
CCDB-28096-G05%2B1456166520.jpg from: https://v3.boldsystems.org/index.php/Taxbrowser_Taxonpage?taxid=461496
Discovering the Delicate Beauty of Brotherella canadensis W.B.Schofield Moss
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play vital roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly fascinating species is
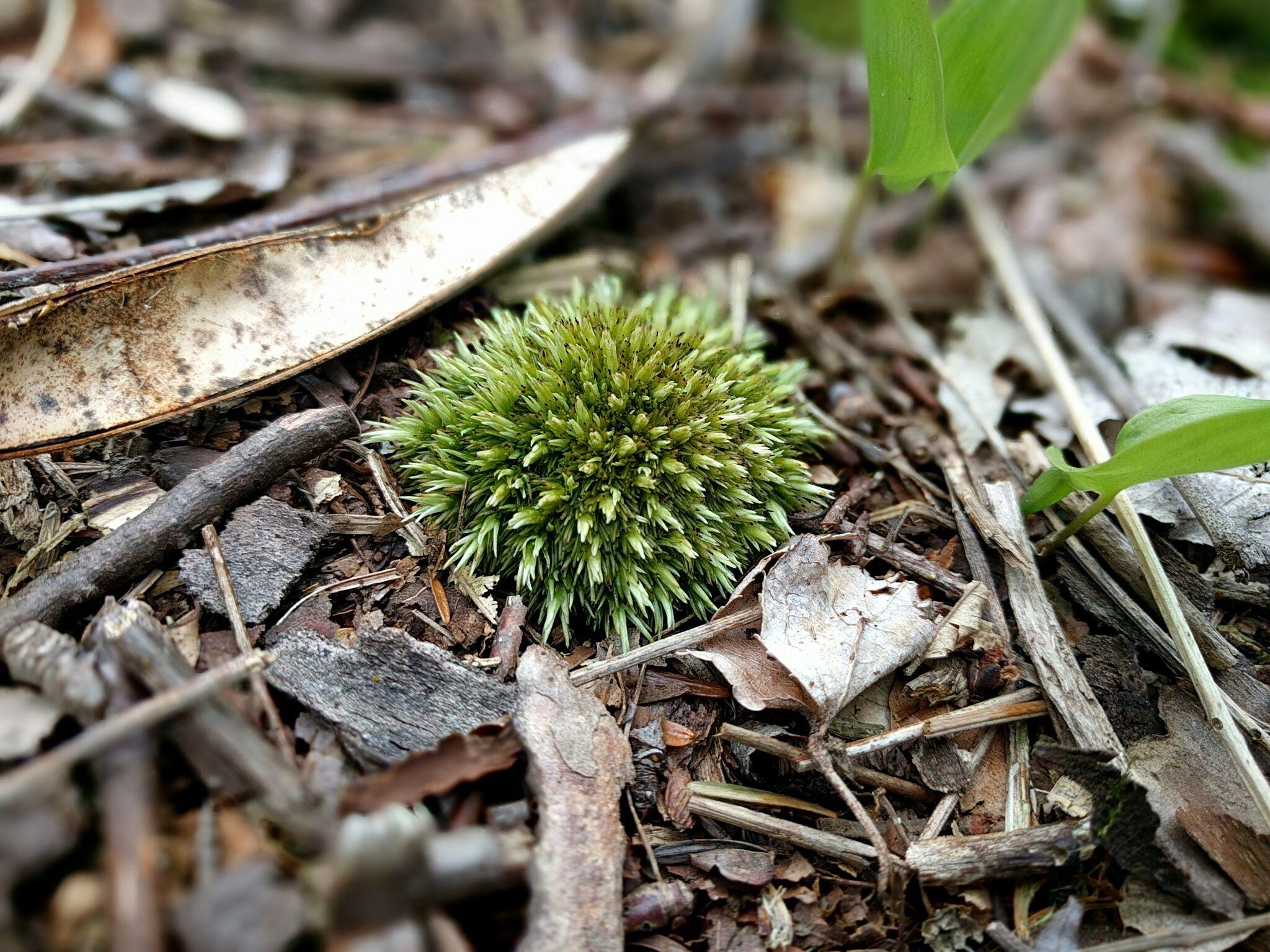

