Discover the Captivating World of Frullania Moss: A Tiny Plant with Big Roles
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!

CINC-B-0047000_a_tn.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxon=182676
Exploring the Fascinating World of Frullania chilensis Steph. Moss
Introduction
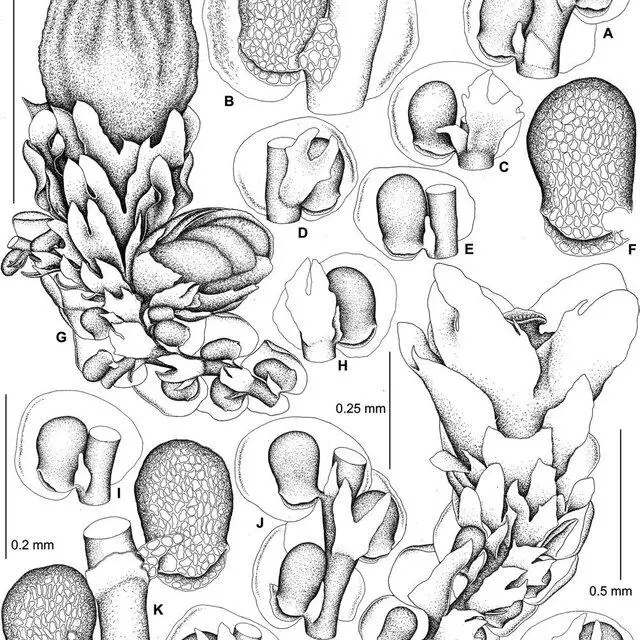

Frullania-chilcootiensis-Steph-A-C-E-H-I-J-L-N-parts-of-shoots-showing-leaves-and_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Frullania-chilcootiensis-Steph-A-C-E-H-I-J-L-N-parts-of-shoots-showing-leaves-and_fig1_346236028
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is
