
10634.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14224
Introduction
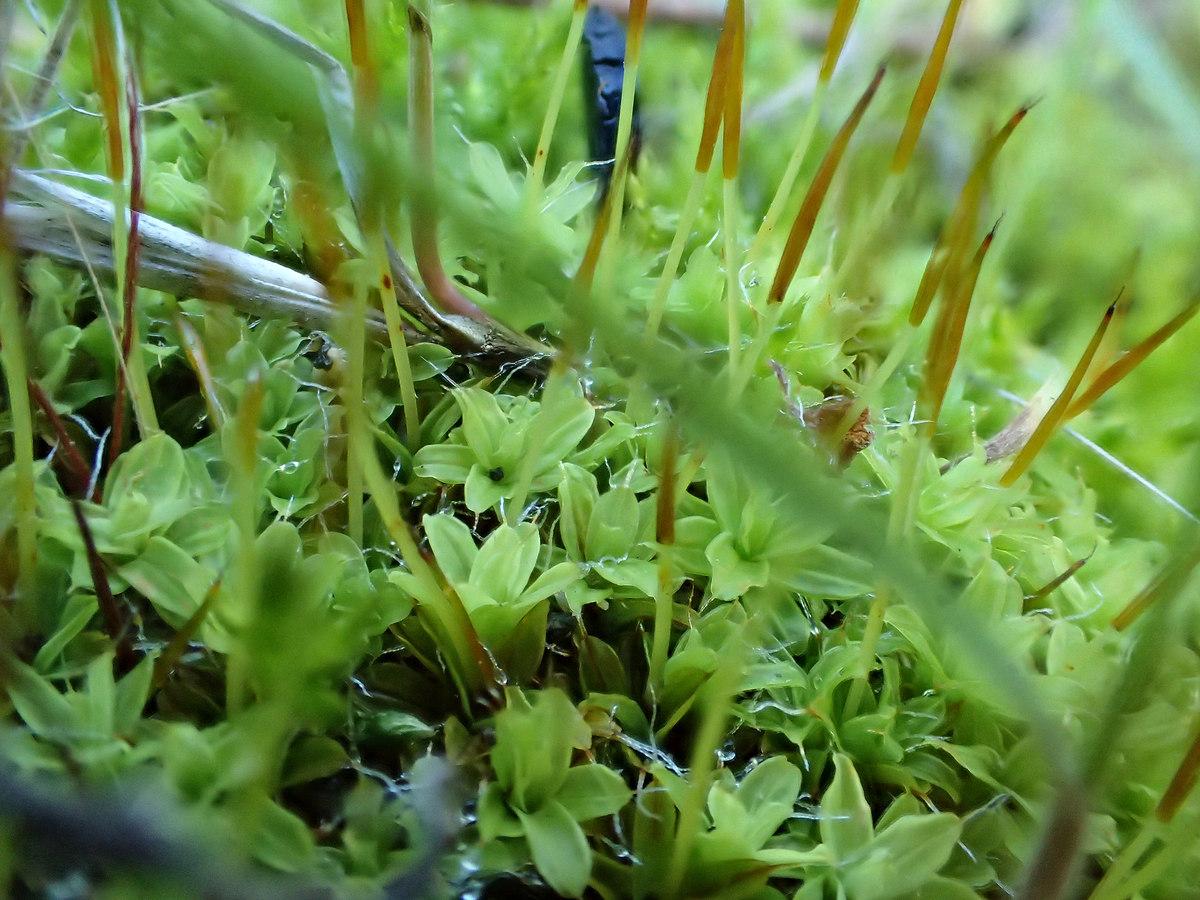
Welcome to the fascinating world of Syntrichia princeps (De Not.) Mitt.

3198-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/english/picture.asp?ID=18559
, a remarkable moss species belonging to the Pottiaceae family. Also known simply as Syntrichia, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Syntrichia princeps, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, play a crucial role in various ecosystems worldwide. Despite their diminutive size, they contribute significantly to nutrient cycling, soil formation, and moisture retention.

