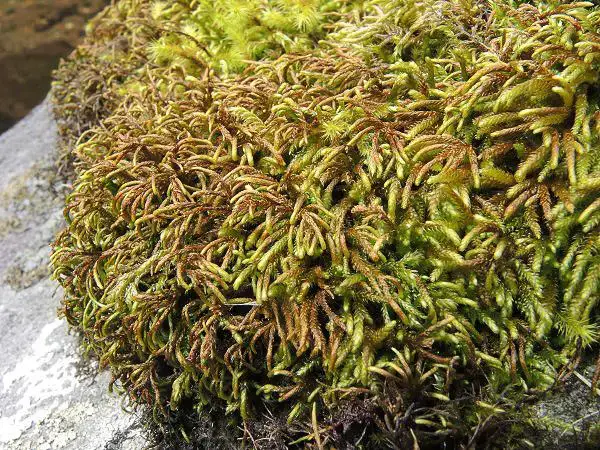

2019-12-Pterogonium-gracile-Jo-Denyer.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/bryophyte-of-the-month/pterogonium-gracile/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its delicate beauty and fascinating adaptations – the Pterogonium gracile (Hedw.) Sm., commonly known as Pterogonium. This moss belongs to the Lembophyllaceae family and is a true marvel of nature, thriving in diverse habitats and playing crucial ecological roles.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Pterogonium gracile, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a vital role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have evolved remarkable strategies for survival and reproduction.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
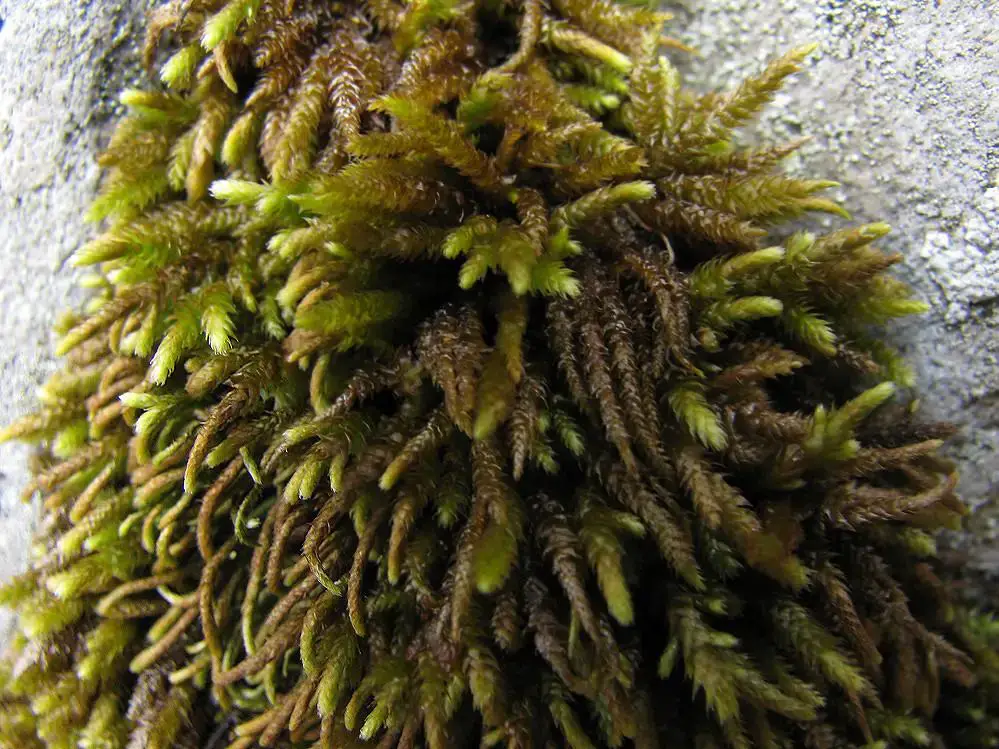

