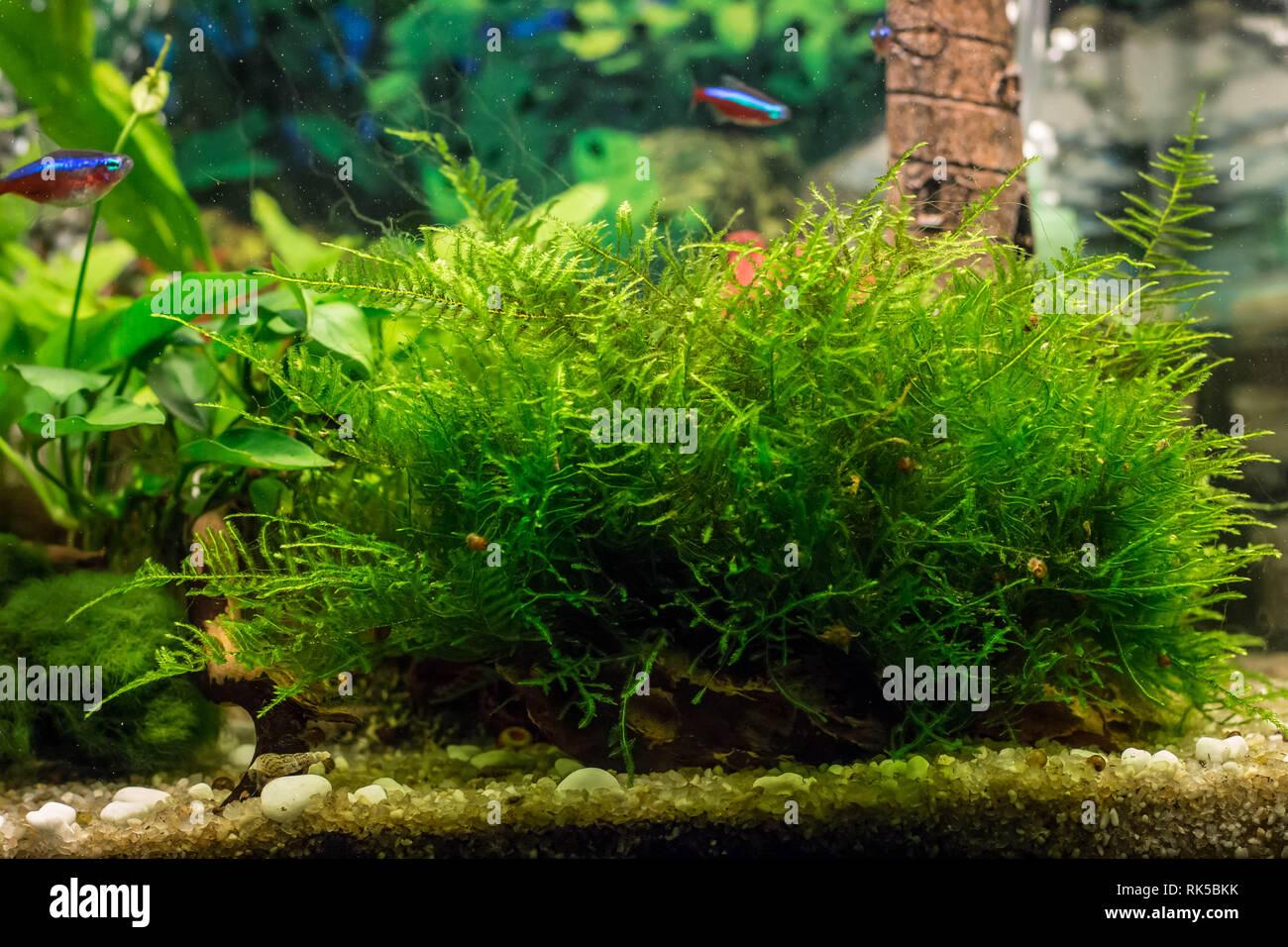

turf-of-java-moss-latin-name-vesicularia-in-aquarium-RK5BKK.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/turf-of-java-moss-latin-name-vesicularia-in-aquarium-image235532183.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Vesicularia debilis Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Vesicularia debilis (Besch.) Broth. ex Paris, a moss in the Hypnaceae family. Also known simply as Vesicularia, this moss has some fascinating characteristics. Let’s dive in and learn more about this unique plant!
