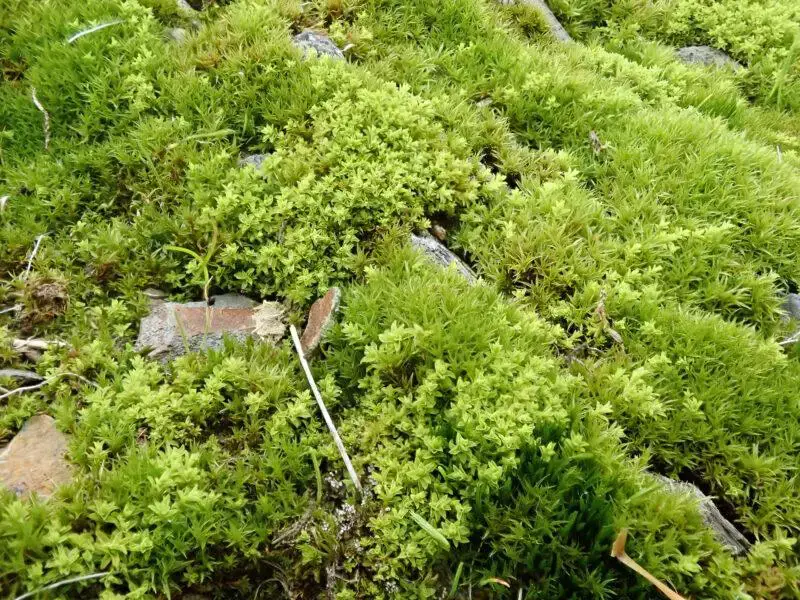

2021-10-14-10-22-58-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/leptodontium-flexifolium/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Leptodontium pungens (Mitt.) Kindb. moss, belonging to the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Leptodontium, this diminutive yet resilient plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Bryophytes, a group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These ancient organisms have played a crucial role in the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems, paving the way for more complex plant life to flourish.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
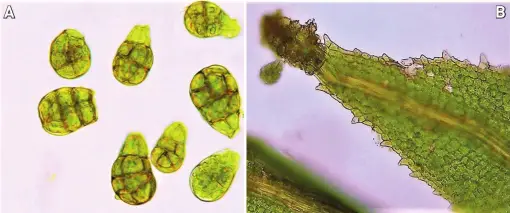
The Leptodontium pungens moss is a true marvel of nature, boasting a distinctive appearance that sets it apart from its bryophyte brethren. Its slender, pungent (sharply pointed) leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem, creating a delicate yet intricate structure. The leaves themselves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and acuminate
img-z2-1_208.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-34/issue-1/heia.34.1.2021.208/Leptodontium-gemmascens–ein-seltenes-Laubmoos-neu-für-Brandenburg/10.13158/heia.34.1.2021.208.full
(tapering to a slender point), with a costa (midrib) that extends to the leaf tip.
One of the most striking features of this moss is its vibrant green coloration, which can range from a deep emerald hue to a more golden-green shade, depending on the environmental conditions. This coloration is due to the presence of chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, which allow the moss to thrive in a wide range of habitats.
Global Distribution and Habitat
The Leptodontium pungens moss is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It is particularly abundant in areas with temperate and subtropical climates, where it can be found growing on a variety of substrates, such as soil, rocks, tree bark, and even man-made structures like walls and roofs.
This moss is well-adapted to a range of environmental conditions, thriving in both dry and moist habitats. Its ability to withstand desiccation (drying out) and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available is a testament to its remarkable resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, the Leptodontium pungens moss plays a vital role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it is often one of the first plants to colonize disturbed or newly exposed areas, helping to stabilize the soil and pave the way for other plant species to establish themselves.

CDS_46779_DX_3191_print_1555698951.jpg from: https://lichenportal.org/cnalh/collections/individual/index.php?occid=3157062
Moreover, this moss serves as a crucial microhabitat for a diverse array of microscopic organisms, including fungi, bacteria, and invertebrates. These tiny creatures rely on the moss for shelter, food, and moisture, creating intricate and interdependent relationships within these miniature ecosystems.

cari70_001_shp.jpg from: https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CARI70
One of the most fascinating adaptations of the Leptodontium pungens moss is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, the moss produces sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) that release spores, enabling the species to disperse and colonize new areas. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, occurs through the production of gemmae (specialized reproductive structures) or fragmentation, allowing the moss to rapidly propagate and establish new colonies in its immediate vicinity.