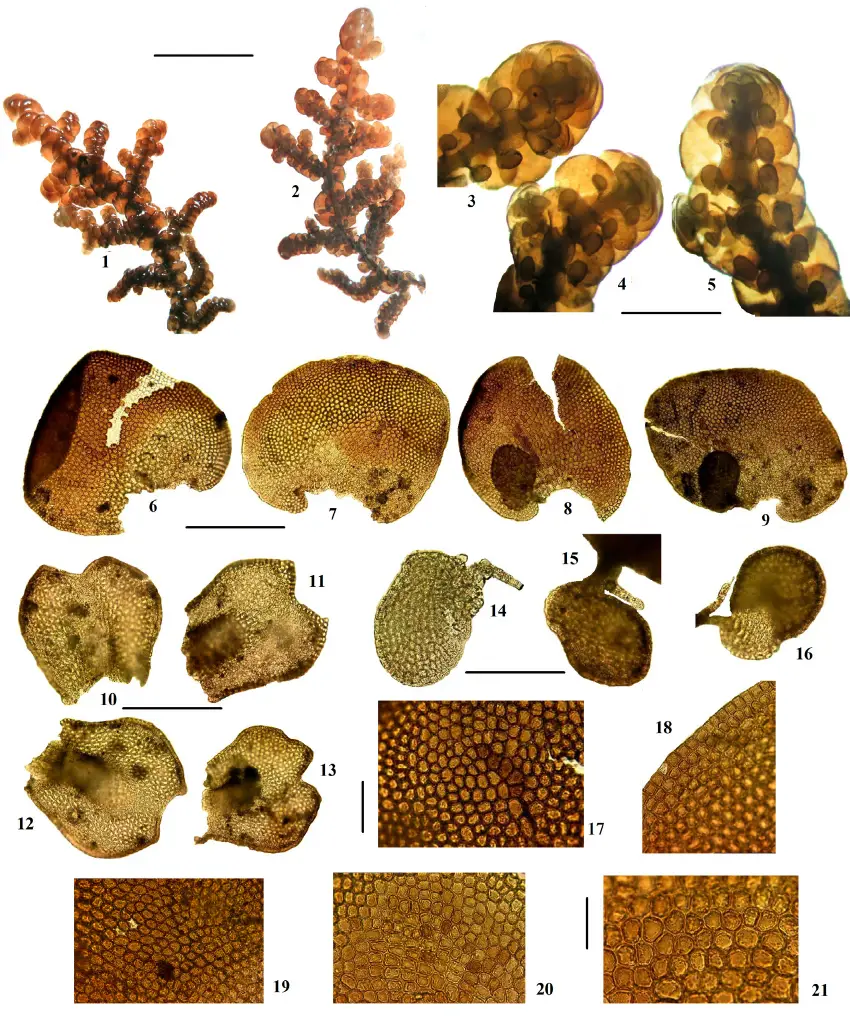

Frullania-calcarifera-Steph-from-the-Crimean-Peninsula-5VI1964-Partyka-sn-1.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Frullania-calcarifera-Steph-from-the-Crimean-Peninsula-5VI1964-Partyka-sn-1_fig1_283100707
Frullania chilensis Steph., a type of leafy liverwort moss in the Frullaniaceae
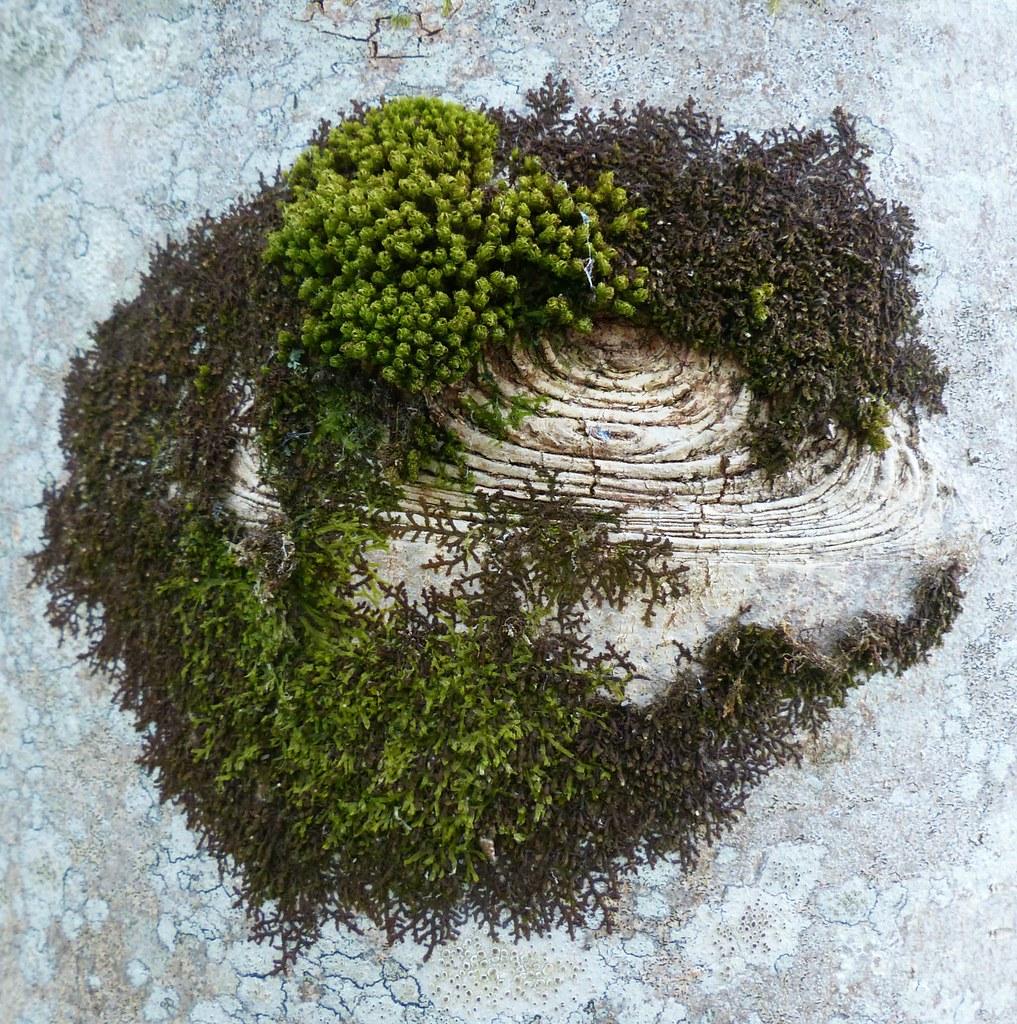

50969912581_a2d7aee797_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/41066614@N05/50969912581/
family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the captivating details of this small but mighty plant.
