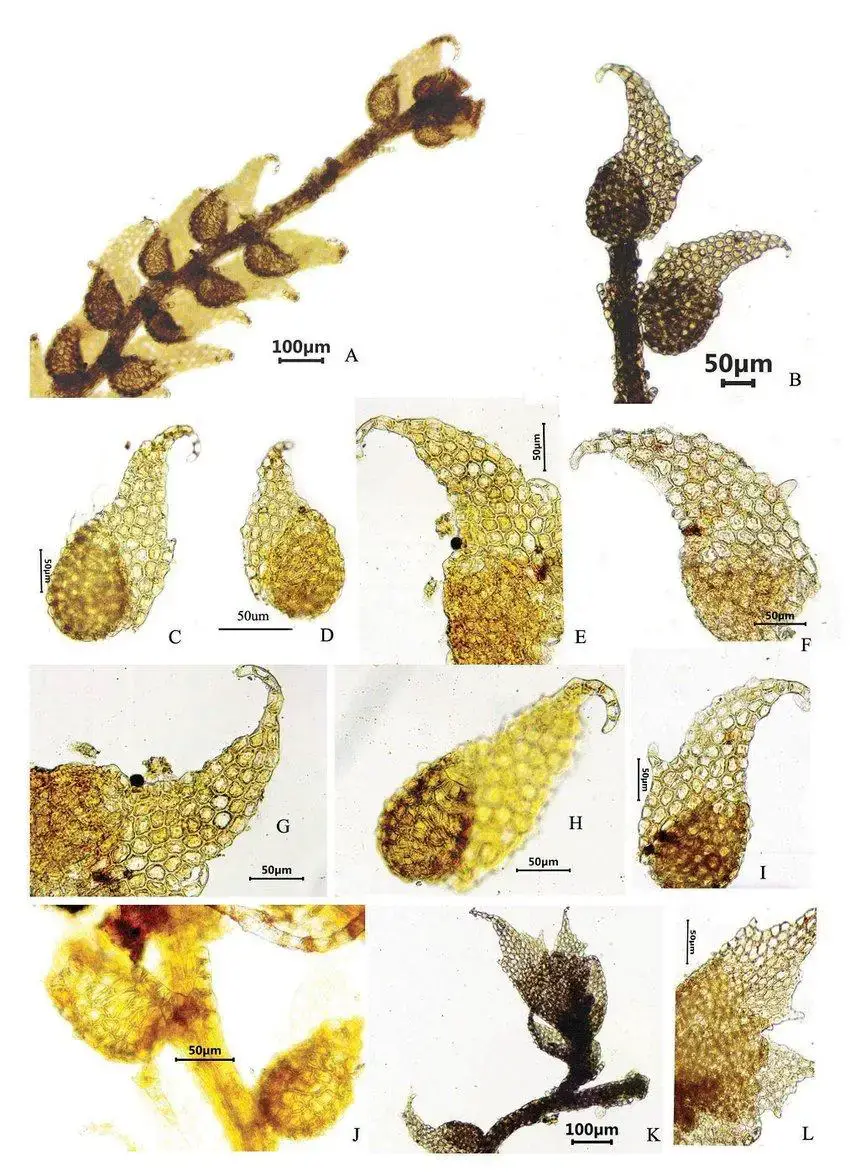

A-L-Drepanolejeunea-ternatensis-Gottsche-Steph-A-portion-of-plant-with-cauducous.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-L-Drepanolejeunea-ternatensis-Gottsche-Steph-A-portion-of-plant-with-cauducous_fig9_343694914
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Diplophyllum domesticum (Gottsche) Steph. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Scapaniaceae family. Also known simply as Diplophyllum, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Diplophyllum domesticum, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
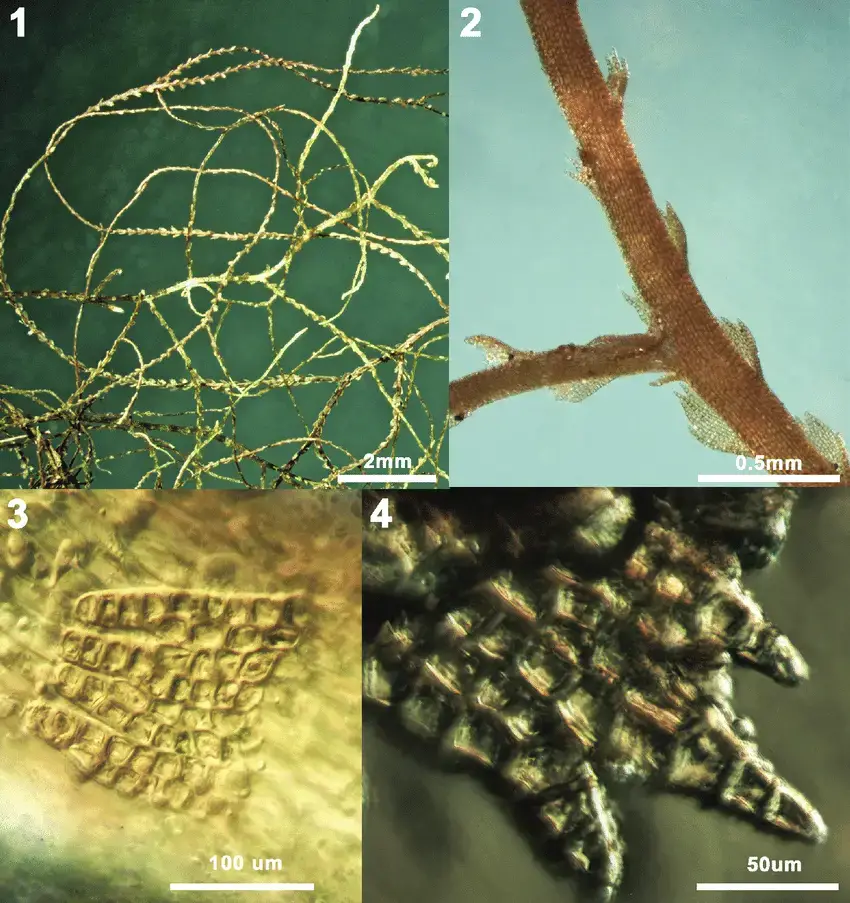

