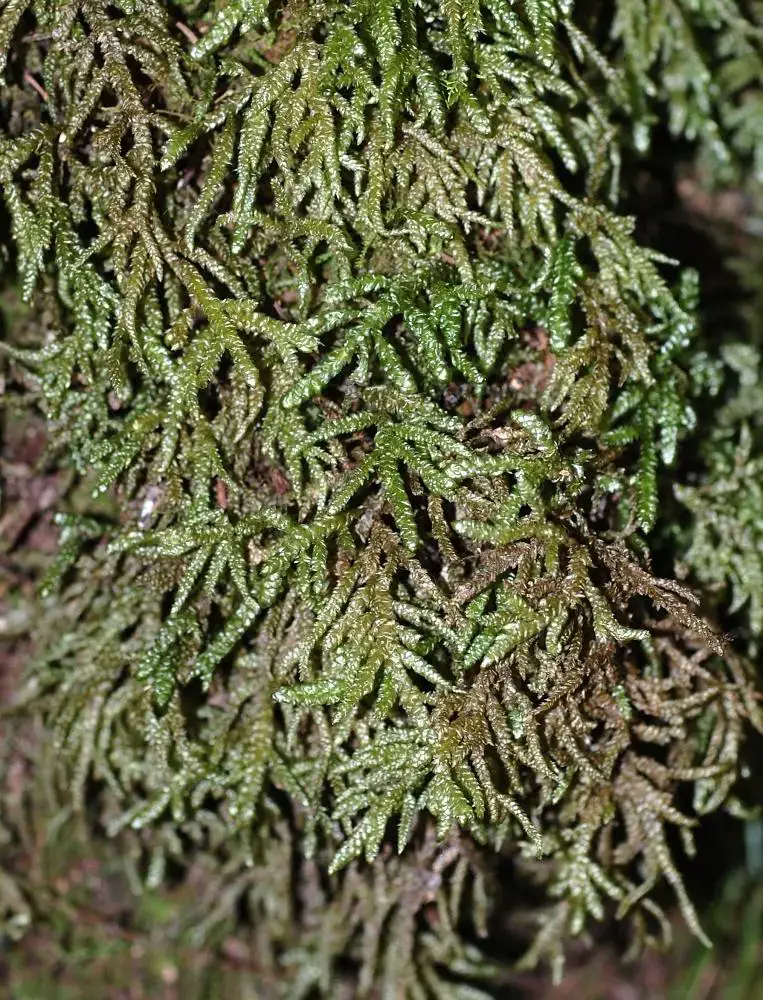

DT_Camptochaete_arbuscula.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/30_Lembophyllaceae_images.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Camptochaete excavata (Taylor) A.Jaeger. Belonging to the Lembophyllaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable moss is commonly referred to as Camptochaete. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this bryological wonder.
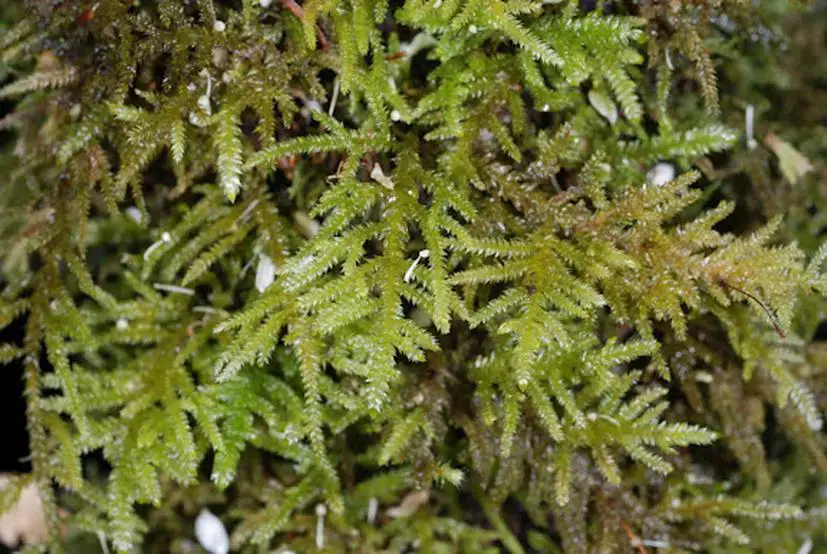