9481782628_1a162f36be_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/100093500@N04/9481782628/
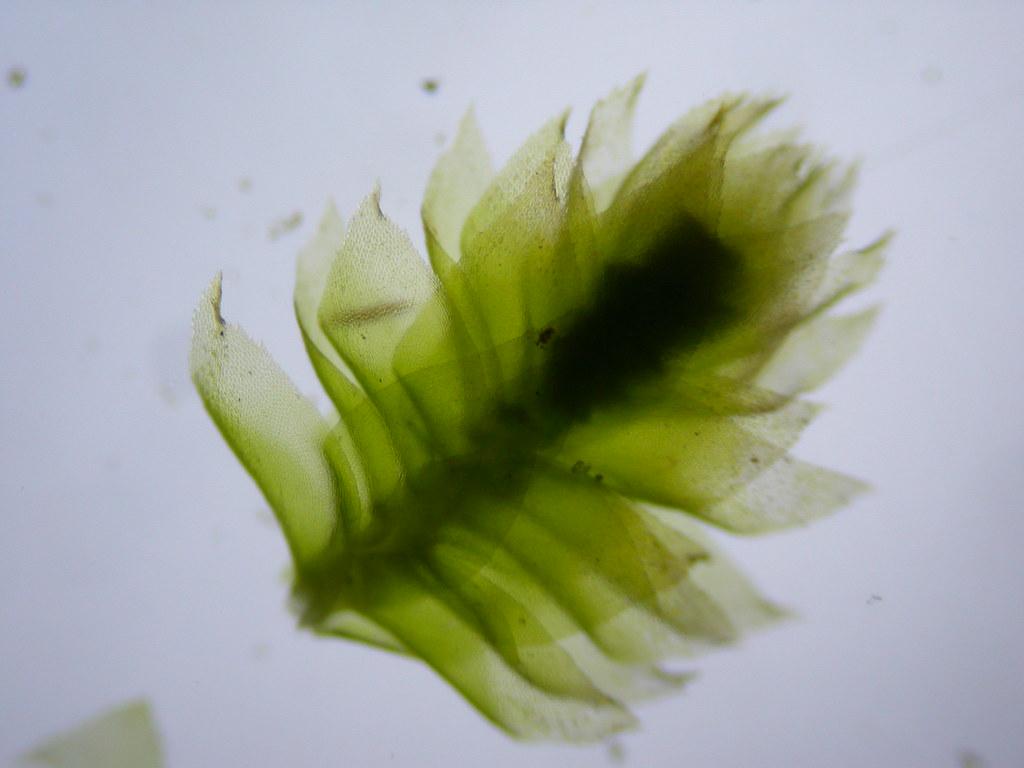
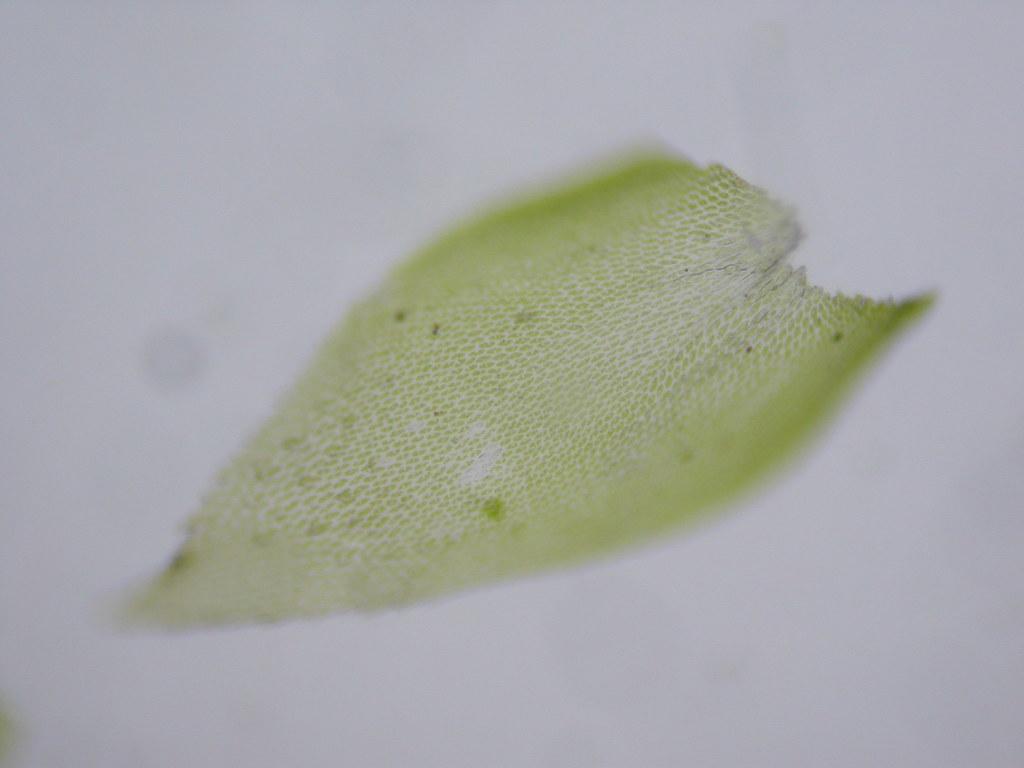
Pterogonium gracile is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, feathery appearance is truly captivating, with delicate, curved leaves arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal intricate patterns and structures that aid in identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