6c5f833e4a87d67b0532ff05e581dbac.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/c042054f370bfcfd0c8ddff5f5f9b1ca
Case Studies/Examples
The Leptodontium pungens moss has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its ecological significance and potential applications. For instance, researchers have investigated the moss’s ability to accumulate heavy metals from the environment, making it a potential biomonitor for air pollution levels.
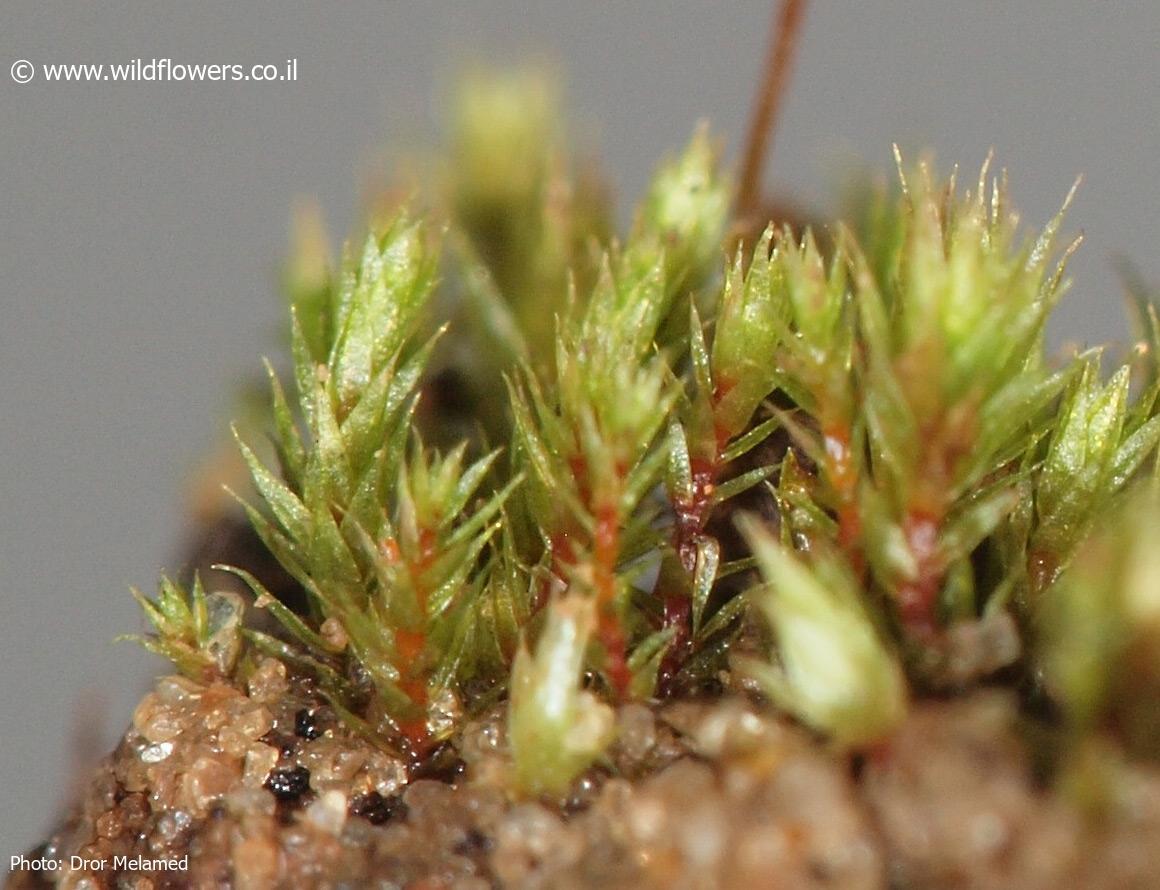

3375-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21459
In urban areas, this moss has been observed growing on various man-made structures, such as concrete walls and roofs, demonstrating its adaptability and resilience in human-modified environments.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptodontium pungens (Mitt.) Kindb. |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Common Name | Leptodontium moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous (upright) moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, acuminate |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Reproduction | Sexual (sporophytes) and asexual (gemmae, fragmentation) |
| Habitat | Soil, rocks, tree bark, man-made structures |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, Africa, North America |
Conclusion
The Leptodontium pungens moss, a true marvel of the bryophyte world, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of these ancient plant lineages. From its intricate morphology and vibrant coloration to its remarkable adaptations and ecological significance, this moss captivates the hearts and minds of enthusiasts worldwide.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, the Leptodontium pungens moss reminds us of the intricate web of life that surrounds us, even in the most unassuming of places. Perhaps the next time you encounter this diminutive yet extraordinary moss, you’ll pause to appreciate the intricate beauty and resilience that it embodies.