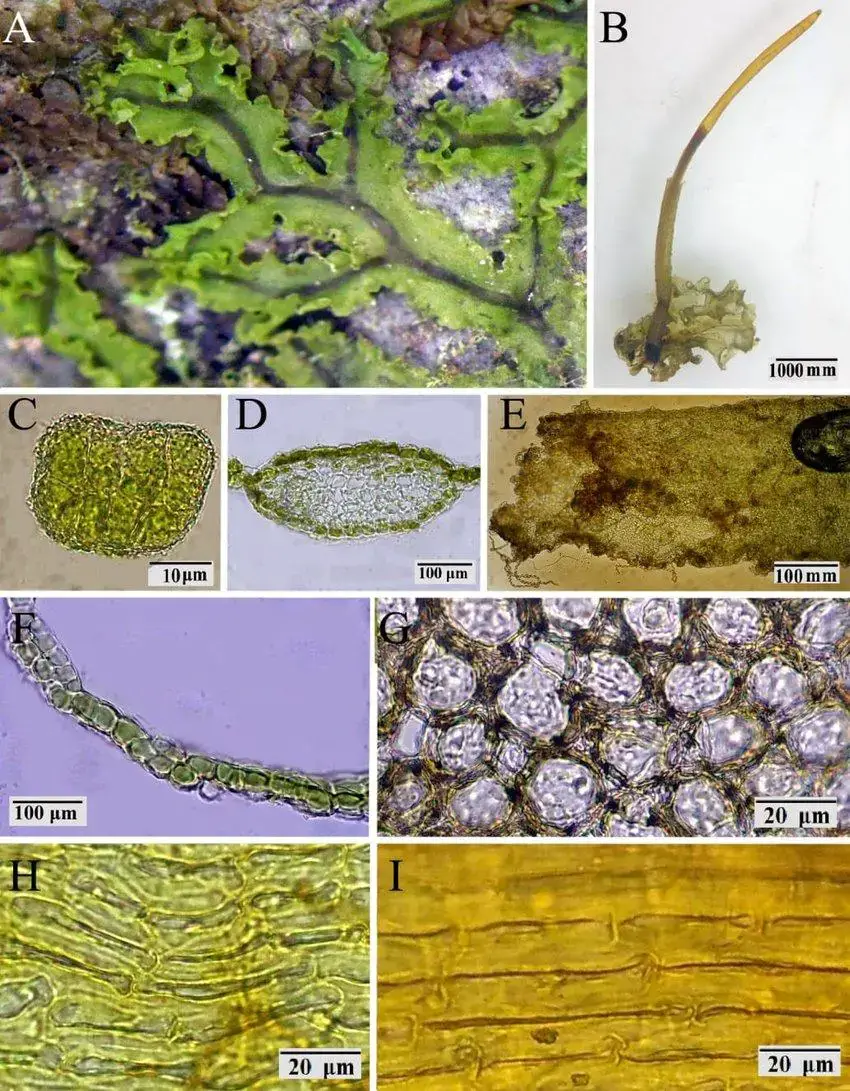

A-G-Dendroceros-breutelii-Nees-A-Gametophyte-on-substrate-B-General-aspect-of-the.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-G-Dendroceros-breutelii-Nees-A-Gametophyte-on-substrate-B-General-aspect-of-the_fig1_349894951
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Neurolejeunea breutelii (Gottsche) A.Evans moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Lejeuneaceae family. Often referred to simply as Neurolejeunea, this tiny yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Marchantiophyta (liverwort) species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Neurolejeunea breutelii, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, which encompasses liverworts, a group of bryophytes that are closely related to mosses and hornworts. Within this phylum, Neurolejeunea breutelii is a member of the class Jungermanniopsida, a diverse group of leafy liverworts.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Neurolejeunea breutelii is a tiny, delicate plant that often forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its leaves are deeply lobed, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. The plant’s color can range from vibrant shades of green to reddish-brown, depending on its environment and growth stage.
One of the most remarkable features of Neurolejeunea breutelii

