B1368376244.jpg from: https://v3.boldsystems.org/index.php/Taxbrowser_Taxonpage?taxid=446904
, this tiny but mighty moss is worth taking a closer look at.
Background on Lophozia Moss
Lophozia grandiretis var. proteidea is a species of leafy liverwort, which are non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta. Liverworts are some of the oldest land plants, with fossils dating back over 400 million years. There are over 7000 species of liverworts found all over the world.
Lophozia belongs to the order Jungermanniales, the largest group of leafy liverworts. The Scapaniaceae family contains around 85 species across several genera.
Morphology and Identification
Lophozia grandiretis var. proteidea forms small, green mats on rocks, tree bark, and soil. The shoots are prostrate to ascending and irregularly branched. Leaves are succubous (lying flat and overlapping like shingles), bilobed, and lack underleaves.
The leaf cells have thin walls and are longer than wide. Oil bodies, unique organelles found in liverworts that contain terpenes and other aromatic compounds, are present. Rhizoids are scattered along the underside of the stem.
bad+stem+cross+section.jpg from: https://mosswalks.blogspot.com/2012/06/lophozio-sudetica.html?m=0
Lophozia is

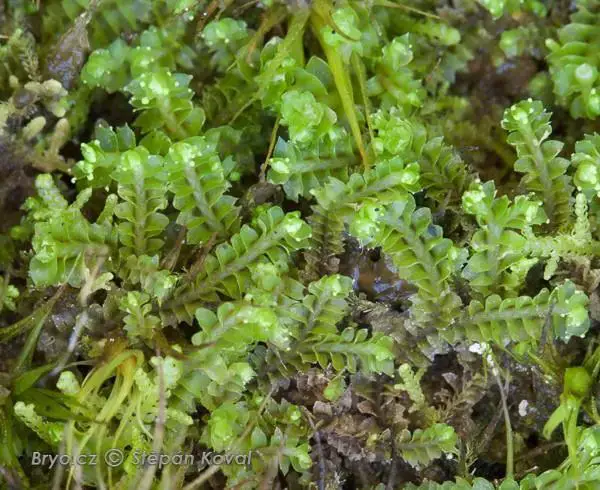
Lophozia_excisa_4.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Lophozia_excisa.html
dioicous, meaning male and female reproductive structures are on separate plants. Antheridia (male) are found in the axils of bracts. Archegonia (female) are on short lateral branches. Spores are released from capsules that split into four valves when mature.

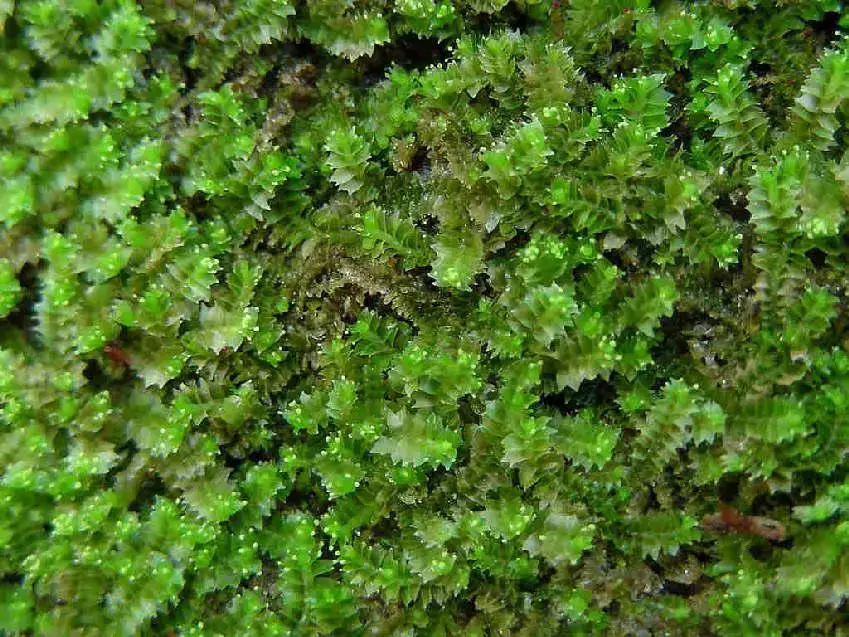
3338_Lophozia_ventricosa_2008_08_19_1591.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=lophozia_ventricosa_var_silvicola&id=3338
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lophozia grandiretis var. proteidea has a circumboreal distribution, occurring in northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. It grows in a variety of habitats including:
- Coniferous and deciduous forests
- Bogs and fens
- Tundra and alpine areas
- Cliffs and rock outcrops
This species prefers acidic substrates and is often found growing with other bryophytes like Sphagnum mosses. In some areas, it is used as an indicator of old-growth forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses and liverworts, Lophozia plays important roles in its ecosystem:
Lophozia-guttulata-A-habitus-B-leaf-C-Median-leaf-cells-and-oil-boides-D-Gemmae.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lophozia-guttulata-A-habitus-B-leaf-C-Median-leaf-cells-and-oil-boides-D-Gemmae_fig3_350635294
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion

Lophozia_ventricosa_3b.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Lophozia_ventricosa.html
- Provides shelter and food for invertebrates
- Colonizes disturbed areas and stabilizes soil
- Contributes to nutrient cycling as it grows and decays
Lophozia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Poikilohydry – can tolerate drying out and rehydrate quickly
lo_obtusa3.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lophozia_obtusa.html
- Asexual reproduction via gemmae – small propagules that disperse the plant
- Cold tolerance – can photosynthesize under snow
- Associations with cyanobacteria for nitrogen fixation
Conclusion
From its tiny oil bodies to its global distribution, Lophozia grandiretis var. proteidea is a fascinating and important member of the bryophyte world. Next time you’re out in a northern forest, keep an eye out for this small but significant moss. What other secrets of the Scapaniaceae await discovery?