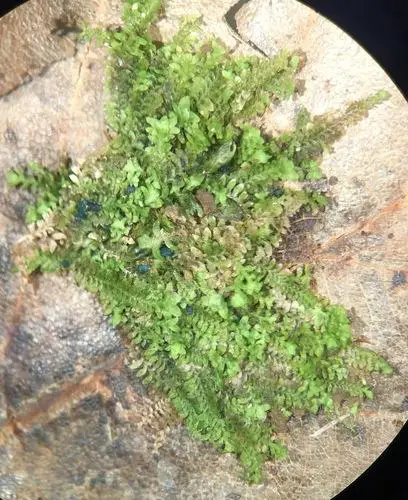

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/161955-Diplophyllum-apiculatum
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Diplophyllum apiculatum (A.Evans) Steph. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Scapaniaceae family. Often referred to simply as Diplophyllum, this unassuming yet intriguing moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this remarkable plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the depths of Diplophyllum apiculatum, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. The Scapaniaceae family, to which
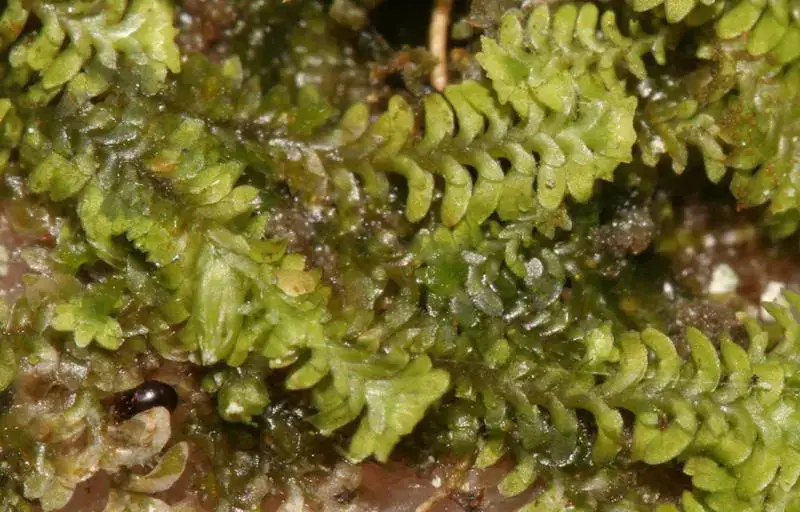