Lepidozia-haskarliana-Gottsche-Lindenb-Nees-Steph-1-plant-habit-2-scale-like.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lepidozia-haskarliana-Gottsche-Lindenb-Nees-Steph-1-plant-habit-2-scale-like_fig1_270575213
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Diplophyllum domesticum

A-Cheilolejeunea-ceylanica-Gottsche-RMSchust-Kachroo-B-Cheilolejeunea.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Cheilolejeunea-ceylanica-Gottsche-RMSchust-Kachroo-B-Cheilolejeunea_fig72_357776052
is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flattened, ribbon-like form. Its gametophyte (the dominant, gamete-producing phase) consists of a prostrate, irregularly branched thallus
Radula-japonica-Gottsche-ex-Steph-1-plant-habit-with-perianth-dorsal-view-2-plant_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-japonica-Gottsche-ex-Steph-1-plant-habit-with-perianth-dorsal-view-2-plant_fig2_342043028
that creeps along the substrate. The thallus is typically green to brownish-green in color and can reach lengths of several centimeters.
One of the distinctive features of Diplophyllum domesticum
![Diplophyllum+albicans+(2)+-+Copie+[800x600].JPG](/img/Diplophyllumalbicans2-Copie800x600.jpg)
Diplophyllum+albicans+(2)+-+Copie+[800×600].JPG from: https://fred-mousses.blogspot.com/2009/12/diplophyllum-albicans.html
is the presence of two rows of leaf-like structures called amphigastria on the underside of the thallus. These structures aid in water absorption and anchoring the plant to its substrate.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Diplophyllum domesticum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, soil, or rocks

16645887975_755812694c_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/131528844@N08/16645887975/
in temperate and boreal forests.
This moss prefers acidic substrates and is commonly associated with coniferous or mixed forests, where it can form dense mats or intermingle with other bryophyte species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Diplophyllum domesticum

A-Acrolejeunea-pycnoclada-Taylor-Schiffn-B-Caudalejeunea-reniloba-Gottsche-Steph.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Acrolejeunea-pycnoclada-Taylor-Schiffn-B-Caudalejeunea-reniloba-Gottsche-Steph_fig71_357780316
plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Like other bryophytes, it contributes to soil formation, water retention, and nutrient cycling. Its ability to colonize and thrive in moist, shaded environments makes it an important component of forest floor communities.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Diplophyllum domesticum

2021-02-27-15-19-50-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/diplophyllum-albicans/
is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the plant can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Diplophyllum domesticum was a significant component of the bryophyte community in old-growth forests. Its presence was closely linked to the availability of decaying logs and the presence of other moisture-loving species, highlighting its role in these unique ecosystems.
Technical Table
| Scientific Name | Family | Common Name | Growth Form | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diplophyllum domesticum (Gottsche) Steph. | Scapaniaceae | Diplophyllum | Thallose liverwort | Moist, shaded environments; decaying logs, soil, rocks in temperate and boreal forests |
Conclusion
The Diplophyllum domesticum (Gottsche) Steph. moss, or simply Diplophyllum

Diplophyllum_albicans_4.jpg from: https://www.jardinsauvage.fr/FLORE/BRYOPHYTES/DIPLOPHYLLUM.html
, is a remarkable member of the Scapaniaceae family and the Marchantiophyta (liverworts) division. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, the humble Diplophyllum domesticum serves as a reminder of the intricate beauty and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the microscopic wonders around us, what other hidden marvels might we be missing, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?

38875045.jpeg from: https://www.yclky.net/productinfo/1713539.html