Background
Frullania chilensis Steph., also simply called Frullania, is classified in the division Marchantiophyta and class Jungermanniopsida. The species name “chilensis

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/509502
” refers to Chile, where it was first described. However, its distribution extends well beyond Chile.
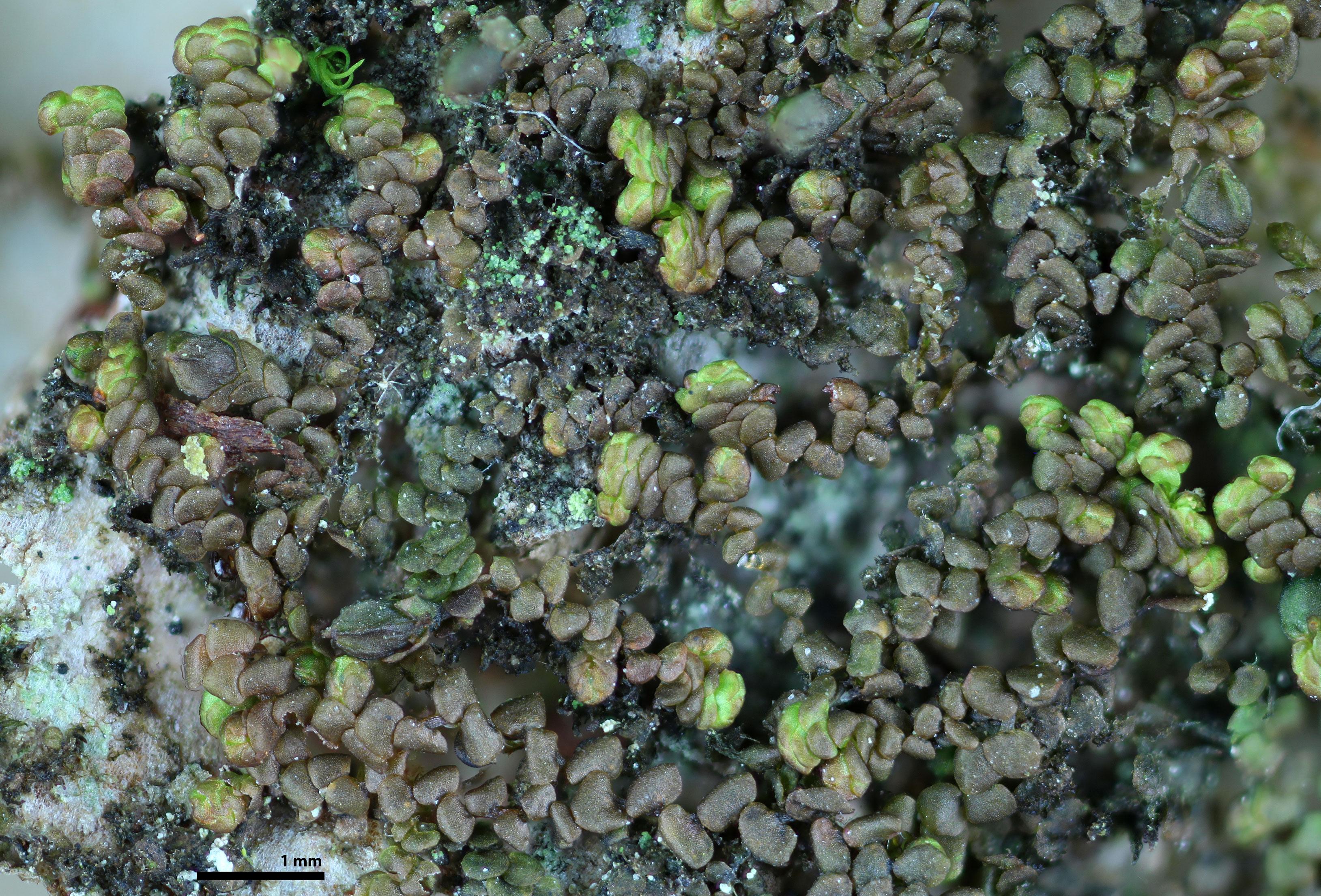
fruoak_pgd10017web1.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/frullaniaoakesiana.html
Morphology and Identification
Frullania is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats. Its leaves are arranged in two rows and have a unique lobule (ear-like structure) at the base, which helps with water retention. The lobules give Frullania a distinctive appearance among mosses. Frullania is dioicous, meaning male and female reproductive structures are on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
F. chilensis has a wide distribution, found in Central and South America, Australia, New Zealand, and some Pacific islands. It grows on various substrates including tree bark, rocks, and soil, from lowland forests to subalpine zones. This adaptability allows it to thrive in diverse habitats.