diplophyllum-apiculatum.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Scapaniaceae/diplophyllum-apiculatum/en/
Diplophyllum belongs, is a group of leafy liverworts known for their unique morphological characteristics.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
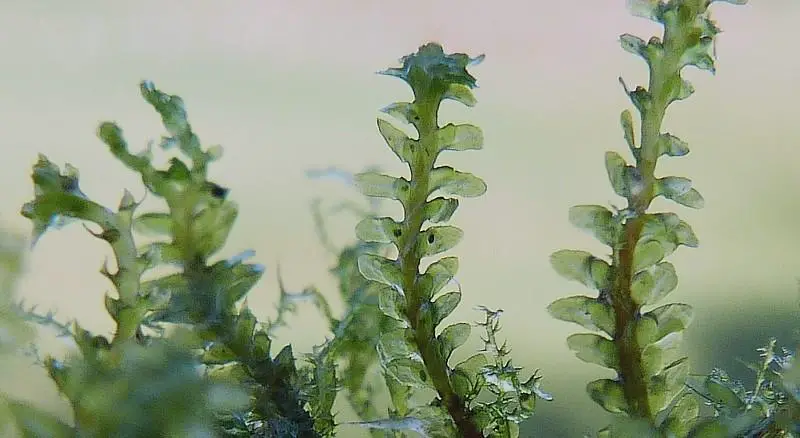
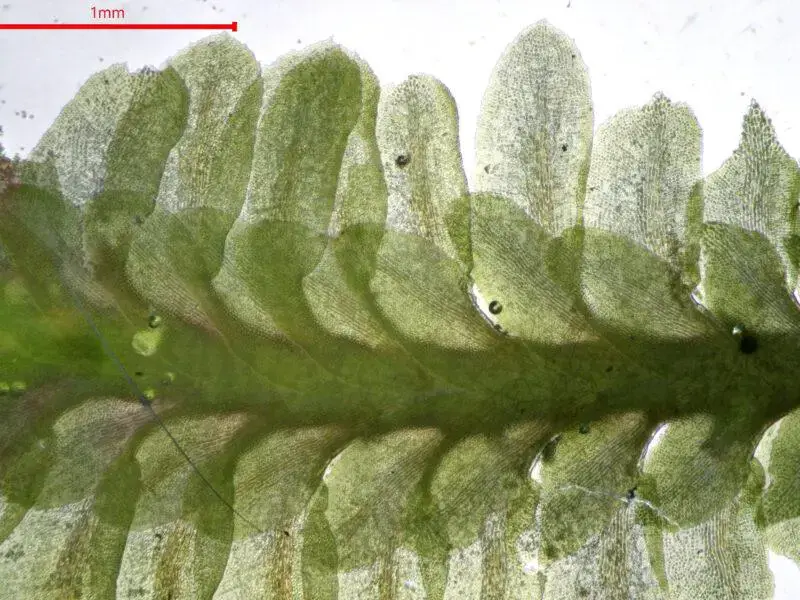
Diplophyllum apiculatum is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the substrate it inhabits. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with closely overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. These leaves are deeply divided into two lobes, giving the moss its distinctive appearance. The upper lobe is typically larger and more rounded, while the lower lobe is smaller and often pointed or apiculate, hence the specific epithet “apiculatum.”
One of the key identifying features of Diplophyllum apiculatum is the presence of underleaves, which are small, scale-like structures found on the underside of the stem. These underleaves are deeply bifid (divided into two parts) and help distinguish this species from other members of the Scapaniaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
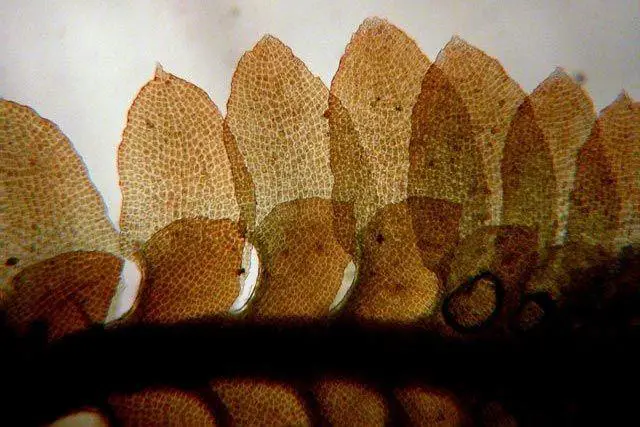
a3cd99ee7fb8f4b17c1b7399c092baf3–reproduction-bugs.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/diplophyllum-apiculatum-approx-40x-microscope-view-original-diplophyllum-like-many-plants-can-reproduce-in-two-ways-1–289919294733305520/
Diplophyllum apiculatum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, stumps, or humus-rich soil in coniferous or mixed forests.
This moss prefers cool, humid conditions and is commonly found in areas with high rainfall or near streams, waterfalls, and other sources of moisture. Its ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats has contributed to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Diplophyllum apiculatum plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Diplophyllum apiculatum is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture and reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found Diplophyllum apiculatum