3198-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/english/picture.asp?ID=18568
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
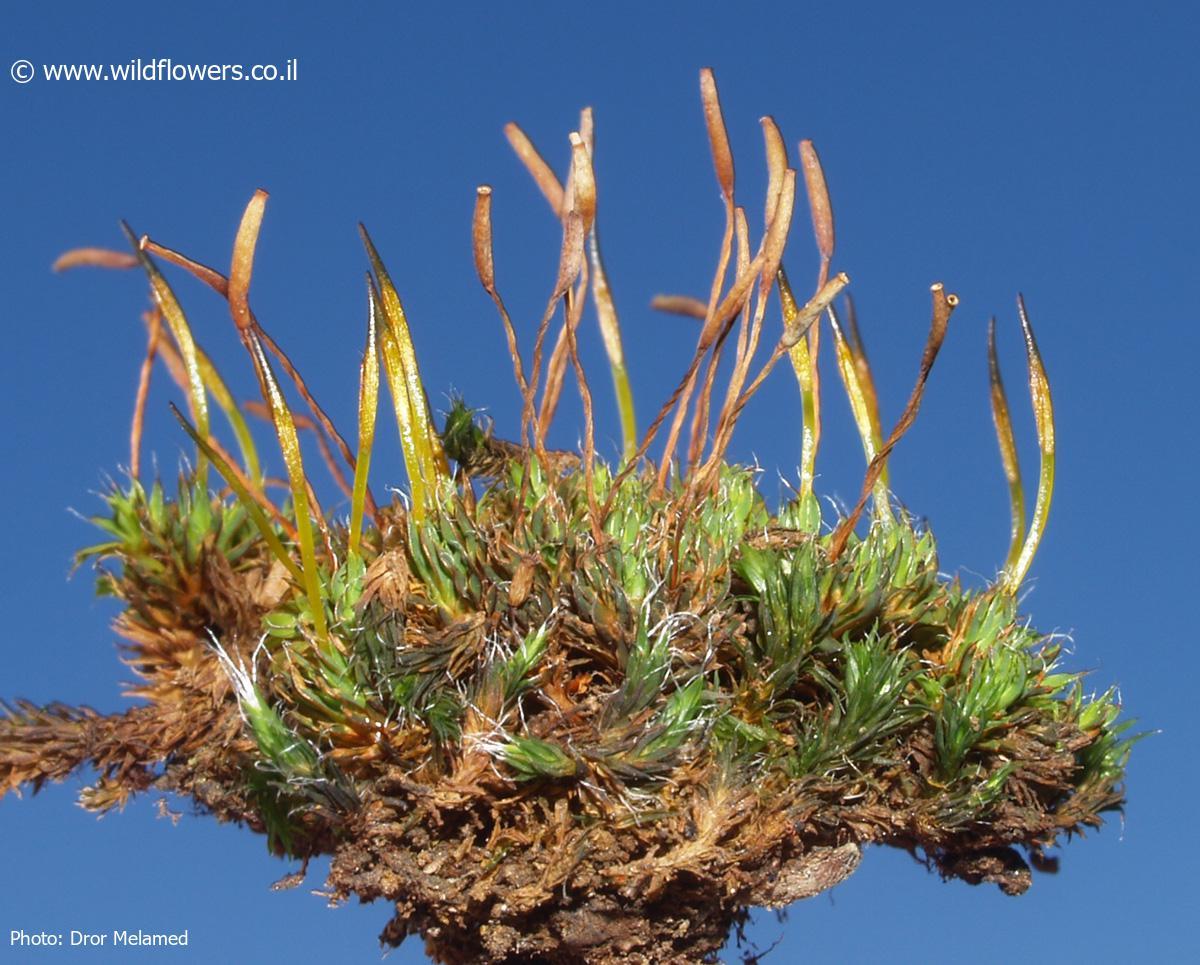
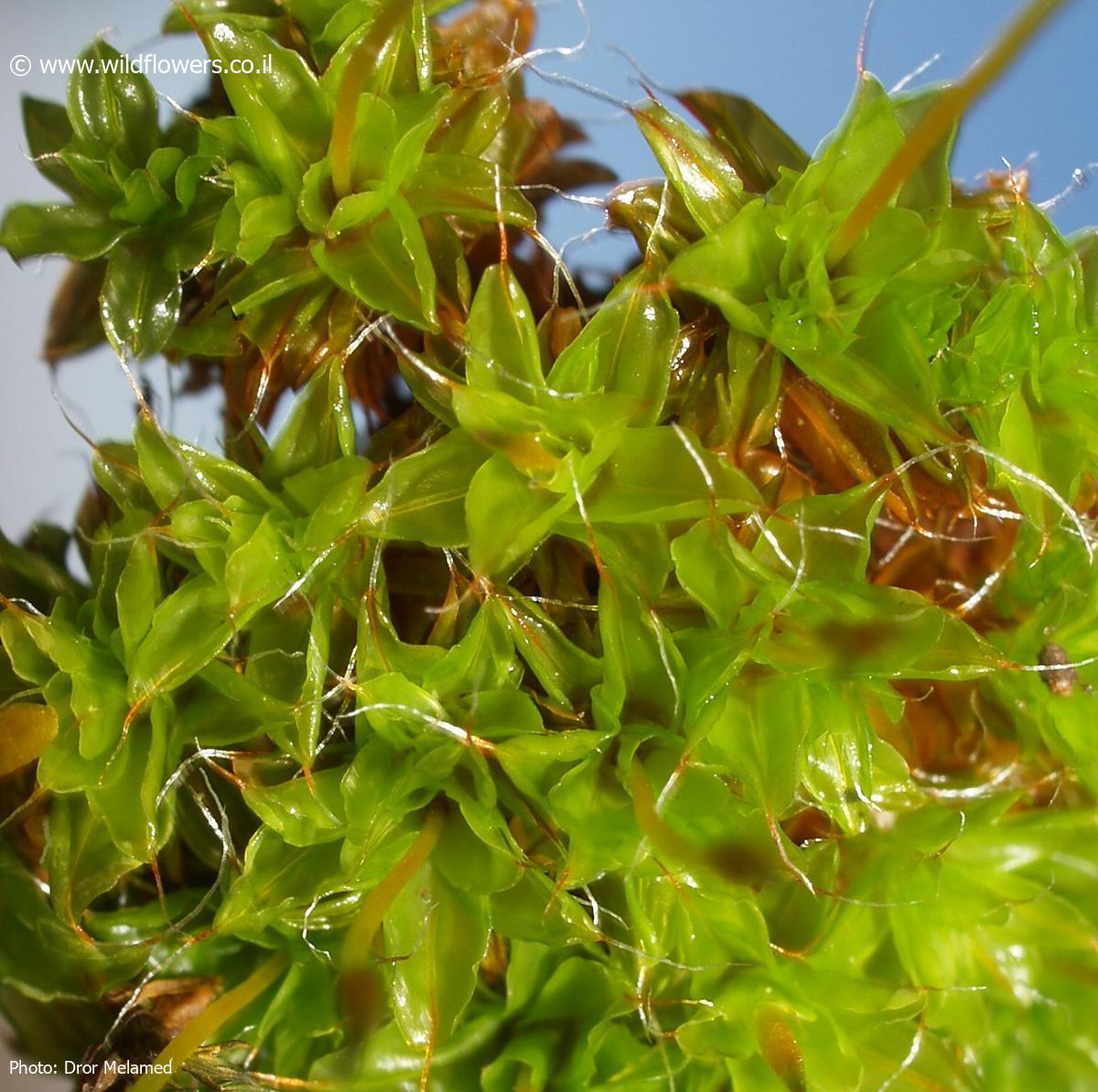
Syntrichia princeps is a acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the stems. Its leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and crisped when dry, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. The calyptra (a cap-like structure covering the developing sporophyte) is cucullate
3198-l-5.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=20332
(hood-shaped), and the capsules (spore cases) are cylindrical and erect.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a cosmopolitan distribution, meaning it can be found on almost every continent. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from urban areas to natural environments, showcasing its remarkable adaptability. Syntrichia princeps is commonly found growing on soil, rocks, tree bark, and even concrete surfaces.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small stature, Syntrichia princeps plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to

3198-l-8.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=20335
soil formation and stabilization, acting as a pioneer species in disturbed areas. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms, supporting biodiversity.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Syntrichia princeps is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself when moisture becomes available again. This remarkable adaptation allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban environments, Syntrichia princeps has been observed growing on concrete sidewalks, building walls, and even rooftops. Its resilience and ability to colonize these man-made surfaces have made it a subject of interest for researchers studying the impact of urbanization on biodiversity.