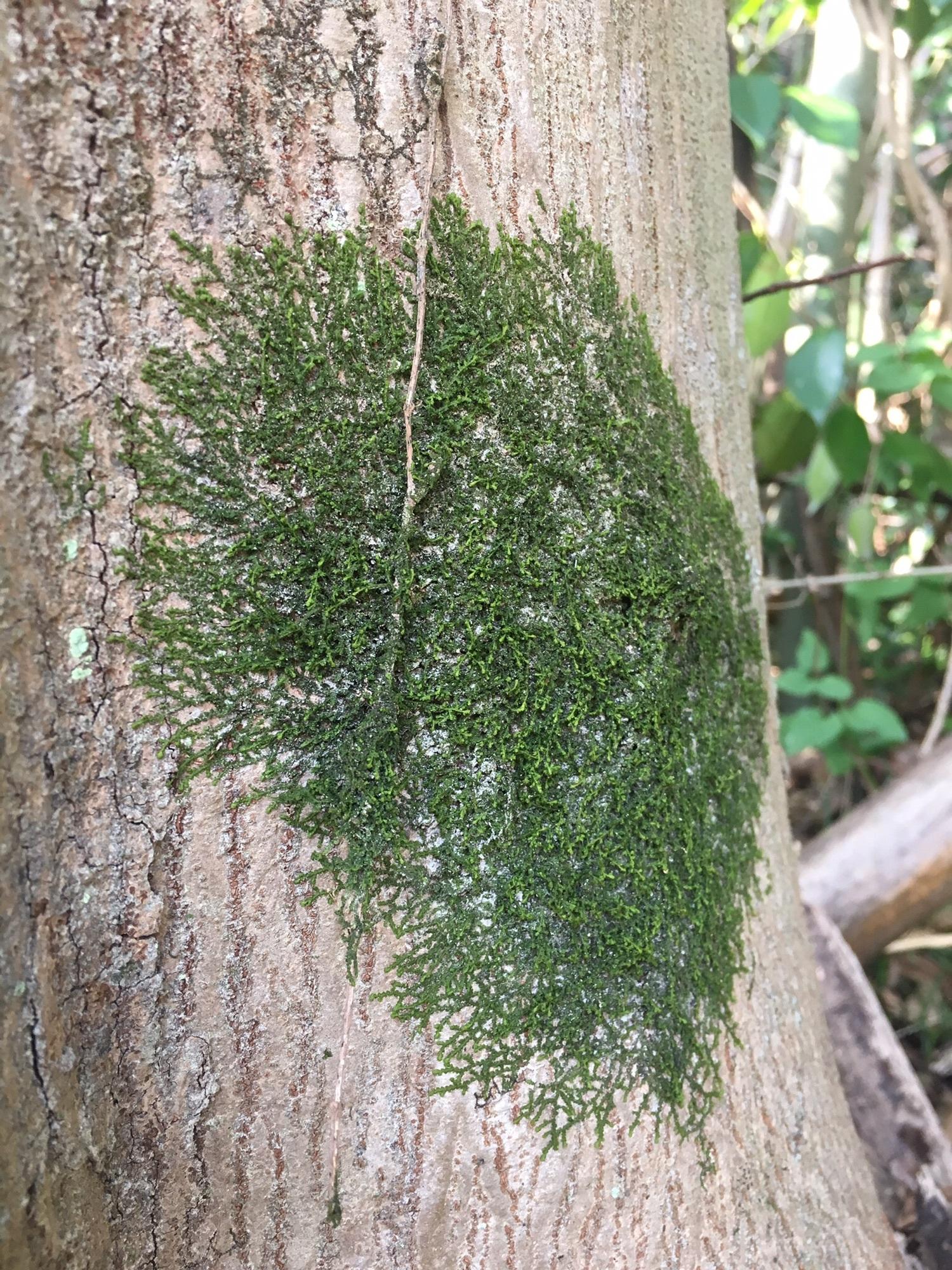

3605b045faa0d53175ff3dea23481155_5842dac27d5e8d2b7c273f6e6500e445.jpg from: https://kokeakari.amebaownd.com/posts/2064712
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
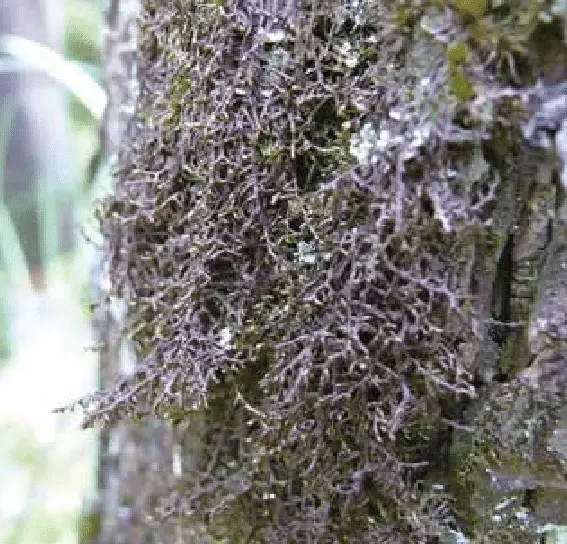

Rare-moss-species-Frullania-tamarisci-Photo-S-Ikauniece.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Rare-moss-species-Frullania-tamarisci-Photo-S-Ikauniece_fig6_337951281
As with other mosses, Frullania plays important roles in its ecosystems:
Moisture retention: Its mat-like growth and lobules help retain moisture, preventing erosion and maintaining humidity.
Nutrient cycling: It helps capture and cycle nutrients that can be used by other plants.
Microhabitats: Frullania mats provide shelter for micro-organisms and small invertebrates.
