Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Shoot-dorsal-view-B-part-of-shoot_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Shoot-dorsal-view-B-part-of-shoot_fig3_29813448
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Bazzania manillana (Gottsche ex Steph.) S.Hatt. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Lepidoziaceae family. Often referred to simply as Bazzania, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.

blog_sj26.jpg from: https://www.sweetjusticephoto.com/shawwedding/
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Bazzania manillana, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
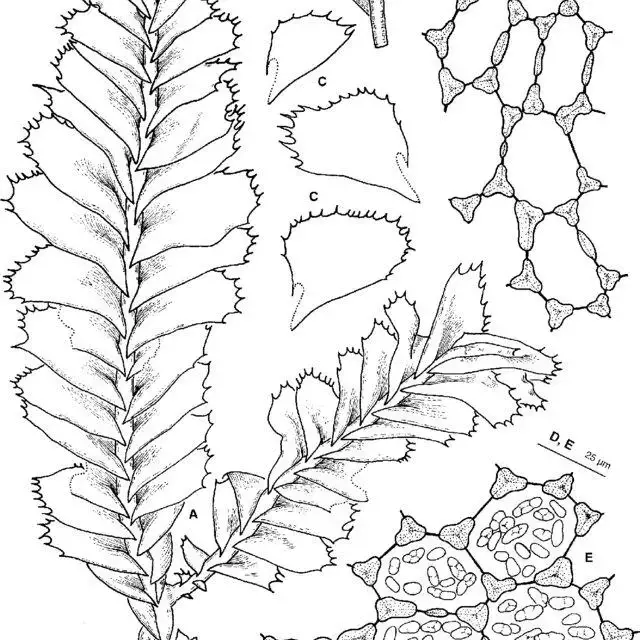
Bazzania manillana is a leafy liverwort that exhibits a distinctive appearance. Its creeping and irregularly branched stems are adorned with overlapping and obliquely inserted leaves, creating a visually striking pattern. The leaves themselves are ovate to oblong in shape, with a rounded or obtuse apex. One of the key identifying features of this moss is the presence of underleaves, which are smaller structures found on the underside of the stem.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Bazzania manillana is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Pacific Islands. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock surfaces to decaying logs and tree bark. This moss exhibits a remarkable ability to adapt to different environmental conditions, making it a resilient and versatile species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Bazzania manillana plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to the moisture retention and nutrient cycling processes within its habitat. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various tiny organisms, providing shelter and sustenance for a diverse array of microscopic life forms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Bazzania manillana is its ability to reproduce through both sexual and asexual means. This versatility ensures the continuity of the species and allows it to colonize new areas effectively.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve in China, researchers discovered a rich diversity of Bazzania species, including Bazzania manillana. This study highlighted the importance of preserving these bryophyte communities, as they contribute significantly to the overall biodiversity of the region.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Genus | Bazzania |
| Species | Bazzania manillana (Gottsche ex Steph.) S.Hatt. |
Conclusion
The Bazzania manillana (Gottsche ex Steph.) S.Hatt. moss, a member of the Lepidoziaceae family, is a remarkable example of the diversity and resilience found within the bryophyte world. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, let us ponder: What other hidden wonders await discovery within the realm of these unassuming yet extraordinary plants?