Digging into Plagiothecium succulentum: The Allure of a Modest Moss
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
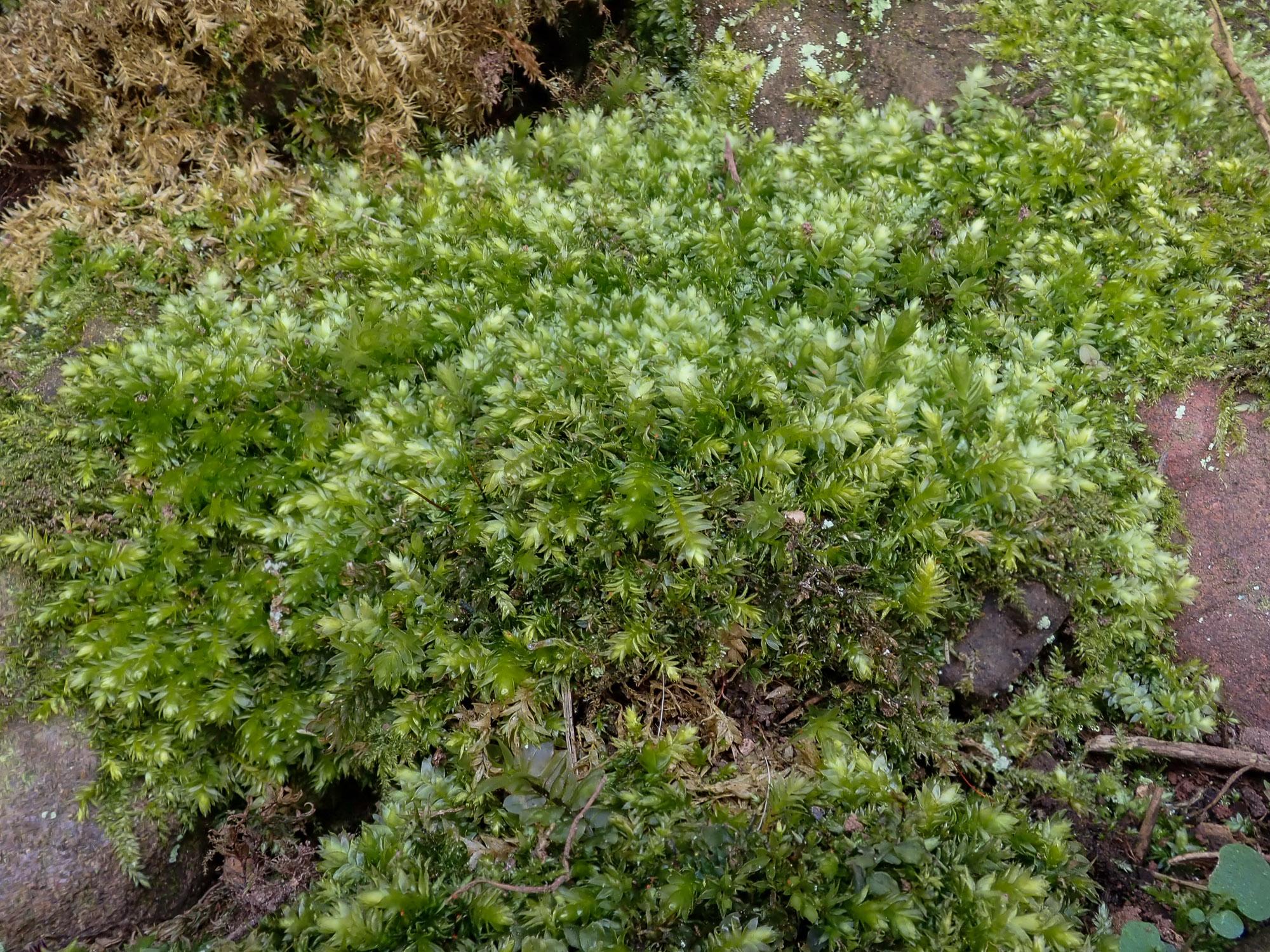

2021-03-22-14-26-41.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/plagiothecium-succulentum/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Plagiothecium succulentum (Wilson) Lindb. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Plagiotheciaceae family. Often referred to simply as Plagiothecium, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Plagiothecium succulentum belongs to the phylum Bryophyta, which encompasses all mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Within this phylum, it falls under the class Bryopsida, commonly known as the true mosses.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Plagiothecium succulentum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its vibrant green hue and delicate, feathery appearance make it a true delight to behold. One of its most distinctive features is the succulent or fleshy texture of its leaves, which gives rise to its specific epithet, “succulentum.”
