Dicranodontium Uncinatum: An Enchanting Moss for Enthusiasts
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!

2022-08-20-18-09-55.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranodontium-uncinatum/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Dicranodontium uncinatum (Harv.) A.Jaeger. Belonging to the Leucobryaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is commonly referred to as Dicranodontium. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this remarkable plant and explore its intricate world.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Dicranodontium uncinatum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
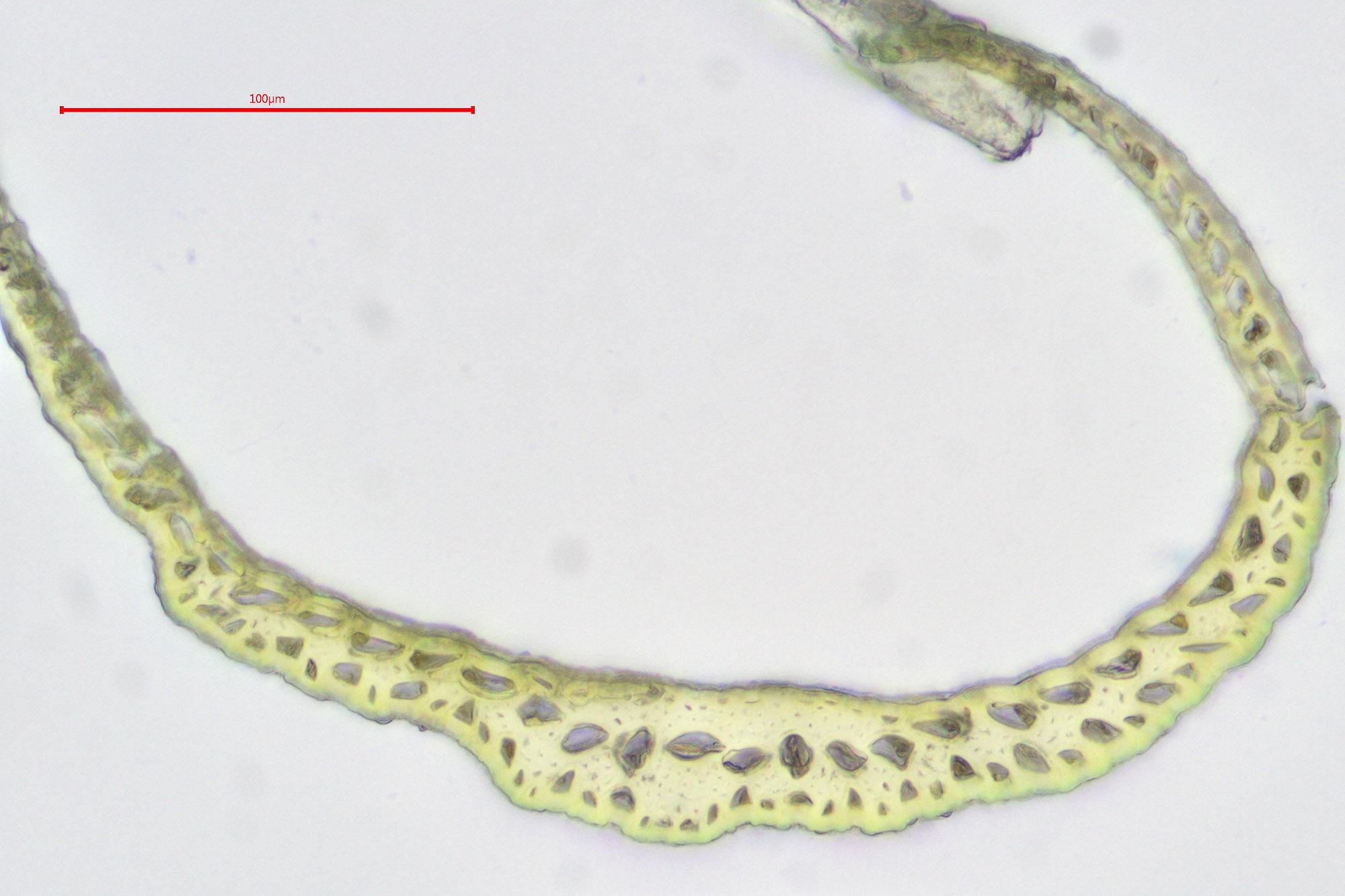
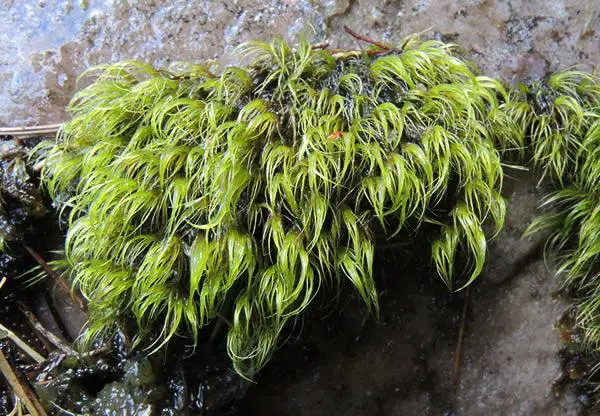
Dicranodontium uncinatum is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems are typically 1-3 cm tall, and the leaves are lanceolate
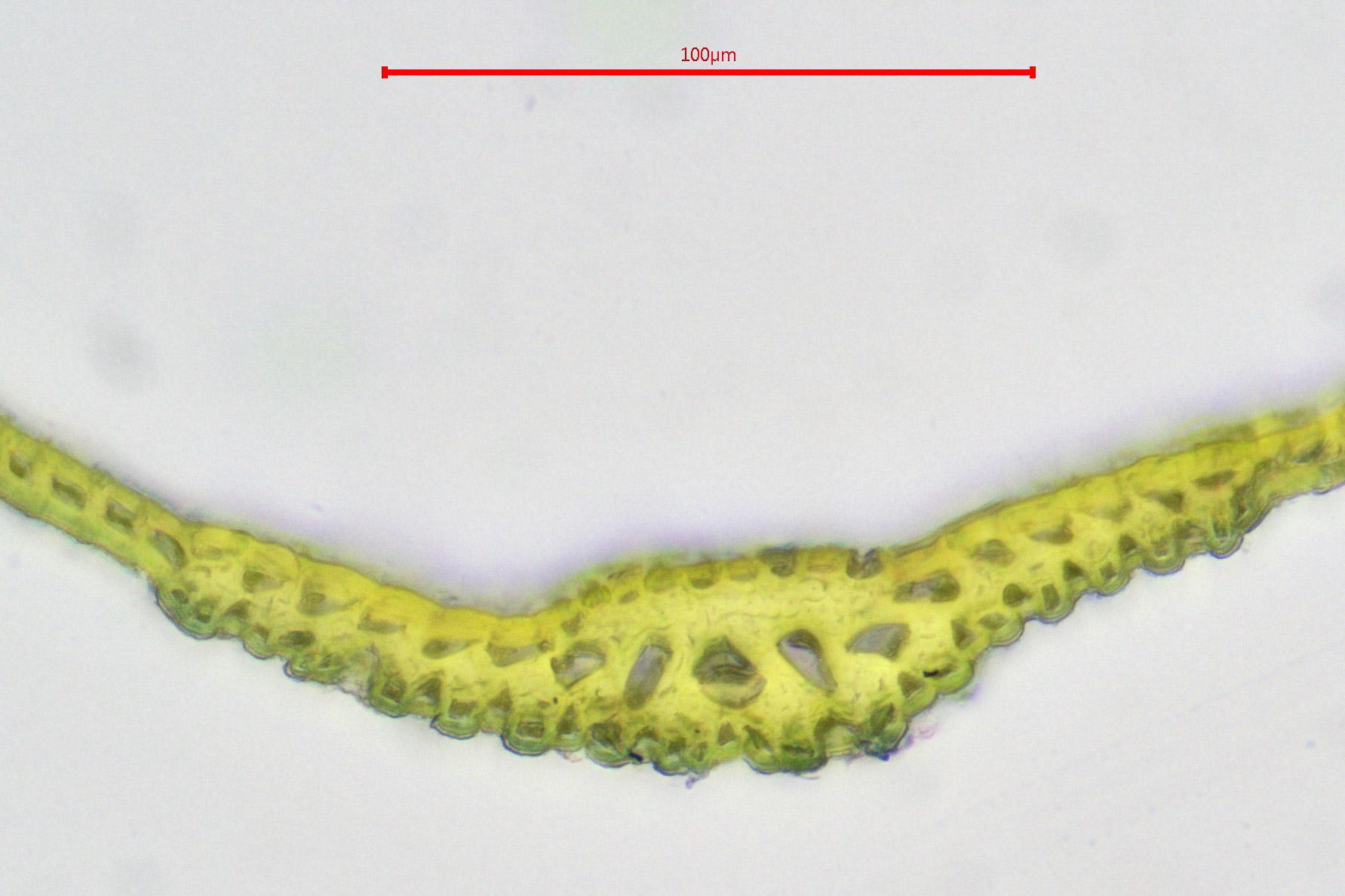
2022-08-19-17-41-07.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranodontium-subporodictyon/
to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive curved or falcate appearance. The leaf margins are entire, and the costa (midrib) is strong and excurrent (extending beyond the leaf apex).