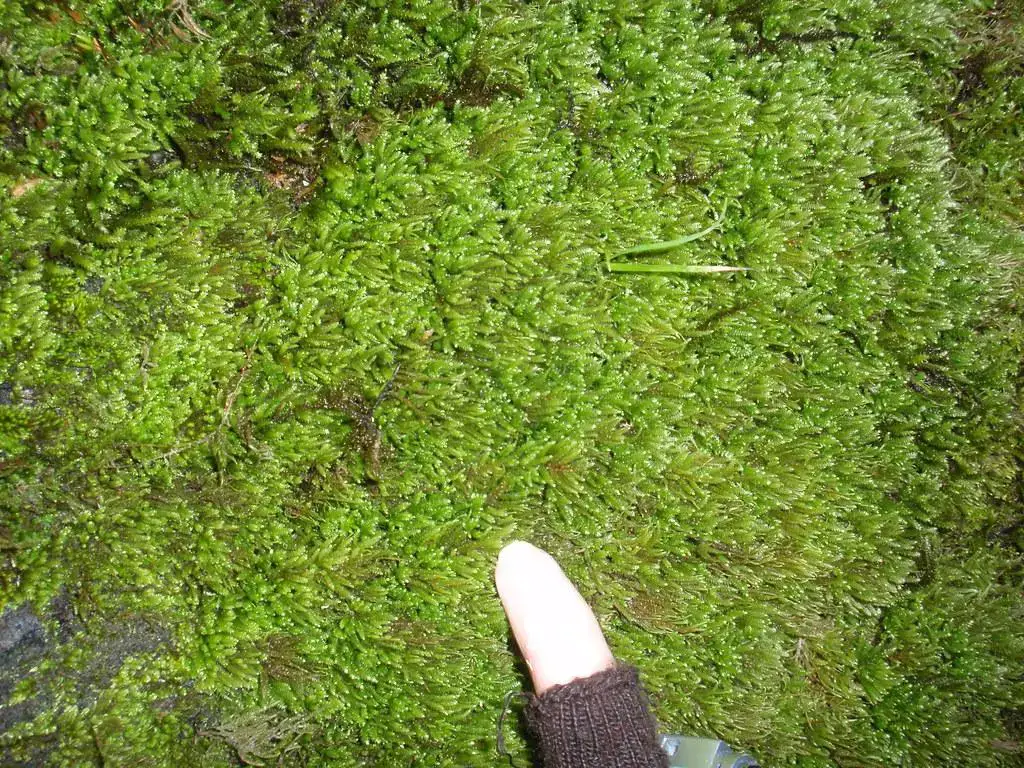
This moss species has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in diverse habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock outcrops to the bark of trees and decaying logs. Pterogonium gracile is particularly well-adapted to humid environments, where it can form lush, verdant carpets or intricate mats on the substrate.
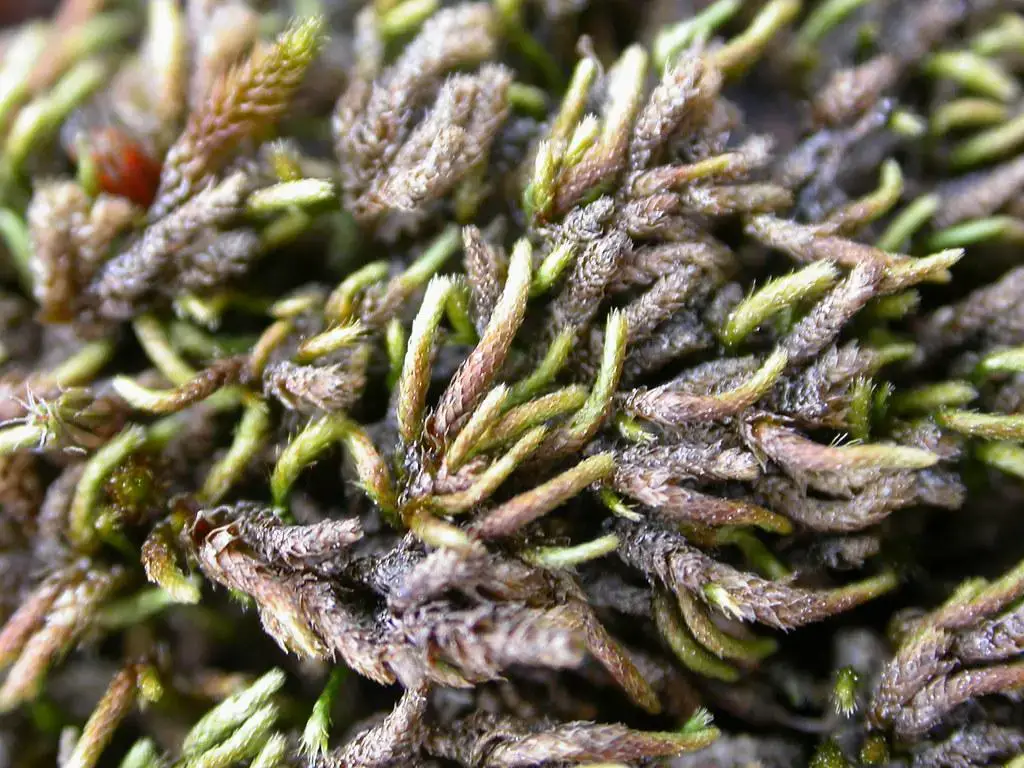