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species boasts a widespread distribution, thriving in various regions across the globe. It can be found in temperate and boreal forests, often growing on decaying logs, tree bases, and moist, shaded areas. Plagiothecium succulentum is particularly fond of acidic substrates, making it a common sight in coniferous and mixed forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
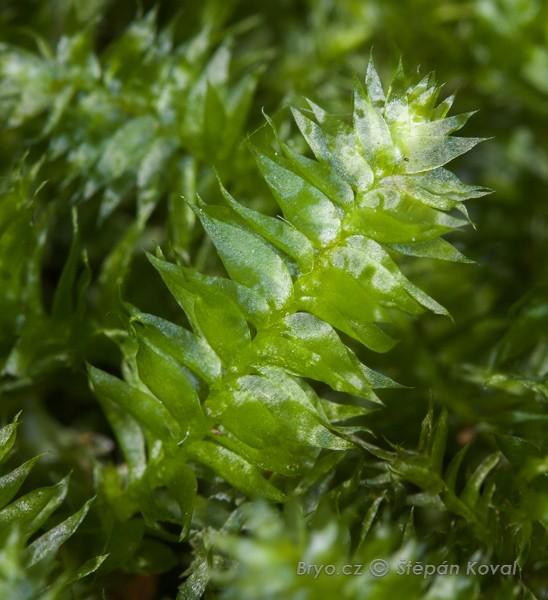

4415_Plagiothecium_succulentum_2010_06_22_4823.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&gallery=plagiothecium_succulentum&id=4415
Despite its diminutive size, Plagiothecium succulentum plays a crucial role in forest ecosystems. Its ability to retain moisture and create microhabitats contributes to the overall biodiversity of the area. Additionally, this moss serves as a vital component of the forest floor, aiding in nutrient cycling and soil formation.

medium-25420.jpg from: https://plantdollar.com/plant/plagiothecium-succulentum/