EsHuZxKXEAAIj26.jpg:large from: https://twitter.com/MichaelLueth2/status/1351624031036993544
One of the most striking features of this moss is its reddish-brown to dark green coloration, which can vary depending on the environmental conditions. The sporophytes (reproductive structures) are relatively rare, but when present, they bear erect, cylindrical capsules on elongated setae (stalks).

07-01-Dicranodontium-uncinatum.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranodontium-denudatum/
Global Distribution and Habitat
Dicranodontium uncinatum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded rock crevices to decaying logs and soil banks in forests.
This moss species is particularly well-adapted to cool, humid environments and is often found in montane and boreal regions. It can also be encountered in urban areas, where it colonizes concrete and brick surfaces, demonstrating its remarkable resilience and adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Dicranodontium uncinatum plays a vital role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it is one of the first plants to colonize disturbed or newly exposed areas, helping to stabilize the soil and facilitate the establishment of other plant species.
This moss is also an important component of the bryophyte layer in many forest ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling, water retention, and soil formation. Its dense mats provide a microhabitat for numerous invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, supporting biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Dicranodontium uncinatum is its ability to desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought and rapidly resume its metabolic activities when conditions improve.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Dicranodontium uncinatum played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of conifer seedlings in disturbed areas. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microhabitat for the seedlings, protecting them from desiccation and promoting their growth and survival.
Another interesting example comes from urban environments, where Dicranodontium uncinatum has been observed colonizing various man-made structures, such as concrete walls and brick pavements. This ability to thrive in human-modified habitats highlights the moss’s resilience and adaptability, making it a valuable subject for studying the impacts of urbanization on bryophyte communities.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dicranodontium uncinatum (Harv.) A.Jaeger |
| Family | Leucobryaceae |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense cushions or mats |
| Stem Height | 1-3 cm |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, curved or falcate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Costa | Strong, excurrent |
| Color | Reddish-brown to dark green |
| Sporophytes | Erect, cylindrical capsules on elongated setae |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Australia |
| Habitat | Moist rock crevices, decaying logs, soil banks, urban areas |
| Adaptations | Poikilohydry (desiccation tolerance), pioneer species |
| Ecological Roles | Soil stabilization, nutrient cycling, water retention, microhabitat provision |
Conclusion
The Dicranodontium uncinatum (Harv.) A.Jaeger moss, or simply Dicranodontium, is a remarkable example of the incredible diversity and resilience found within the bryophyte world. From its unique morphology and adaptations to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant deserves our appreciation and admiration.
As we continue to explore and understand the intricate relationships between bryophytes and their environments, we may uncover new insights into the intricate web of life that surrounds us. Perhaps the next time you encounter a small, cushion-like moss, you’ll pause and wonder if it’s the fascinating Dicranodontium uncinatum, a true marvel of nature’s ingenuity.
Ponder this: In a world where biodiversity is under constant threat, how can we better appreciate and protect the often-overlooked bryophyte communities that play such crucial roles in our ecosystems?
