
fissidens-zollingeri-1.jpg from: https://www.premiumbuces.com/en/fissidens-zollingeri/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Fissidens zollingeri Mont. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Fissidentaceae family. Often referred to simply as Fissidens, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of
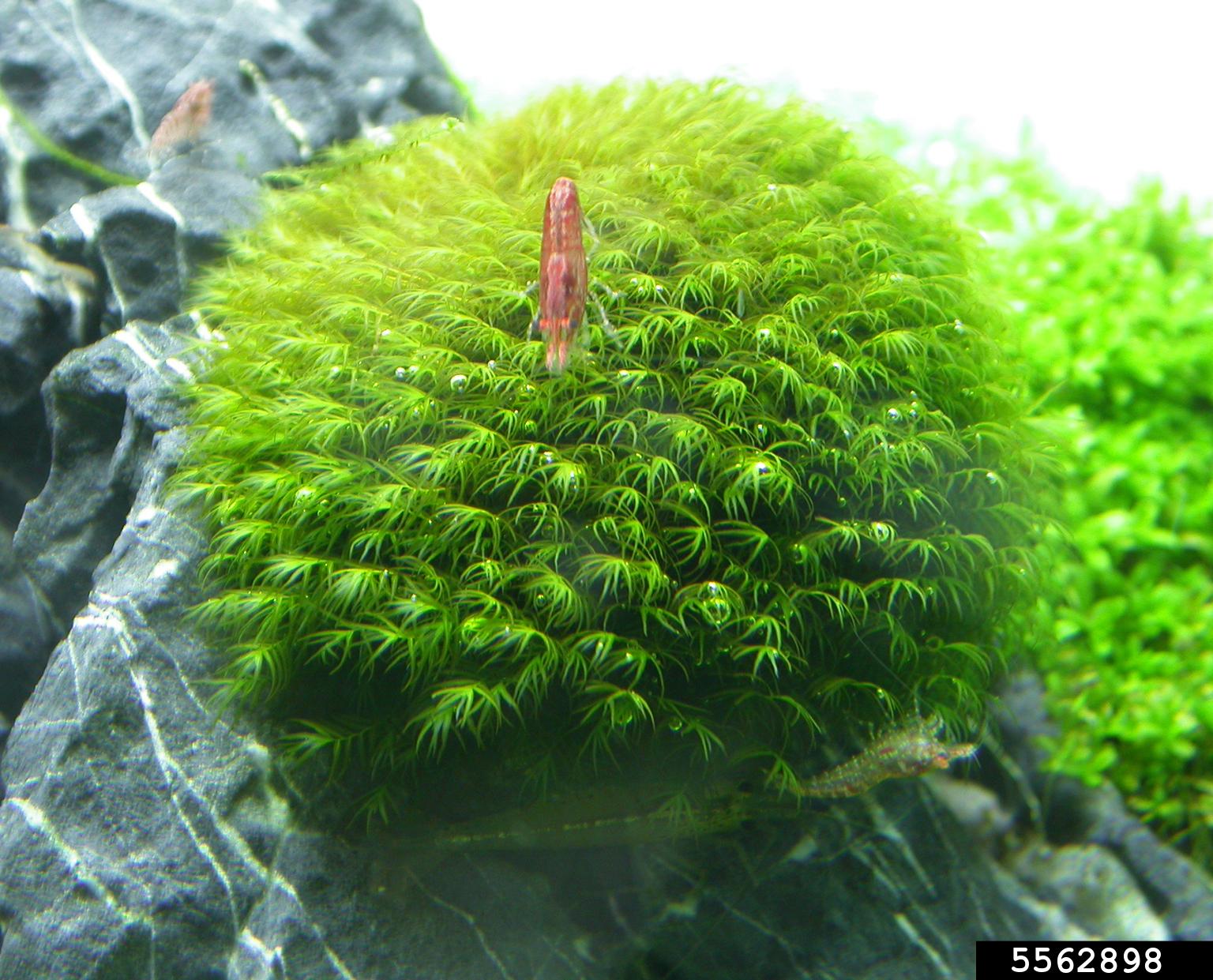