32070500b904cef3255b5acaf96bdcb0.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/small-ball-of-moss-in-canadensis-pa-not-sure-of-the-name-oc2048x1536-rbotanicalporn–408490628683863535/
Brotherella canadensis W.B.Schofield, a moss in the Pylaisiadelphaceae family. Also known simply as Brotherella, this diminutive plant is worth getting to know. In this post, we’ll explore the unique features and importance of Brotherella canadensis.
Background on Brotherella Moss
Brotherella canadensis is a species of moss first described by bryologist Wilfred Borden Schofield in 1965. It belongs to the Pylaisiadelphaceae family in the order Hypnales. The Pylaisiadelphaceae includes around 170 species found worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
Brotherella canadensis forms small, delicate tufts or mats. The stems are creeping to ascending, irregularly branched, and typically less than 2 cm long.

shining-club-moss-lycopodium-and-bunchberry-cornus-canadensis-in-the-DF89H9.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/shining-club-moss-lycopodium-and-bunchberry-cornus-canadensis-in-the-image61034101.html
Leaves are ovate-lanceolate, 0.7-1.2 mm long, and have a short double costa. Leaf margins are entire to serrulate near the apex.

bunchberry-cornus-canadensis-leaves-in-a-bed-of-moss-halfway-lake-HMJ3F9.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bunchberry-cornus-canadensis-leaves-in-a-bed-of-moss-halfway-lake-133163613.html
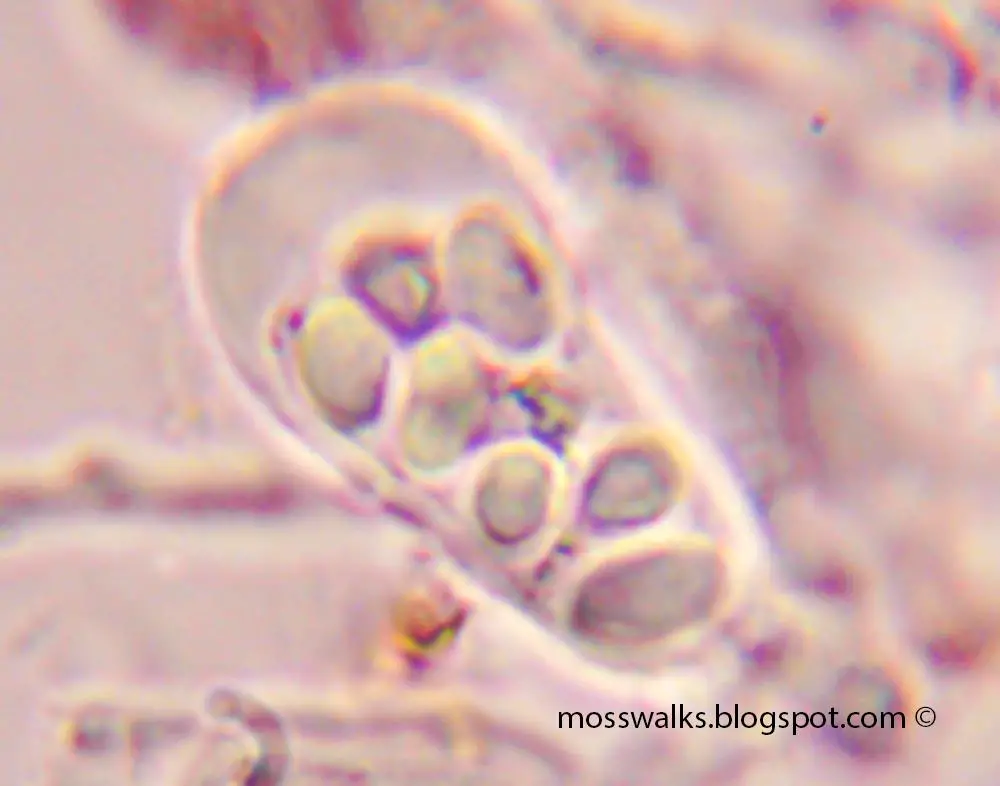
Sporophytes are uncommon. When present, the seta
vul-ascus-for-web.jpg from: https://mosswalks.blogspot.com/2013/01/vulpicida-canadensis.html
is reddish, 1-2 cm long, and the capsules are inclined to horizontal, cylindrical, and 1.5-2 mm long.

medium.jpg from: https://inaturalist.ca/taxa/282124-Brotherella-tenuirostris
Spores are spherical and papillose, 10-14 μm in diameter.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Brotherella canadensis is native to North America. It occurs across Canada and the northern United States, extending south in the mountains to North Carolina.
This moss grows on tree bases, logs, and rocks in moist forests. It is often found in mixed hardwood-conifer forests