Moss_B53199_Weissia-breutelii_3_StE.jpg from: https://sweetgum.nybg.org/science/projects/st-eustatius/portfolio/bryophytes/
is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, it produces specialized structures called archegoniophores and antheridiophores, which bear the female and male reproductive organs, respectively.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Neurolejeunea breutelii is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Oceania. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments, where it can be found growing on tree bark, rocks, and soil.
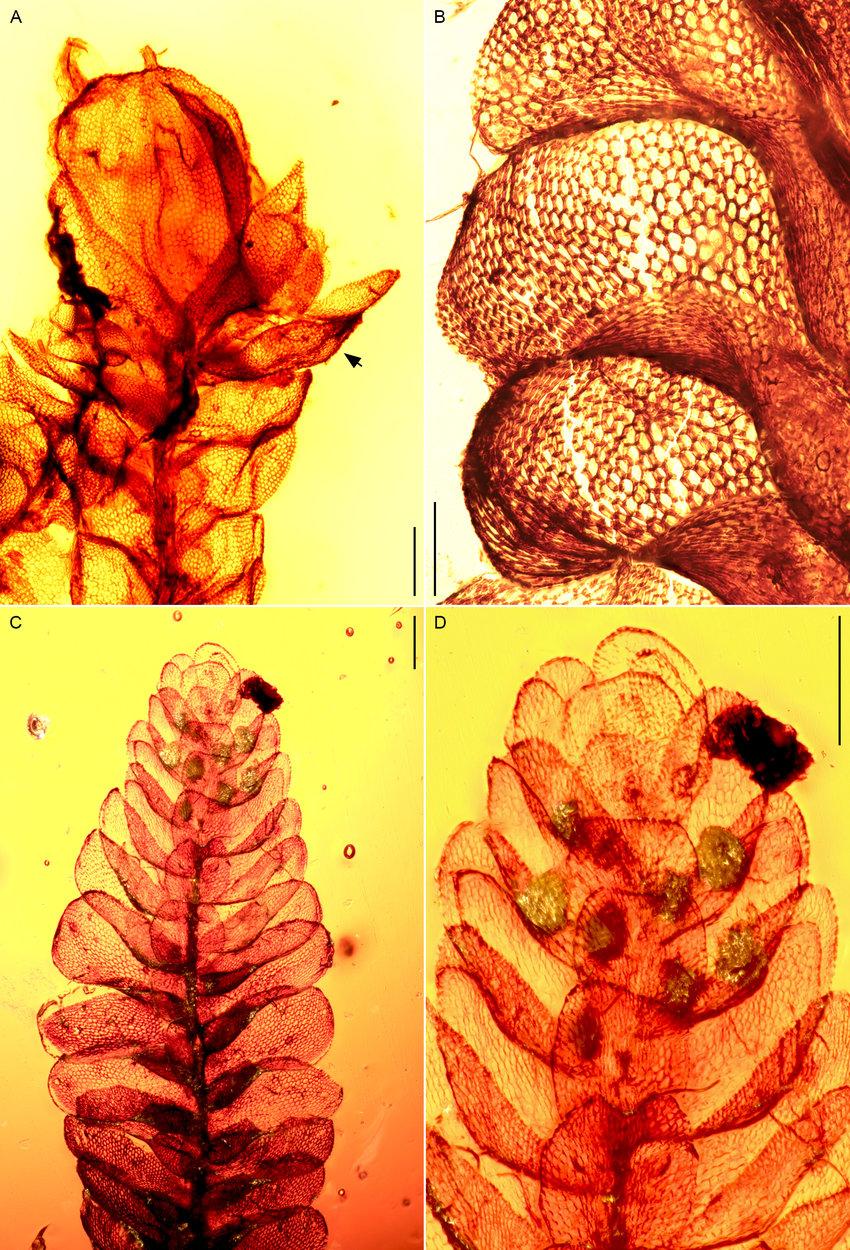

Lejeuneaceae-subfam-Ptychanthoideae-A-D-Spruceanthus-extinctus-from-Mexican-amber-A.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lejeuneaceae-subfam-Ptychanthoideae-A-D-Spruceanthus-extinctus-from-Mexican-amber-A_fig5_352836886
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Neurolejeunea breutelii plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps in the colonization of new habitats and contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Neurolejeunea breutelii

pyrenula-breutelii-china-andre-aptroot-5183.jpg from: https://www.tropicallichens.net/5363.html
is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the plant can enter a dormant state, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives and resumes its growth and metabolic activities.

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362501753_Caudalejeunea_lehmanniana_Gottsche_A_Evans_Hepaticae_Lejeuneaceae_-_A_new_record_for_Indian_Bryoflora_from_Lohit_district_Arunachal_Pradesh
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a unique population of Neurolejeunea breutelii thriving in an old-growth forest. This population exhibited a remarkable diversity of genetic variations, highlighting the importance of preserving such habitats for the conservation of bryophyte biodiversity.
Technical Table

gigaspermum-repens-185.jpg from: https://cpbr.gov.au/bryophyte/photos-captions/gigaspermum-repens-185.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Porellales |
| Family | Lejeuneaceae |
| Genus | Neurolejeunea |
| Species | breutelii
 pyrenula-breutelii-china-andre-aptroot-2212.jpg from: https://www.tropicallichens.net/5364.html |
| Growth Form | Mat-forming, cushion-like |
| Leaf Morphology | Deeply lobed, feathery appearance |
| Color | Green to reddish-brown |
| Reproduction | Sexual and asexual |
| Habitat | Moist forests, rocky outcrops, tree bark, soil |
| Distribution | Widespread across multiple continents |
Conclusion
The Neurolejeunea breutelii (Gottsche) A.Evans moss, a member of the

f02_50.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-28/issue-1/heia.28.1.2015.50/Additions-to-the-Liverwort-and-Hornwort-Flora-of-São-Tomé/10.13158/heia.28.1.2015.50.full
51-Lejeunea-alata-Gottsche-37-Part-of-plant-in-ventral-view-38-39-Leaves-40_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/51-Lejeunea-alata-Gottsche-37-Part-of-plant-in-ventral-view-38-39-Leaves-40_fig1_281129131
Fig-1-Notothylas-irregularis-C-hantanaorr-A-B-tha-llus-w-ith-s-poroph-y-t-es-C.png from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/02/antherosofita-notothylas-breutelii.html
Lejeuneaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve the habitats of these remarkable organisms, ensuring their survival for generations to come?