Bazzania-recurva-Mont-Trevis-from-Ridley-615-a-Habitb-Leaves-c_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Bazzania-recurva-Mont-Trevis-from-Ridley-615-a-Habitb-Leaves-c_fig4_252982531
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Bazzania duplex (De Not.) Trevis., a captivating moss species from the Lepidoziaceae family, commonly known as Bazzania. Prepare to be enchanted by the intricate beauty and remarkable adaptations of this tiny, yet mighty, plant.
Background

B-denudata-AH-266-under–768×574.jpg from: https://sites.cortland.edu/bryophytes/field-guide/liverworts/bazzania-denudata/
Before we dive into the specifics of Bazzania duplex, let’s set the stage with a brief introduction to mosses. These diminutive, non-vascular plants belong to the Marchantiophyta division and the Jungermanniopsida class, often referred to as liverworts. Despite their unassuming appearance, mosses play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
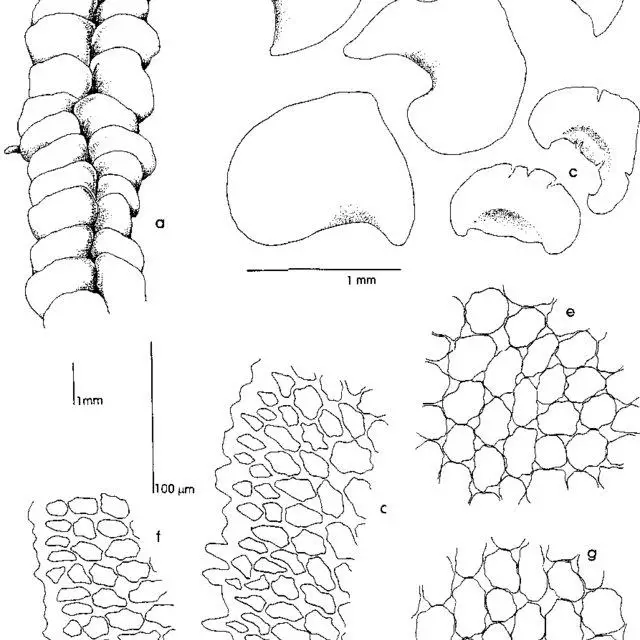
Bazzania duplex is a striking moss species that forms dense, creeping mats or tufts on the surfaces it inhabits. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. These leaves are deeply divided into two lobes, giving the moss its distinctive “duplex” appearance. The upper lobe is typically larger and more rounded, while the lower lobe is smaller and often curved or hooked.
One of the most remarkable features of Bazzania duplex is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive phase, tiny umbrella-like structures called “archegoniophores” emerge, bearing the female reproductive organs. These structures are truly a sight to behold under a microscope!
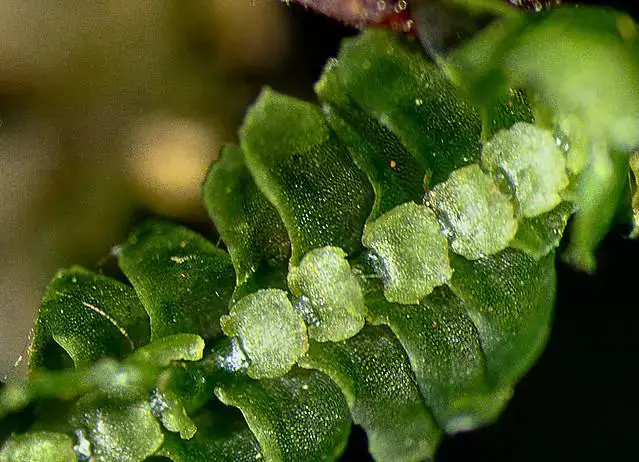

4197325358_0e9d8aca63_z.jpg from: http://www.flickr.com/photos/gjshepherd/4197325358/
Global Distribution and Habitat
Bazzania duplex is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. This moss thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, tree trunks, and rocks in cool, temperate forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Bazzania duplex plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Its dense mats help retain moisture and create microhabitats for other organisms, such as invertebrates and fungi. Additionally, this moss contributes to the breakdown of organic matter, facilitating nutrient cycling and soil formation.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Bazzania duplex is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can curl up and enter a dormant state, only to revive and continue its growth once moisture returns. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Study: Bazzania duplex in the Pacific Northwest
In the lush, temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest, Bazzania duplex is a common sight, carpeting the forest floor and adorning the trunks of towering conifers. Here, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of these ecosystems, providing habitat for countless microorganisms and contributing to the intricate web of life.
| Technical Data | |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Bazzania duplex (De Not.) Trevis. |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Reproduction | Sexual and Asexual |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, South America |
Conclusion
As we bid farewell to the captivating world of Bazzania duplex, let us reflect on the incredible diversity and resilience of these tiny, yet mighty, mosses. They serve as a reminder that even the smallest organisms can play vital roles in the intricate tapestry of life. So, the next time you venture into a cool, moist forest, take a moment to appreciate the beauty and complexity of these unassuming plants, and ponder the question: What other wonders lie hidden in the world of mosses?