5562898.jpg from: https://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5562898
Fissidens zollingeri Mont., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back over 400 million years. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Fissidens zollingeri Mont. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, velvety mats or tufts. Its leaves are distinctively arranged in two rows, giving the appearance of a tiny, flattened feather. Each leaf is composed of a single layer of cells, with a characteristic midrib running along its length. The sporophytes, or reproductive structures, are relatively inconspicuous, with a short seta (stalk) and a small, urn-shaped capsule.
Global Distribution and Habitat
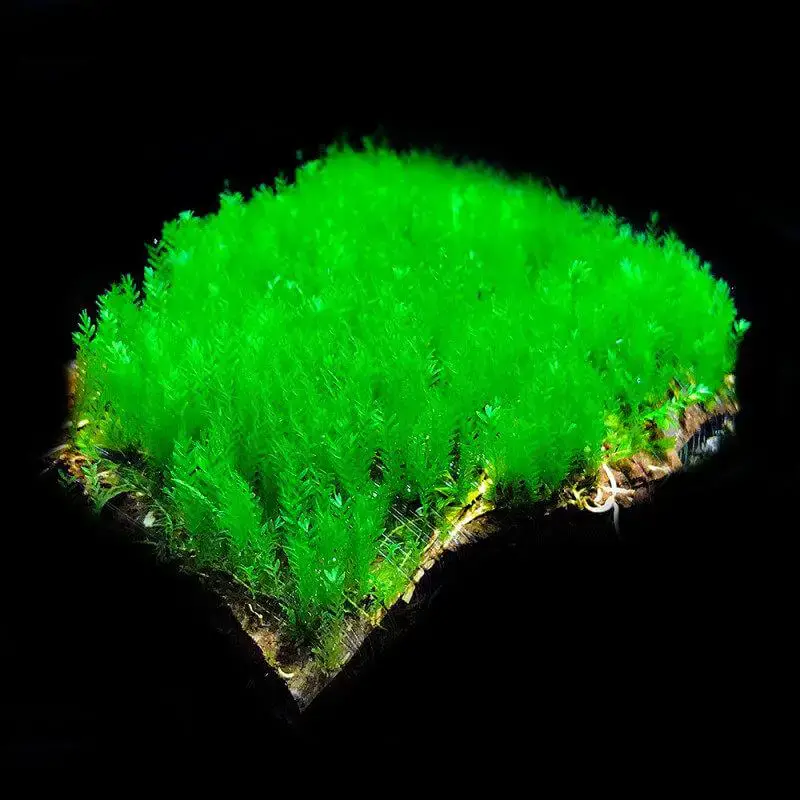

fissidens-zollingeri.jpg from: https://www.aquaplante.fr/mousse-aquatique-de-java-pour-aquarium/aquaplante-plantes/78144-fissidens-zollingeri.html
This moss species is widely distributed across various regions, including Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist, shaded areas in forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even urban environments like old walls and pavements. Fissidens zollingeri Mont. is particularly adept at colonizing disturbed or degraded areas, making it a valuable pioneer species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Fissidens zollingeri Mont. plays a vital role in its ecosystems. Its dense mats help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, these moss colonies provide microhabitats for a diverse array of invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, contributing to overall biodiversity.
Leaf-margins-a-Fissidens-flaccidus-Mitt-KT-Yong-2440-b-F-guangdongensis-Z_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Limbidium-a-Fissidens-zollingeri-Mont-GE-Lee-sn-and-b-F-ceylonensis-Dozy-and_fig6_327838253
One of the remarkable adaptations of
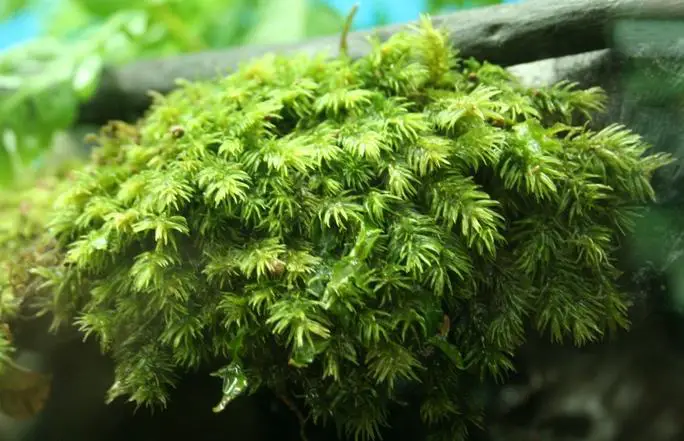

IMG_4746.JPG from: https://www.aquaticquotient.com/forum/showthread.php/25486-Terrestrial-fissidens-moss-)
Fissidens zollingeri Mont. is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating remarkable resilience in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Fissidens zollingeri Mont. has been observed thriving on old brick walls and pavements, adding a touch of green to these man-made structures. Its ability to colonize such environments has made it a subject of interest for researchers studying urban ecology and the role of bryophytes in mitigating the effects of urbanization.
Technical Table

Fissidens-bryoides-21-800×533.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-fissidens-bryoides/

fissidens-fontanus-5194b3092cd02.jpg from: http://www.flowgrow.de/db/aquaticplants/fissidens-fontanus
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Fissidentales |
| Family | Fissidentaceae |
| Genus | Fissidens
 moss_fissidens_species_10-03-06_2.jpg from: https://www.aphotoflora.com/moss_fissidens_species.html |
| Species | Fissidens zollingeri Mont. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense mats or tufts |
| Leaf Arrangement | Distichous (arranged in two rows) |
| Leaf Structure | Single layer of cells, with a midrib |
| Sporophyte | Short seta, small urn-shaped capsule |
Conclusion

fissidens-fontanus-phoenix-moss~2.jpg from: https://www.aquasabi.de/Fissidens-fontanus-Phoenix-Moss-Pad-7-x-4-cm-Dennerle

fissidens-sp-miroshaki-moss.jpg from: https://www.nanoaqua.fr/moss/97-fissidens-sp-miroshaki-moss.html
Fissidens zollingeri Mont., a unassuming yet remarkable moss species, has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique morphology, ecological significance, and resilience. From its ability to colonize diverse habitats to its role in supporting biodiversity and preventing soil erosion, this moss serves as a testament to the incredible adaptations and importance of bryophytes in our ecosystems. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, Fissidens zollingeri Mont. invites us to ponder the intricate web of life that exists even in the smallest of organisms.