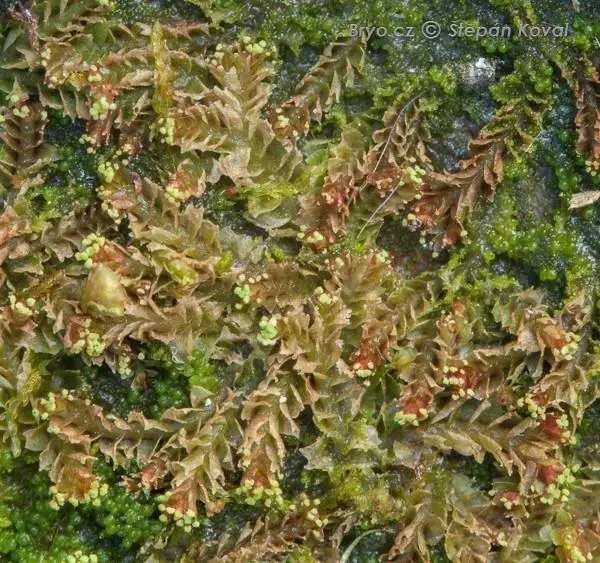

3334_Lophozia_guttulata_2009_09_23_1834.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=lophozia_guttulata&id=3334
Exploring the Fascinating World of Lophozia quadriloba Moss

lo_obtusa.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lophozia_obtusa.html
Lophozia quadriloba (Lindb.) A.Evans, commonly known as Lophozia, is a captivating species of moss belonging to the Anastrophyllaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant plays a significant role in its ecosystems and boasts unique adaptations. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Lophozia quadriloba and discover what makes it so special.
Background on Lophozia Moss
Lophozia quadriloba is classified under the Marchantiophyta division and Jungermanniopsida class. It is a leafy liverwort, meaning