Technical Table
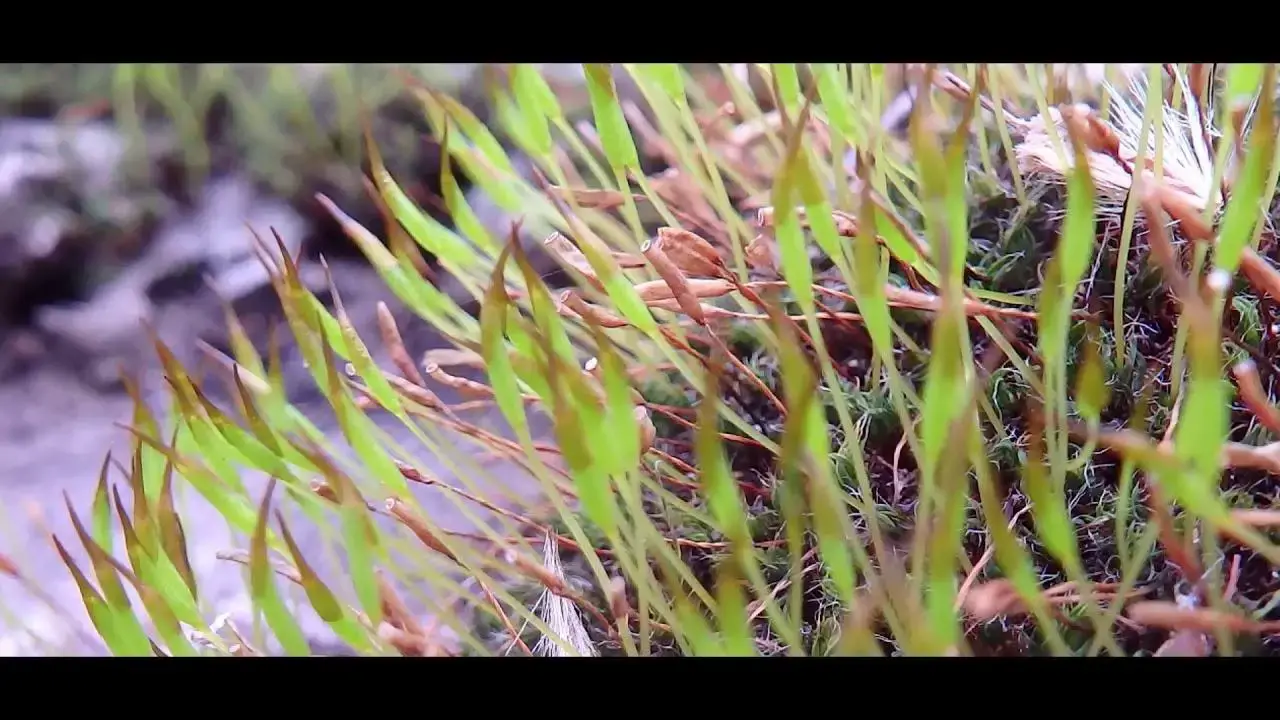

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fd4ODZTsUUU
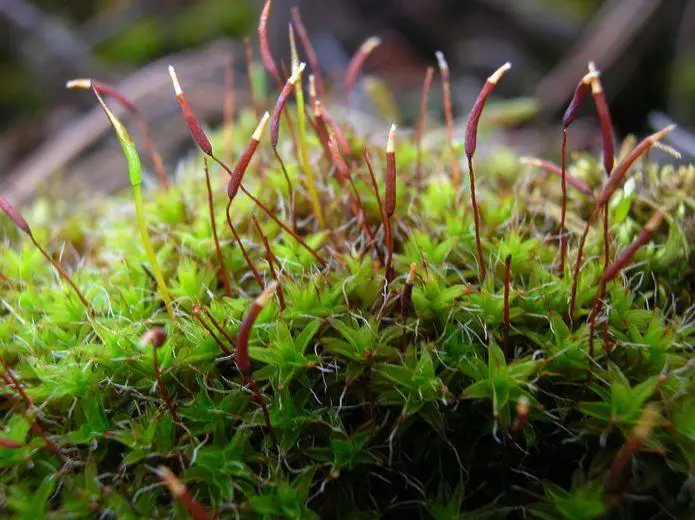

1ce0e7a7cb1d768f818c13c41313f03a.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.fr/pin/777152479423470149/
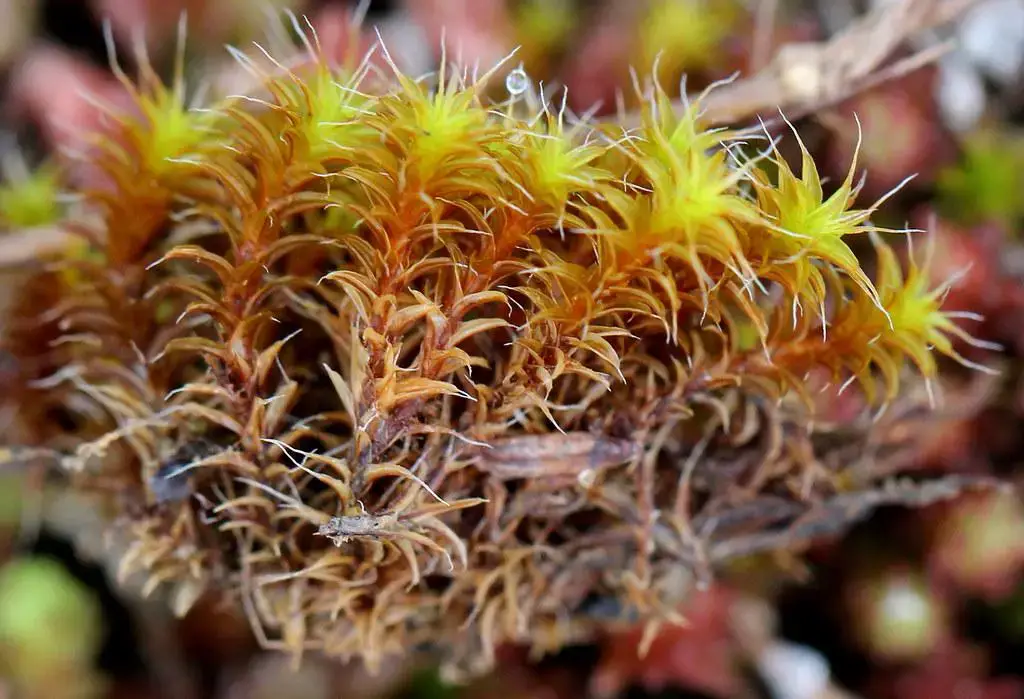

26534657817_29cc730dd4_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/12639178@N07/26534657817/

medium.jpeg from: https://inaturalist.ca/taxa/67915-Syntrichia-princeps
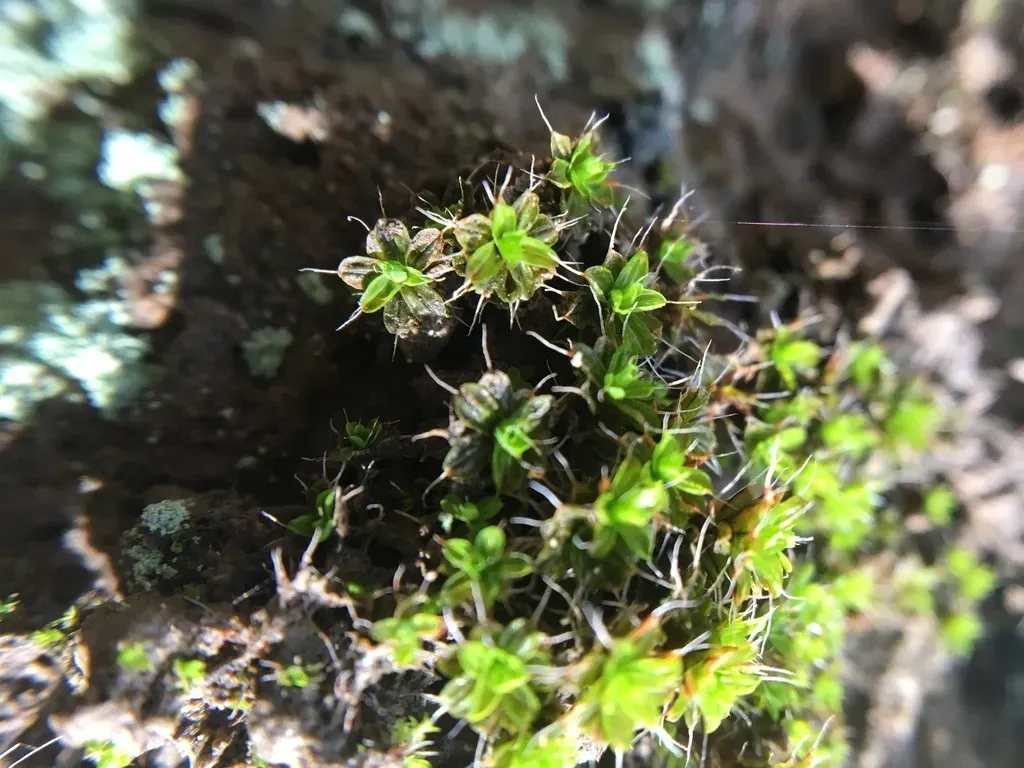

154227795990413335.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/es/wiki/Syntrichia_princeps.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiales |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Syntrichia |
| Species | Syntrichia princeps (De Not.) Mitt. |
| Common Name | Syntrichia |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, crisped when dry |
| Calyptra | Cucullate |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, erect |
Conclusion
Syntrichia princeps (De Not.) Mitt., a humble yet remarkable moss, has proven its resilience and adaptability across diverse environments. From urban landscapes to natural habitats, this species plays a vital role in ecosystem functioning and biodiversity. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder: What other secrets might this unassuming moss hold, waiting to be uncovered?