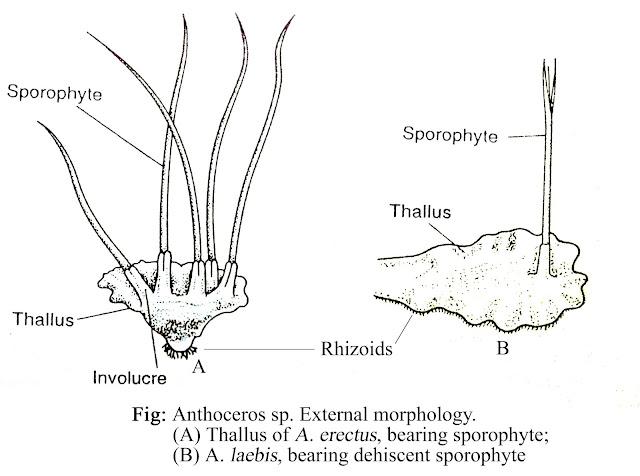
1.jpg from: http://premabotany.blogspot.com/2018/12/anthoceros.html
Anthoceros tuberosus Taylor: A Fascinating Moss of the Notothyladaceae Family
Anthoceros tuberosus Taylor, also known simply as Anthoceros, is a unique and intriguing species of moss belonging to the Notothyladaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant plays important ecological roles and has adapted to thrive in a variety of habitats around the world. Let’s dive in and learn more about this fascinating moss!
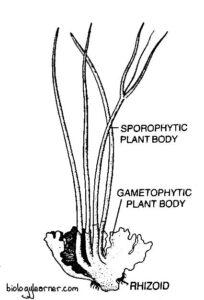
Anthoceros-thallus-bearing-sporophyte-204×300.jpg from: https://biologylearner.com/anthoceros-distribution-structure-reproduction/
Background on Anthoceros tuberosus Taylor
Anthoceros tuberosus is a species of hornwort, which are non-vascular plants in the division Anthocerotophyta. Hornworts get their name from their elongated sporophytes that resemble tiny horns emerging from the plant’s gametophyte. A. tuberosus was first described by the botanist Thomas Taylor in 1836.
Morphology and Identification
Anthoceros tuberosus has a thalloid gametophyte, meaning its body is a flattened, leaf-like structure rather than having stems and leaves like other mosses. The thallus is dark green, often with a
maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tsvyzb7DWiU
bluish tint, and forms small rosettes. Its cells contain a single large chloroplast. The plant produces cylindrical sporophytes that split open to release spores when mature.
Global Distribution and Habitat
A. tuberosus has a widespread distribution
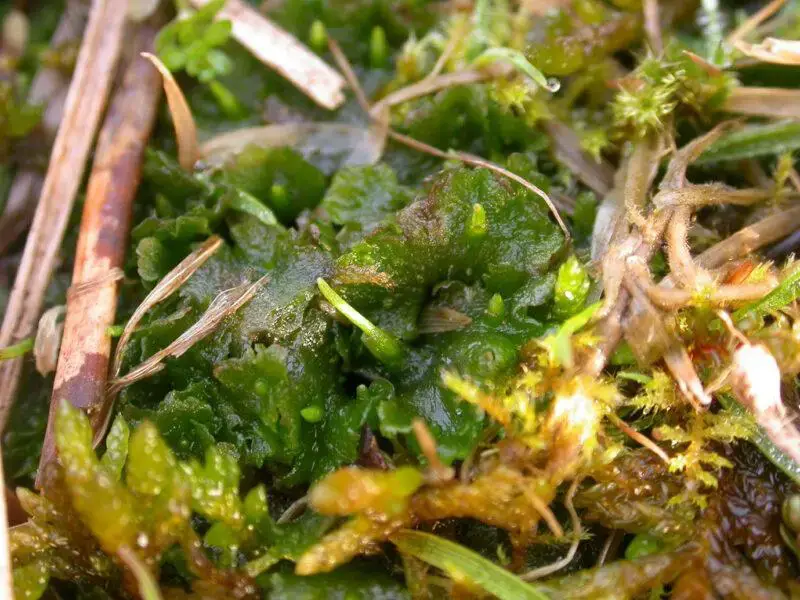

VC45-06-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/anthoceros-punctatus/
, found on several continents including North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia
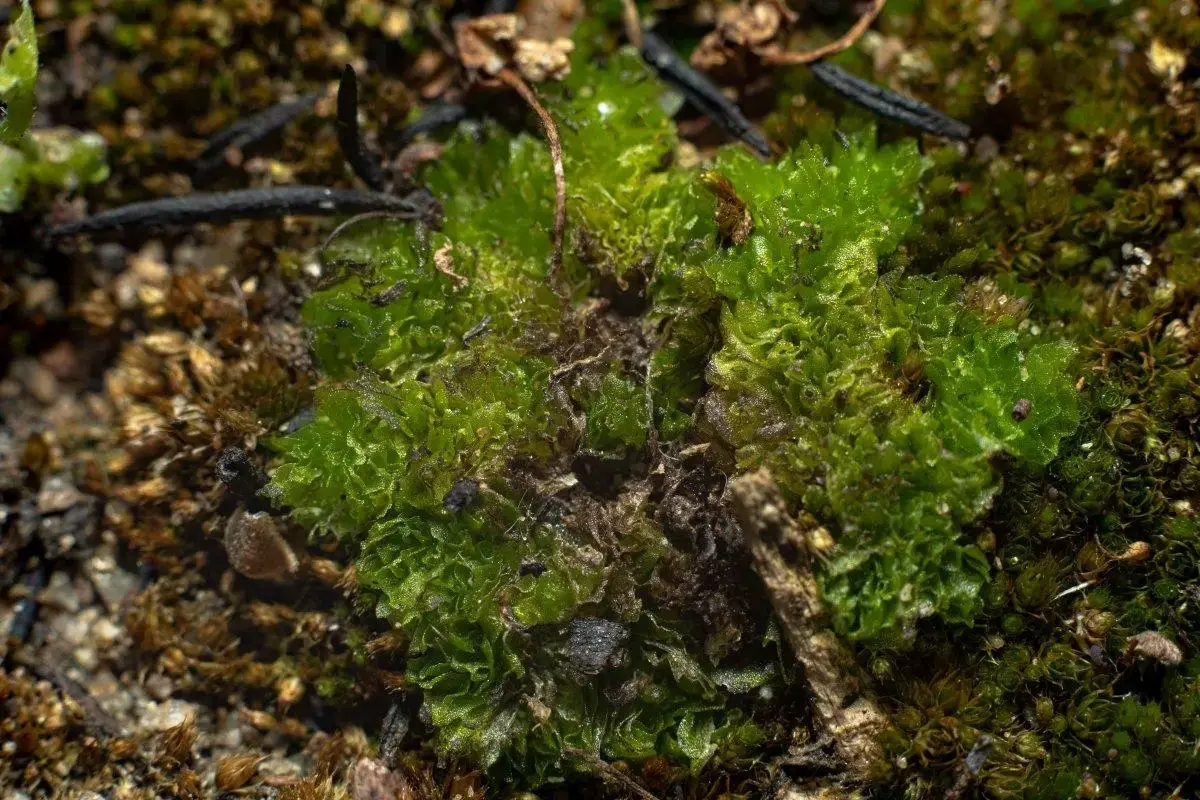

154895.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=8804
. It grows in a variety of habitats, from damp soils and rocks to disturbed sites like gardens, greenhouses, and agricultural fields. This adaptable moss can tolerate a range of environmental conditions.
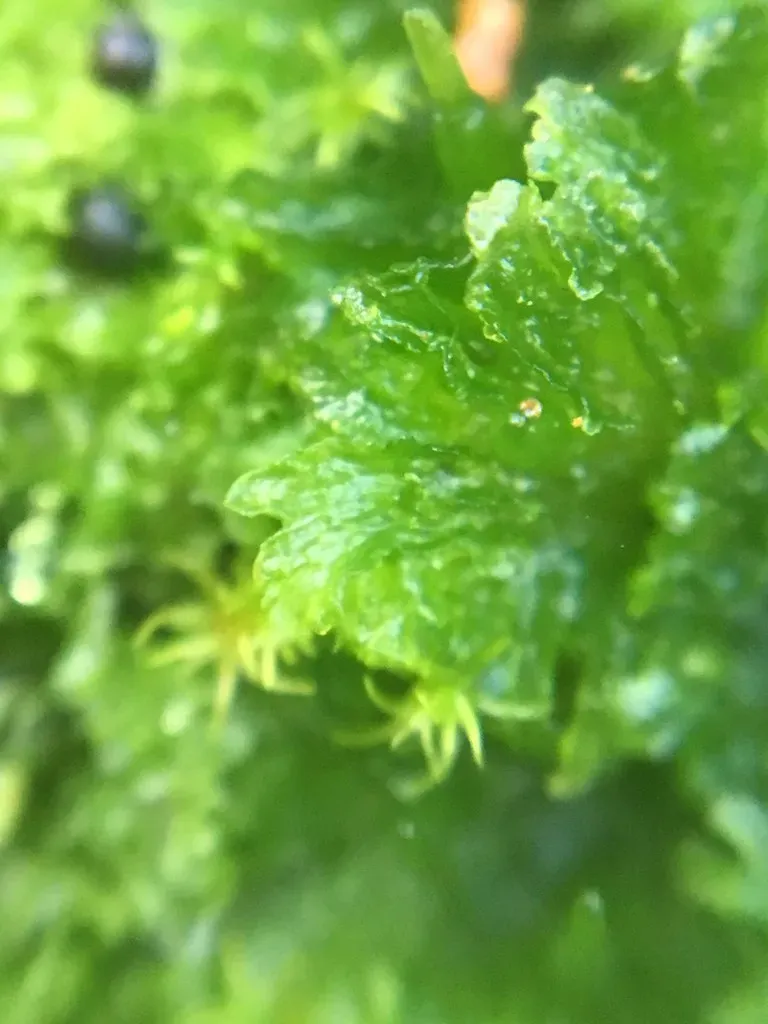

152654038368780290.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/ru/wiki/Anthoceros_fusiformis.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Anthoceros tuberosus plays several important roles in its ecosystems:
- Pioneer species: As an early colonizer of disturbed soils, it helps prevent erosion and paves the way for other plants to establish.