One of the remarkable adaptations of Plagiothecium succulentum is its tolerance to desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
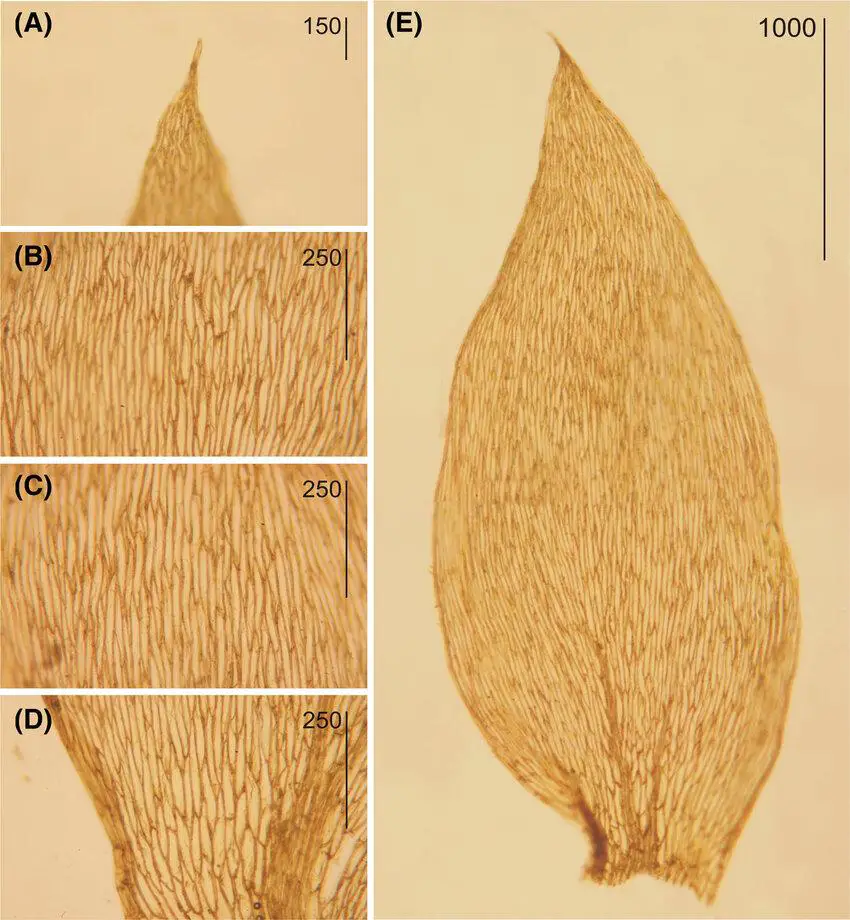

Plagiothecium-succulentum-f-propaguliferum-specimens-from-North-America-from-A-J.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiothecium-succulentum-f-propaguliferum-specimens-from-North-America-from-A-J_fig4_344171641
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers discovered that Plagiothecium succulentum played a significant role in the regeneration of certain tree species. The moss provided a suitable microhabitat for tree seedlings, facilitating their establishment and growth.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta
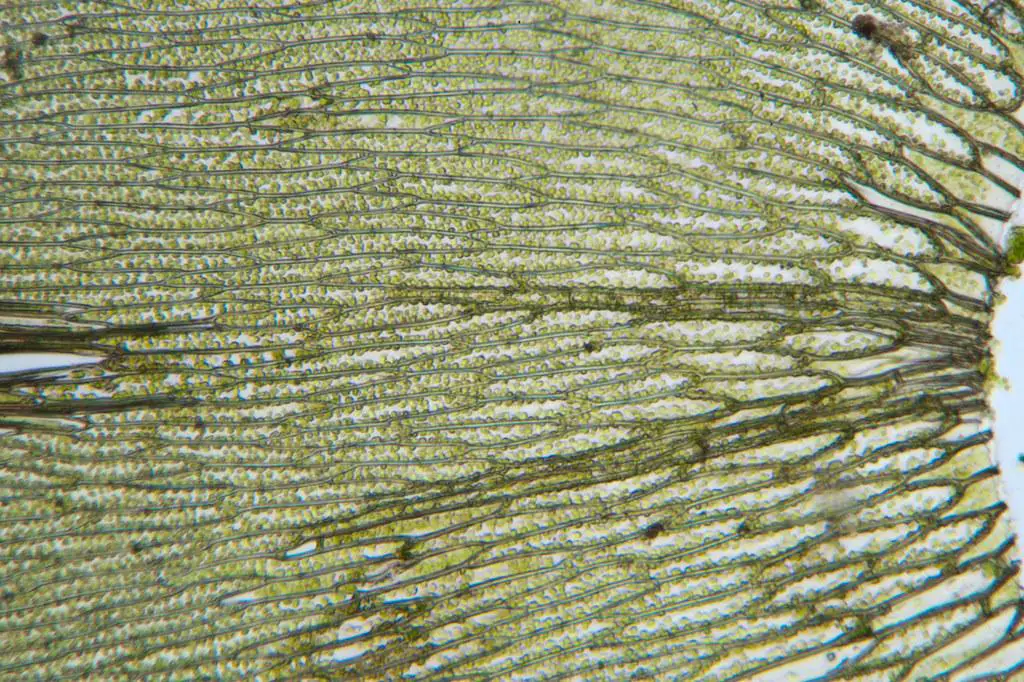 12777854203_ba3a0e3abe_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/stephenbuchan/12777854203/ |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Plagiotheciaceae |
| Genus | Plagiothecium
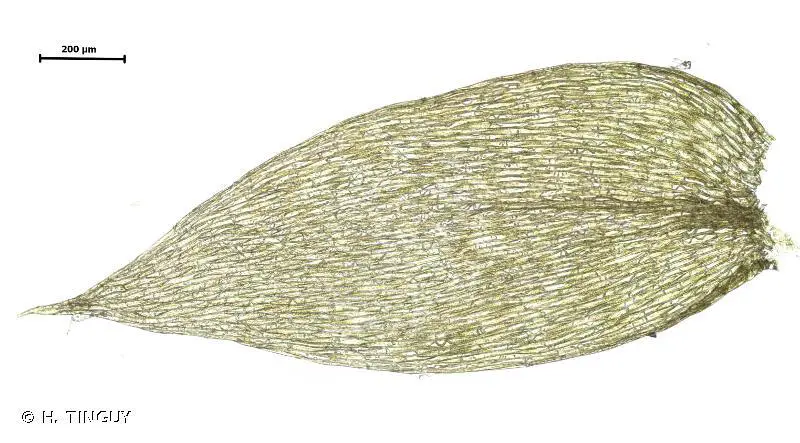 432123.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5975 |
| Species | Plagiothecium succulentum (Wilson) Lindb.