it has leaf-like structures arranged on a stem. Liverworts are non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they absorb water and nutrients directly through their body surfaces.
Morphology and Identification
Lophozia quadriloba has several distinguishing features:
- Leaves: The leaves are divided into 4 lobes (hence the name “quadriloba”) and are arranged in two rows along the stem.
- Color: The plant appears yellowish-green

880973.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/880967.html

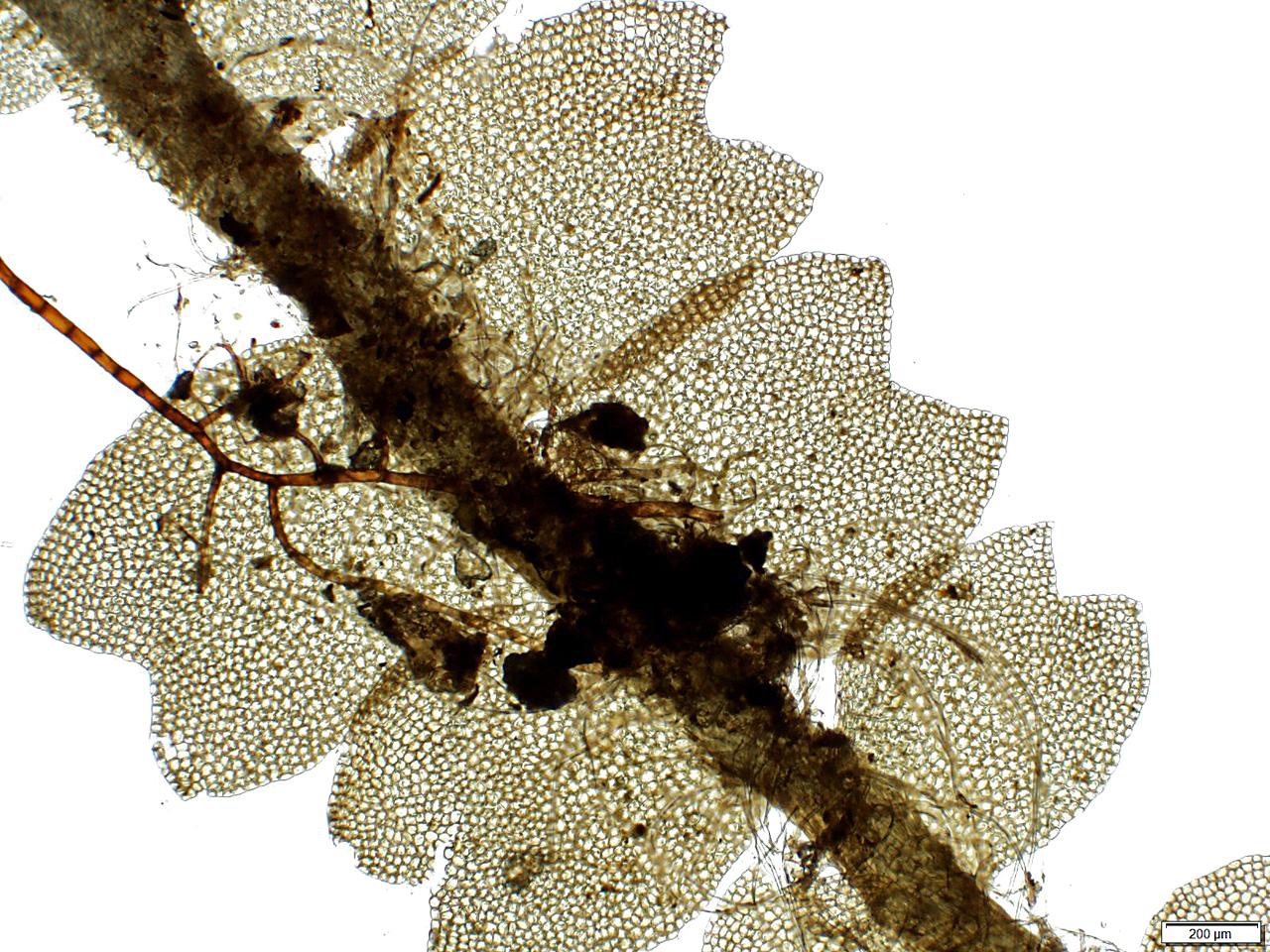
881027.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/881020.html
to reddish-brown.
- Size: Shoots are typically 1-3 cm long and

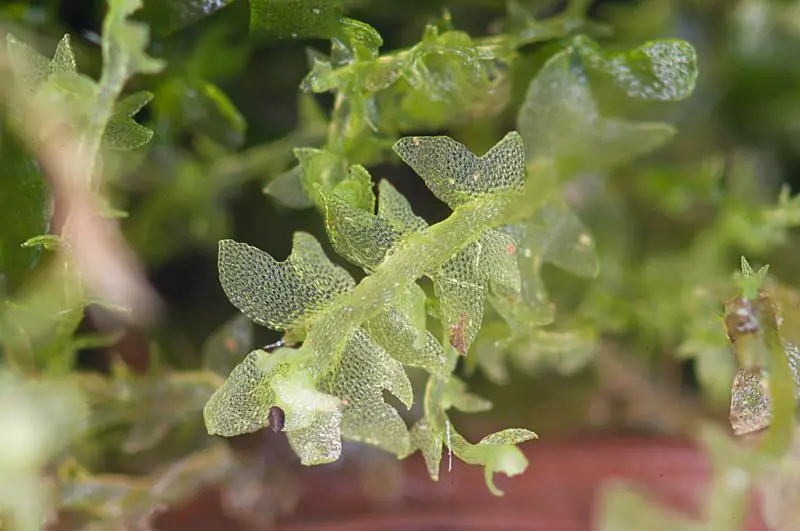
lo_sp.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lophozia_sp.html
0.5-1.5 mm wide.