Background
Vesicularia debilis is a species of moss, which are non-vascular plants in the division
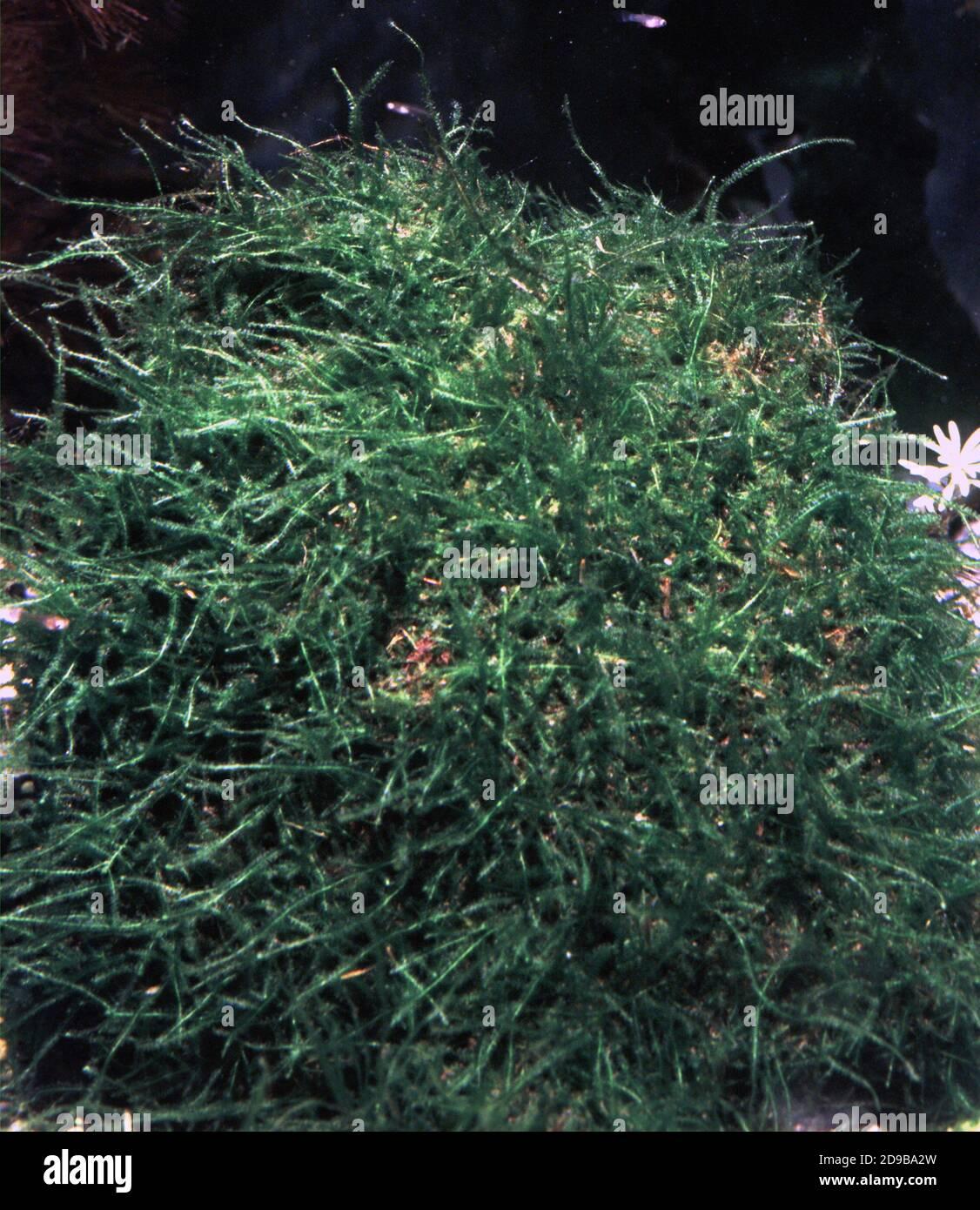

creeping-moss-vesicularia-sp-2D9BA2W.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/creeping-moss-vesicularia-sp-image384409393.html

il_1588xN.2880629813_9o30.jpg from: https://www.etsy.com/listing/938785302/weeping-moss-vesicularia-ferriei-live?frs=1
Bryophyta. Mosses lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. They reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide.