9781930665262.jpg from: https://www.ebay.com/itm/Introduction-to-Bryology-by-W-B-Schofield-Paperback-Book-English-/150680179811
and riparian areas. Brotherella canadensis prefers shaded, humid microhabitats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Brotherella canadensis plays important ecological roles:
- Helps retain moisture in forest ecosystems
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms and invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling and soil formation as it decomposes
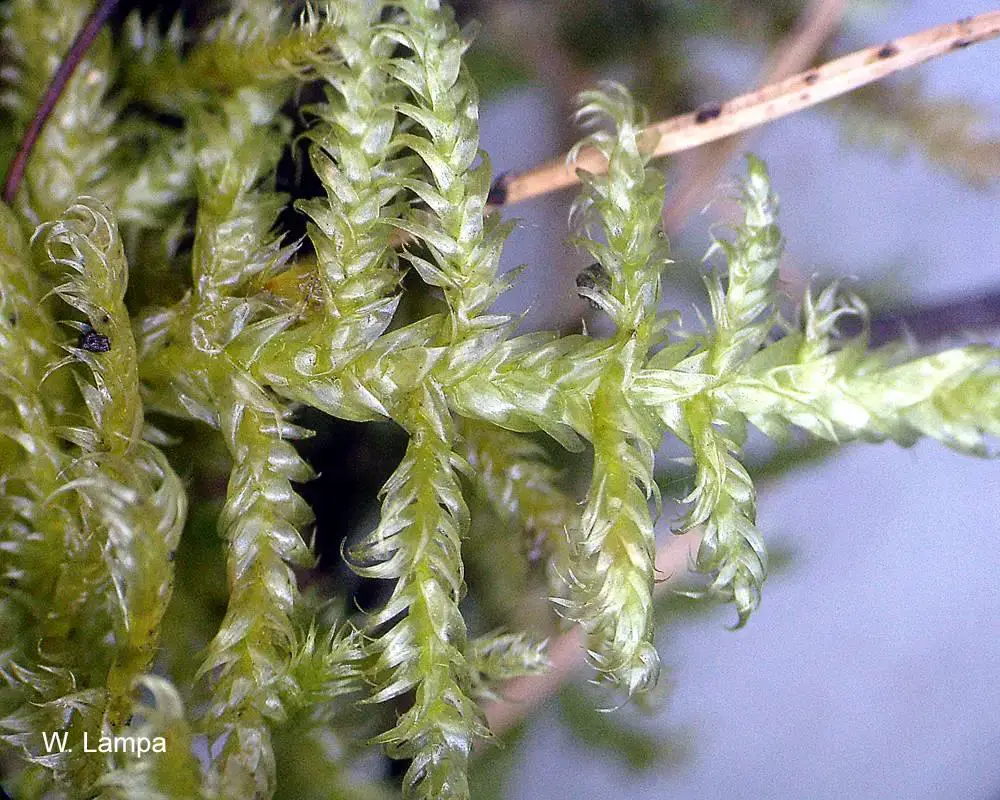
Brotherella has several

Brotherella_recurvens_M2_1590419306.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/collections/individual/index.php?occid=4581908
adaptations for survival:
- Tolerates low light levels in shaded understory habitats
- Desiccation tolerance allows it to dry out and rehydrate
- Reproduces through fragmentation when conditions are too dry for sexual reproduction
Although it has a broad distribution, Brotherella canadensis is not common throughout its range. It is sensitive to disturbance and air pollution. Protecting mature forests and maintaining good air quality will help conserve this intriguing moss species.

Aquilegia-canadensis-.jpg from: https://catskillnativenursery.shop/product/aquilegia-canadensis-wild-columbine-1-quart/
Conclusion
From its delicate beauty to its ecological importance, Brotherella canadensis is a captivating moss species native to North American forests. Though small in stature, it plays an outsized role in the ecosystems it inhabits.
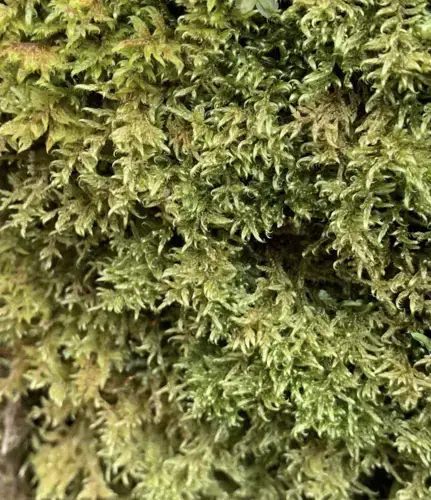

medium.png from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/159479-Brotherella-canadensis
Next time you’re walking through a shaded forest, take a closer look – you might just spot the subtle green of Brotherella adorning logs and tree bases. What other overlooked species share its habitat?