30912503025_36374cd9e1_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/23980231@N07/30912503025/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Pterogonium gracile plays crucial roles in its ecosystem. It serves as a microhabitat for numerous tiny organisms, providing shelter and sustenance for various invertebrates, fungi, and microorganisms. Additionally, this moss acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps regulate the local microclimate and prevent soil erosion.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Pterogonium gracile is its ability to undergo desiccation and revive when moisture becomes available again. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought and rapidly resume its metabolic activities when conditions improve.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers discovered that Pterogonium gracile played a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of epiphytic (tree-dwelling) communities. The moss provided a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates, lichens, and other bryophytes, contributing to the overall health and resilience of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table

16476396310_b54c65d1a8_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/makromaus_ahrweiler/16476396310/

7069078601_03f0660b0b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/40015937@N05/7069078601

30912561125_47f1c2e611_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/23980231@N07/30912561125/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
Order
 30611479730_23334e2058_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/23980231@N07/30611479730/ |
Hypnales
 Repartition-de-Pterogonium-gracile-Hedw-Sm-a-Porquerolles.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Repartition-de-Pterogonium-gracile-Hedw-Sm-a-Porquerolles_fig81_328841440 |
Family
 4808588491_20a6bde458_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/tcorelli/4808588491/ |
Lembophyllaceae |
| Genus | Pterogonium |
| Species | Pterogonium gracile (Hedw.) Sm. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, with distinct patterns |
Conclusion
Pterogonium gracile (Hedw.) Sm., a delicate and captivating moss species, is a true testament to the wonders of nature’s smallest inhabitants. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the importance of preserving these often-overlooked organisms and the vital roles they play in our ecosystems. Perhaps the next time you encounter a verdant carpet of moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the intricate beauty and resilience of

37287359122_f48e61fc59_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/151101253@N08/37287359122/
Pterogonium gracile.