- Nutrient cycling: It aids in breaking down organic matter and cycling nutrients back into the soil.
- Microhabitats: The moss mats provide shelter and moisture for microorganisms and tiny invertebrates.
- Indicator species: Because of its sensitivity to air and water pollution, the presence or absence of A. tuberosus can signal environmental health.
To survive in challenging conditions, A. tuberosus has developed key adaptations like desiccation tolerance to withstand drying out, efficient nutrient uptake and storage, and the ability to reproduce asexually via gemmae or fragmentation.
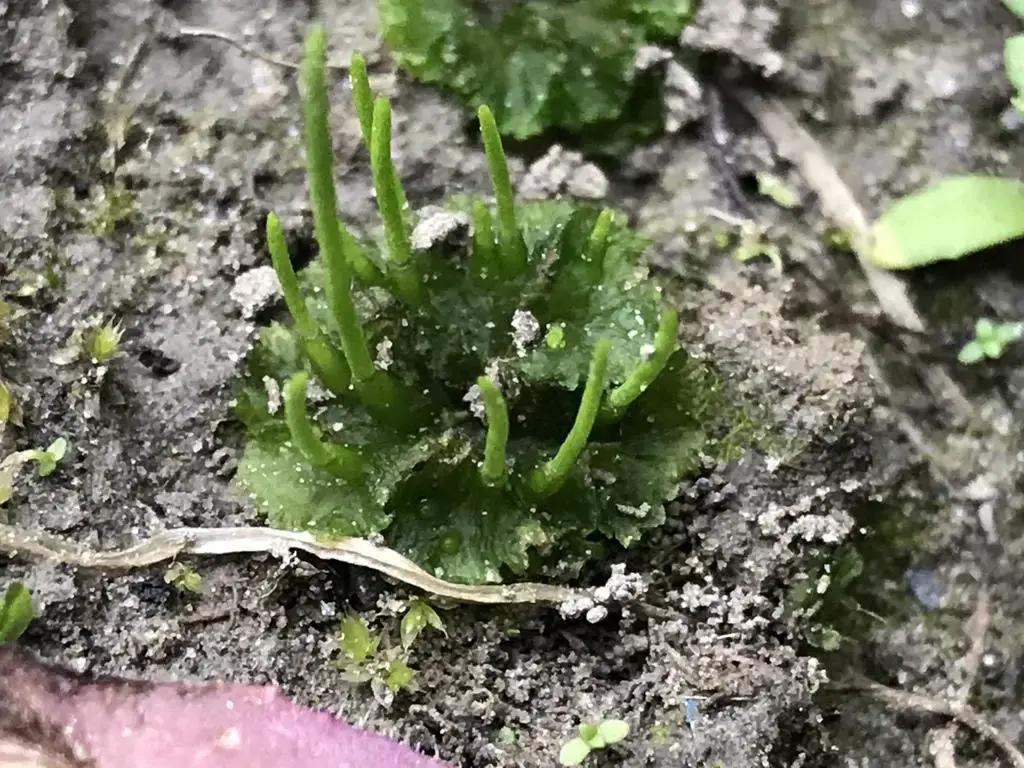

large.jpg from: https://inaturalist.nz/observations/21478020
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Anthocerotophyta |
| Class | Anthocerotopsida |
| Order | Notothyladales |
| Family | Notothyladaceae |
| Genus | Anthoceros |
| Species | A. tuberosus |
| Authority | Taylor |
| Gametophyte | Thalloid |
| Sporophyte | Horn-shaped |
Conclusion
Anthoceros tuberosus Taylor is a remarkable moss that has successfully spread across the globe thanks to its tenacity and adaptability. This tiny plant reminds us not to underestimate the profound ecological importance of even the most unassuming species. What other secrets might the miniature world of mosses hold? The next time you spot a patch of Anthoceros, take a moment to appreciate its vital place in the tapestry of life.