Indicator species: Because it is sensitive to air pollution, changes in Frullania populations can indicate environmental health.
Frullania has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
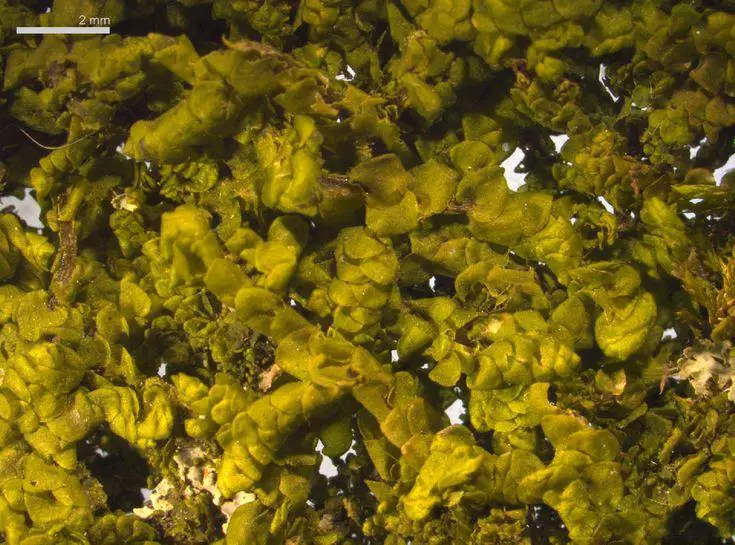

0e2befe94abdd0e13049588f00645a62.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/frullania-image-details-771508–291045194657579822/
Desiccation tolerance: It can survive drying out and quickly rehydrate when moisture is available again.
Asexual reproduction: In addition to sexual reproduction, Frullania can reproduce asexually via fragmentation, allowing quick colonization of new areas.
Secondary compounds: Many Frullania species contain unique secondary compounds that may help deter herbivory.