To identify Lophozia in the field, look for its characteristic 4-lobed leaves on a small, creeping plant. It often grows in dense mats or mixed with other bryophytes.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lophozia quadriloba has a wide distribution, found in many parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. It grows in a variety of habitats, including:
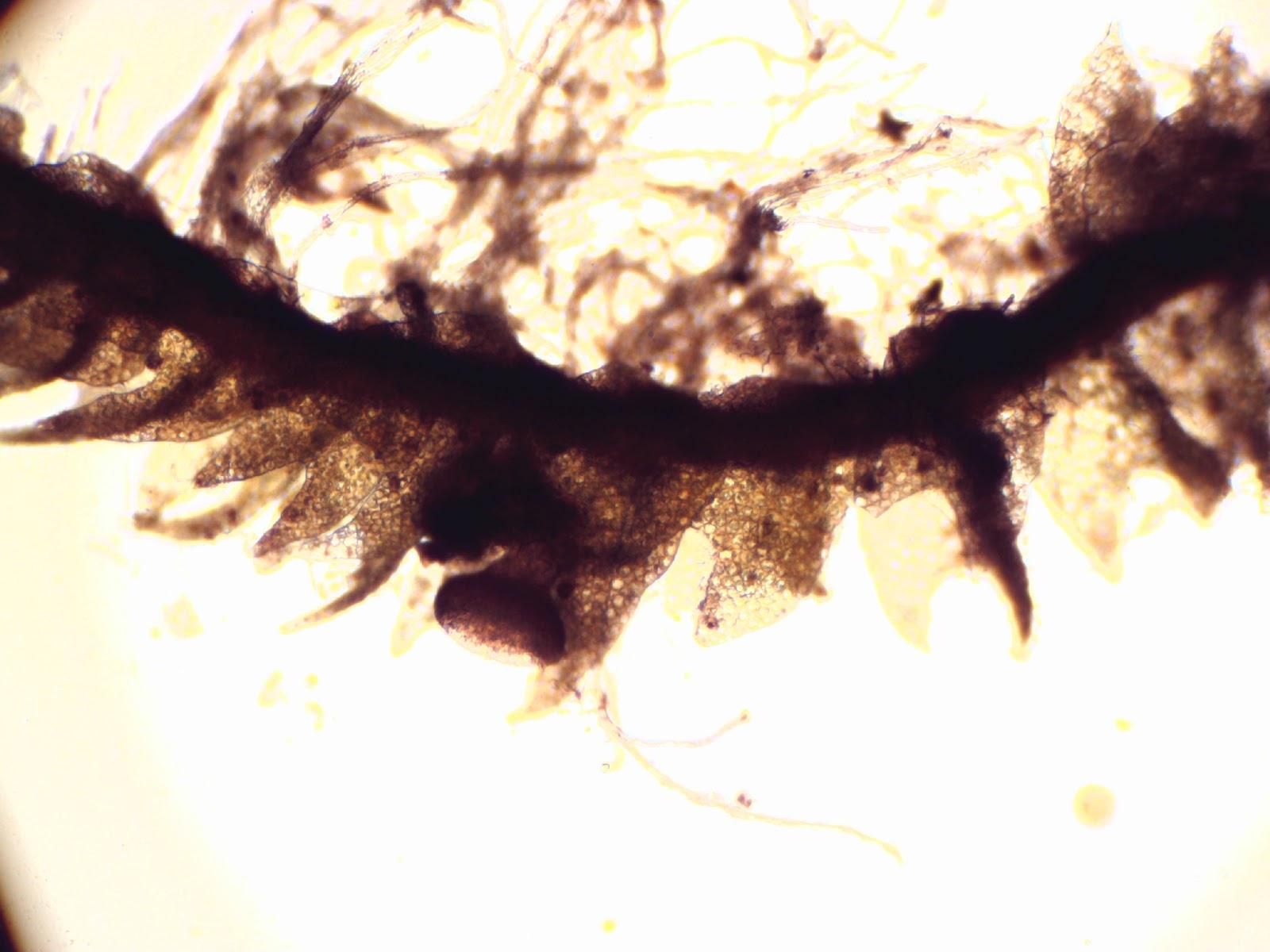
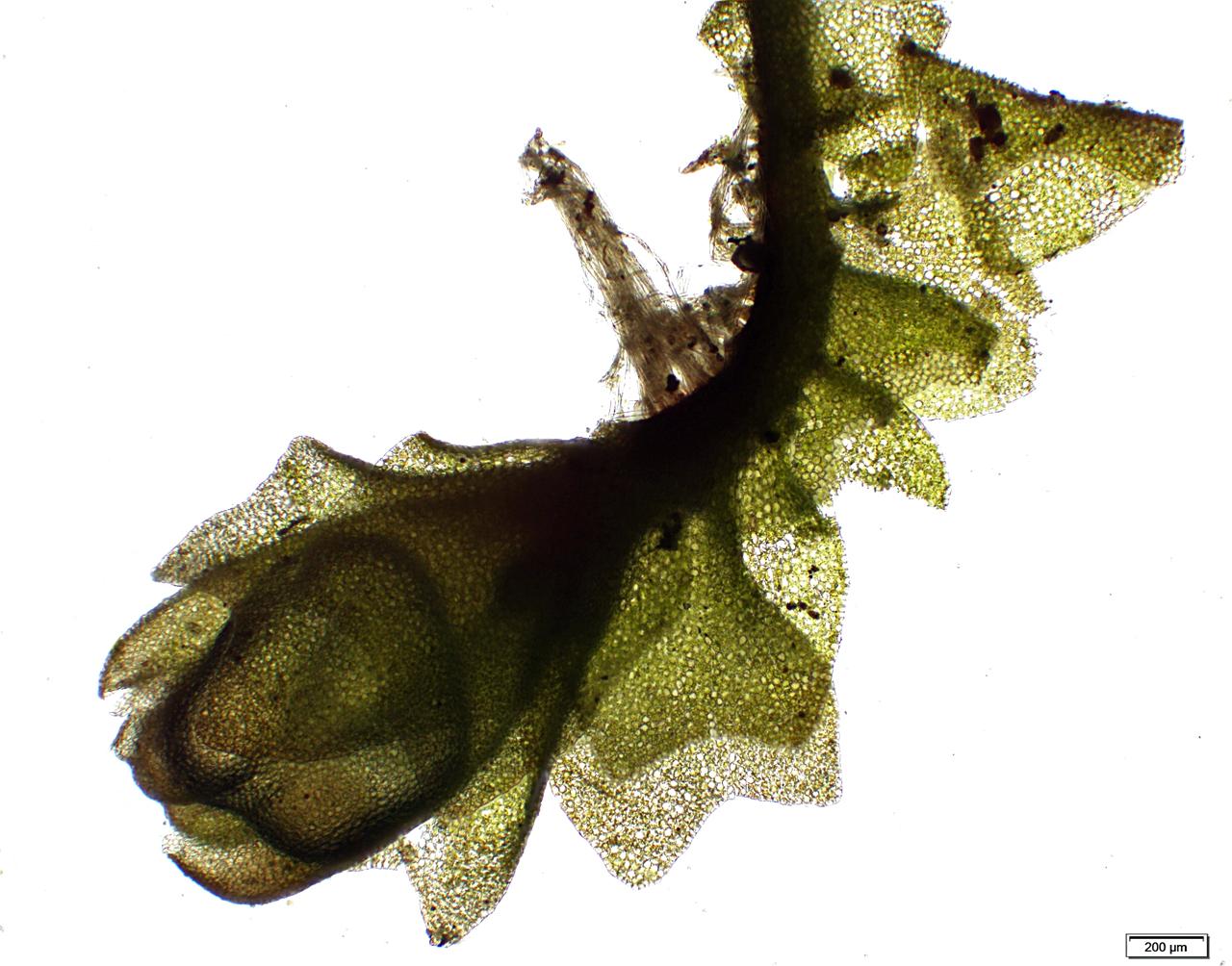
things+sticking+off+stem.jpg from: https://mosswalks.blogspot.com/2012/06/lophozio-sudetica.html
- Shaded rocks and cliffs
- Decaying logs and tree bases
- Soil banks along streams or trails
This adaptable moss can tolerate a range of moisture levels and substrates, from damp to dry conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Lophozia plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Nutrient cycling: It helps break down organic matter and release nutrients back into the soil.
- Moisture retention: The dense mats of Lophozia hold moisture and prevent soil erosion.
- Microhabitats: It provides shelter and humidity for tiny invertebrates.
Lophozia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Desiccation tolerance: It can survive periods of dryness by going dormant until moisture returns.
- Asexual reproduction: In addition to sexual reproduction, Lophozia can regenerate from broken fragments, allowing it to spread easily.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae |
| Genus | Lophozia |
| Species | L. quadriloba |
| Leaf shape | 4-lobed |
| Color | Yellowish-green to reddish-brown |
| Size | 1-3 cm long, 0.5-1.5 mm wide |
Conclusion
Lophozia quadriloba may be small, but it is a fascinating and important member of many ecosystems worldwide. Its unique morphology, wide distribution, and ecological roles make it a compelling subject of study for botanists and nature enthusiasts alike. Next time you’re out in nature, keep an eye out for this marvelous moss! What other tiny wonders might you discover when you take a closer look?