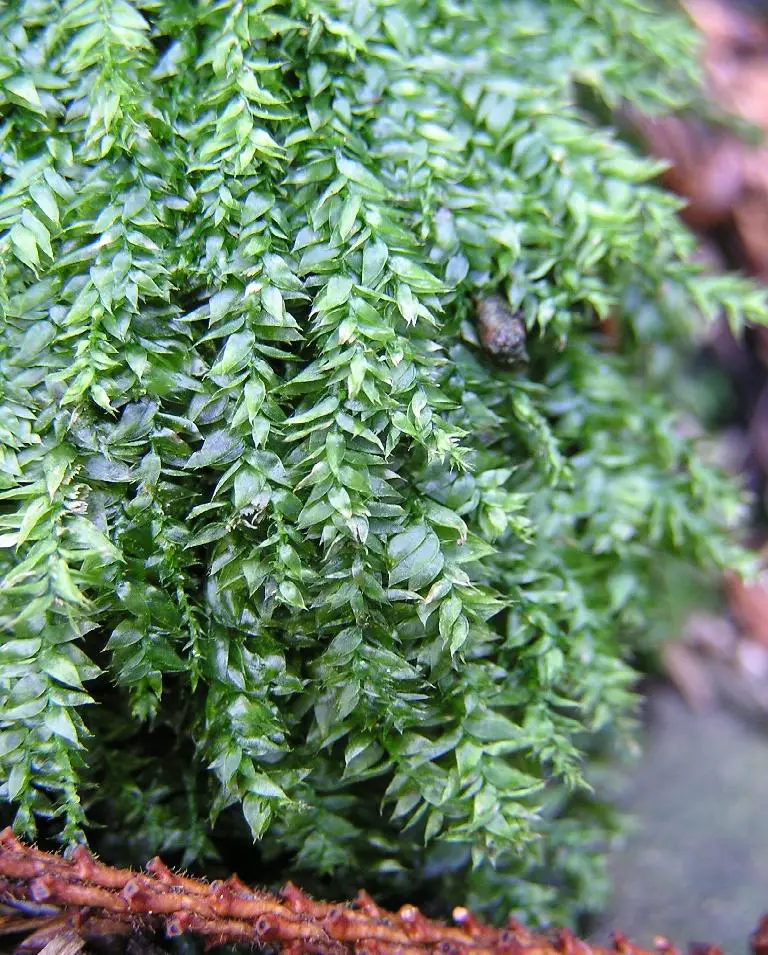 Plagiothecium_succulentum_2006.12.09_12.36.09-pc090086.jpg from: https://de-academic.com/dic.nsf/dewiki/1113656 |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Texture | Succulent or fleshy |
| Habitat | Temperate and boreal forests, decaying logs, tree bases, moist and shaded areas |
| Substrate Preference | Acidic substrates |
Conclusion
The Plagiothecium succulentum (Wilson) Lindb. moss, a member of the Plagiotheciaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you venture into a forest, you’ll pause and appreciate the delicate beauty of Plagiothecium succulentum, a true gem of the moss kingdom.