Diplophyllum-apiculatum.jpg from: https://ohioplants.org/bryophytes-divisions/
to be a significant component of the bryophyte community in old-growth forests. Its presence was closely associated with the availability of decaying wood and high moisture levels, highlighting its preference for specific microhabitats.
Another study in Europe examined the role of Diplophyllum apiculatum
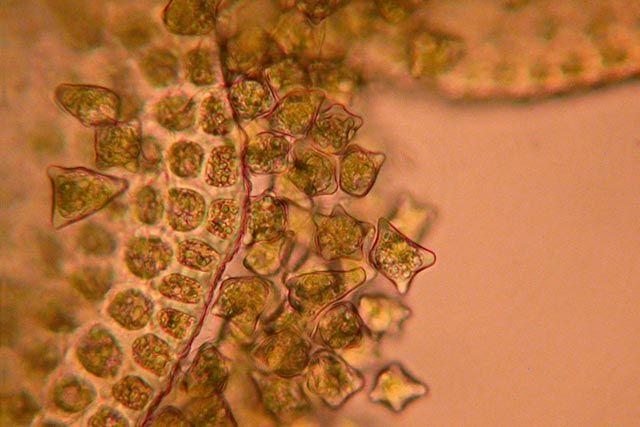
43ee69ee366eaed171bdeeeb415eac8a.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/diplophyllum-apiculatum-gemmae-approx-400x-microscope-view-original–143552306842404556/
in facilitating the establishment of vascular plant seedlings. The moss’s dense mats were found to provide a suitable environment for seed germination and early growth, acting as a nursery for various plant species.
Technical Table

dipapicm.jpg from: https://www.buildingthepride.com/faculty/pgdavison/Liverworts_A_F.htm

Diplophyllum_albicans_4.jpg from: https://www.jardinsauvage.fr/FLORE/BRYOPHYTES/DIPLOPHYLLUM.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida
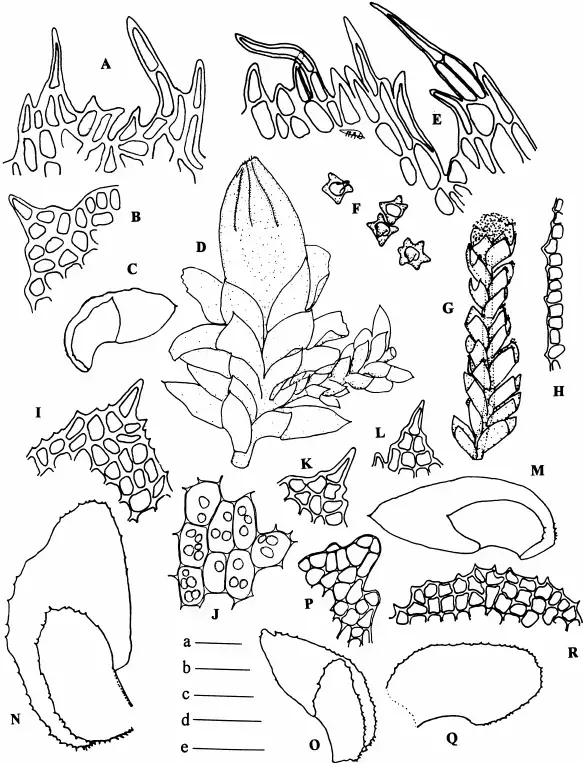 Diplophyllum-apiculatum-A-C-D-serrulatum-D-M-and-D-taxifolium-N-R.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Diplophyllum-apiculatum-A-C-D-serrulatum-D-M-and-D-taxifolium-N-R_fig1_268254992 |
| Family | Scapaniaceae |
| Genus | Diplophyllum |
| Species | apiculatum |
| Common Name | Diplophyllum |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, overlapping |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided into two lobes |
| Underleaves | Present, deeply bifid |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Widespread across various regions |
Conclusion
Diplophyllum apiculatum (A.Evans) Steph., a member of the

2020-11-23-16-51-01-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/diplophyllum-albicans/

nokogirikooigoke.jpg from: https://mikawanoyasou.org/koke/nokogirikooigoke.htm
Scapaniaceae family, is a remarkable moss that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its unique morphology, widespread distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better understand and protect these often overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?