tropica-vesicularia-dubyana-christmas-moss-1-2-grow.jpg from: https://www.pro-shrimp.co.uk/tropica-1-2-grow/1546-tropica-vesicularia-dubyana-christmas-moss-1-2-grow-5703249803122.html
Morphology and Identification
Vesicularia debilis has several distinct features:
- Leaves: The leaves are ovate to oblong-lanceolate in shape and have a short, double costa (midrib). They are arranged in a complanate manner.
- Stems: The stems are creeping and irregularly branched. Branches are complanate-foliate.
- Coloration: This moss is pale-green to yellowish-green in color.
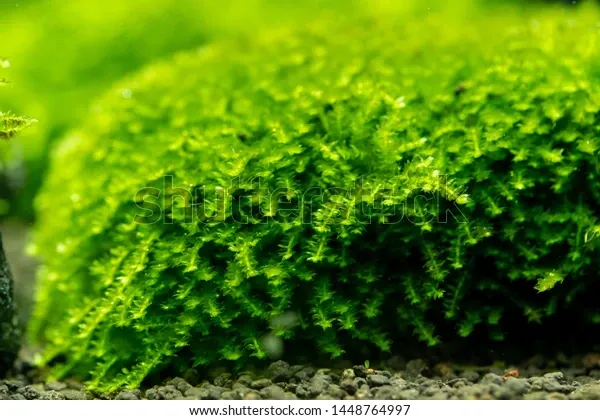

close-mini-pearl-moss-vesicularia-600w-1448764997.jpg from: https://www.shutterstock.com/image-photo/close-mini-pearl-moss-vesicularia-sp-1448764997
- Sporophytes: Sporophytes are uncommon. When present, the seta is elongate and the capsules are inclined to horizontal.
With a hand lens and its unique characteristics, Vesicularia can be identified in the field by those familiar with bryophyte morphology. However, microscopic examination is required for definitive identification to the species level.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Vesicularia debilis has a wide distribution, being found in:
- Asia: China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia
- Africa: Madagascar, Reunion, Mauritius
- Pacific Islands: Hawaii, Fiji, Samoa
- Caribbean: Puerto Rico, Jamaica
- South America: Brazil
This moss grows on various substrates including tree trunks, rocks, and soil in humid forests and near streams. It is particularly abundant in tropical and subtropical regions.

vesicularia-sp-creeping-moss-in-vitro-xl.jpg from: https://www.aquasabi.de/wasserpflanzen/moose/vesicularia-sp-creeping-moss-in-vitro-xl
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Vesicularia plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Nutrient cycling: It helps capture and cycle nutrients, enriching the soil.
- Moisture retention: Moss mats retain moisture, regulating humidity and benefiting other organisms.
- Erosion control: By covering soil and stabilizing surfaces, mosses like Vesicularia help prevent erosion.
- Microhabitats: Mosses provide shelter and habitat for tiny organisms like insects, arthropods, and more.
Vesicularia has adaptations like its complanate growth form that allow it to efficiently capture light and moisture in shaded, humid habitats. Its spores and fragments can disperse to colonize new areas.
sprig-christmas-moss-aquarium-vesicularia-montagnei-sprig-christmas-moss-aquarium-vesicularia-montagnei-soft-169996482.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/sprig-christmas-moss-aquarium-vesicularia-montagnei-sprig-christmas-moss-aquarium-vesicularia-montagnei-soft-image169996482

vesicularia-ferriei-weeping-1-2-grow.jpg from: http://krueger-aquaristik.de/vesicularia-ferriei-weeping-1-2-grow

vesicularia-ferriei-weeping-moss.jpg from: https://www.aquasabi.com/Vesicularia-ferriei-Weeping-Moss-in-Vitro-XL
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Hypnaceae |
| Genus | Vesicularia |
| Species | V. debilis |
Growth Form
 12444347285_36a9bd913a_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21708387@N02/12444347285 |
Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to oblong-lanceolate |
| Leaf Arrangement | Complanate |
| Costa | Short and double |
Conclusion
From its unique morphology to its ecological importance, Vesicularia debilis is a prime example of how fascinating and important mosses can be. The next time you see a patch of moss, take a closer look – you may be gazing at this remarkable species! What other secrets do you think the world of mosses holds?