Conclusion
Frullania chilensis Steph. is a small but fascinating moss with a wide distribution and important ecological roles. Its unique morphology and adaptations showcase the incredible diversity within mosses and other bryophytes. Next time you see a moss mat, take a closer look – you might just be looking at a Frullania! What other secrets do you think these unassuming plants hold?
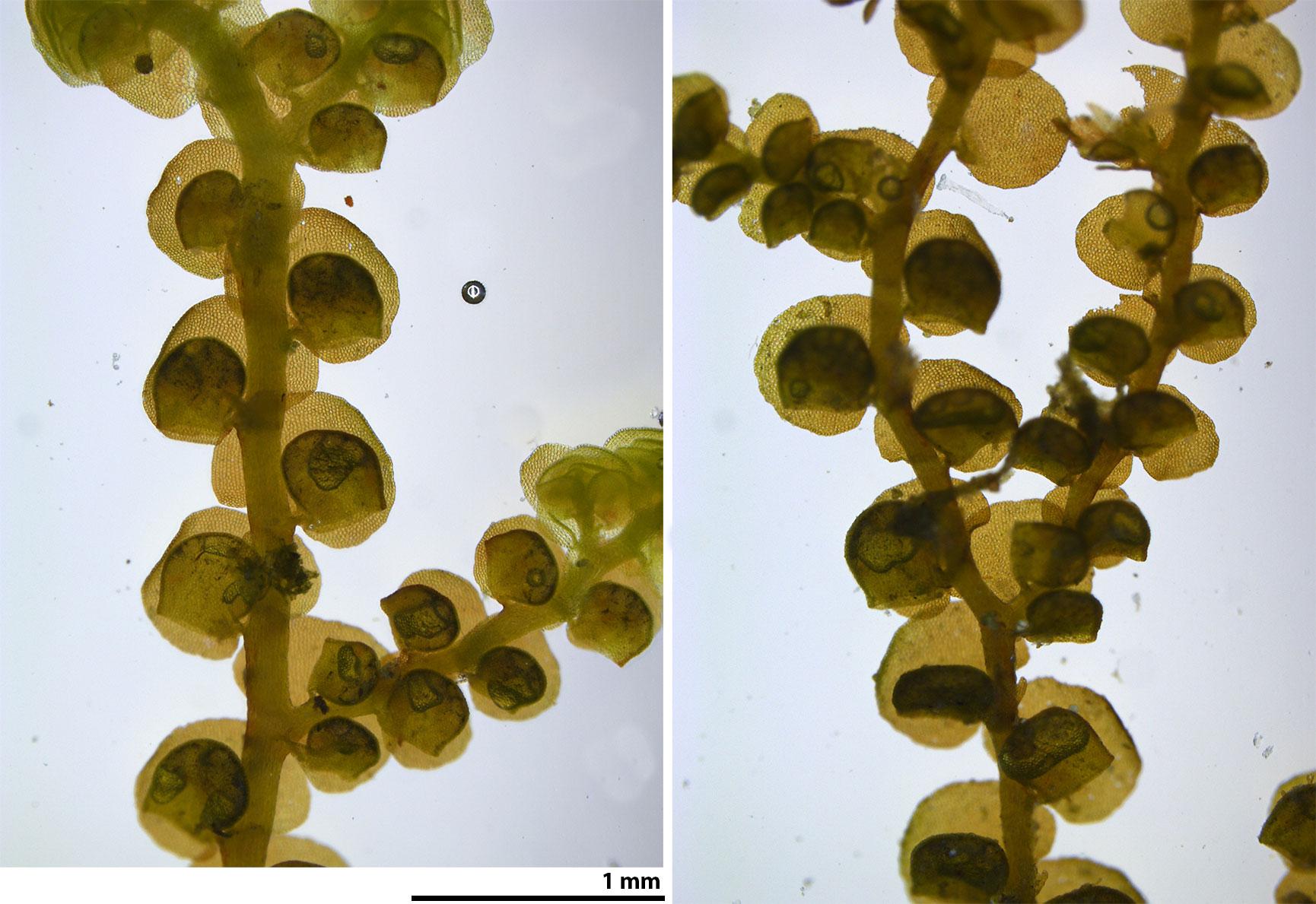

fruoak_pgd10017web6.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/frullaniaappalachiana.html