NK_Camptochaete_deflexa.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/00_AMO_all images.html
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Camptochaete excavata, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse habitats.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
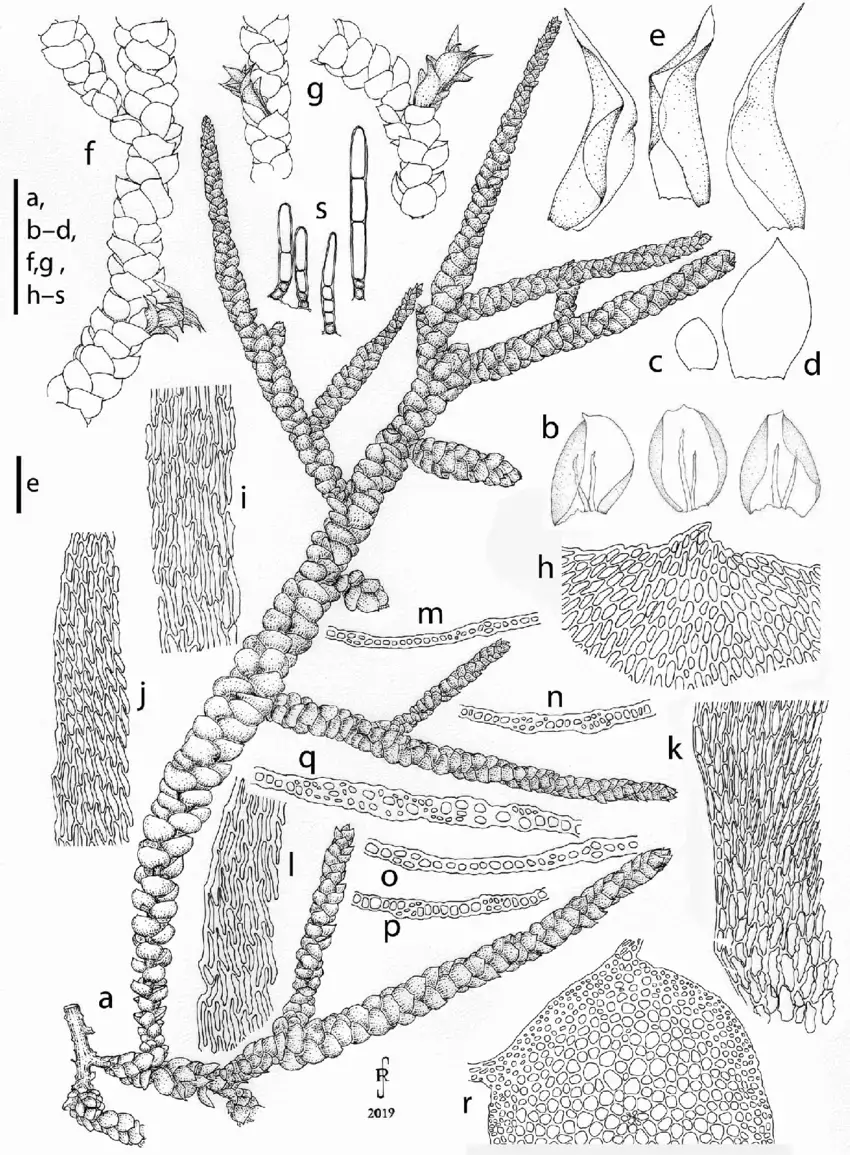
Camptochaete-monolina-a-part-of-plant-when-moist-b-branch-leaves-c-e-perichaetial.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Camptochaete-monolina-a-part-of-plant-when-moist-b-branch-leaves-c-e-perichaetial_fig1_348871519
Camptochaete excavata is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive excavated or concave shape, giving rise to its specific epithet “excavata.” The leaf margins are entire, and the costa (midrib) is single and excurrent (extending beyond the leaf apex). This moss is dioicous, meaning that male and female reproductive structures occur on separate plants.
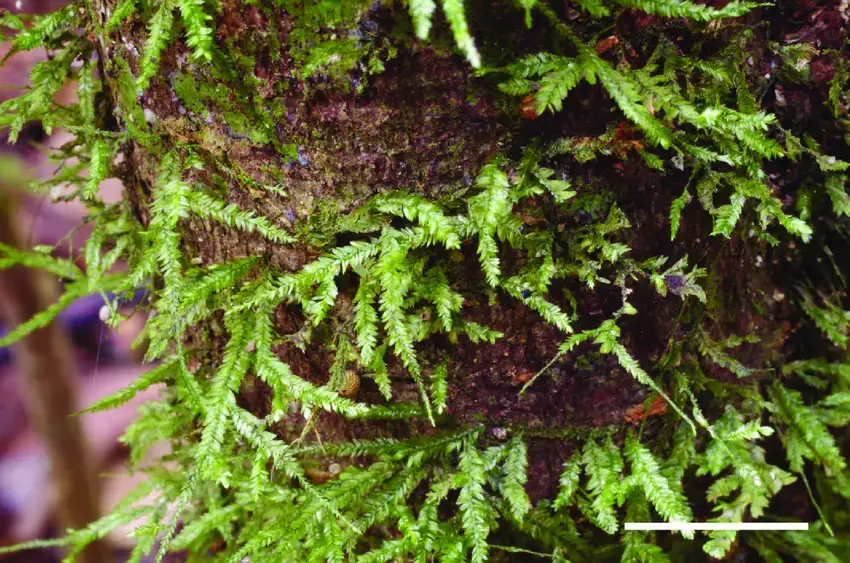

Camptochaete-subporotrichoides-Meagher-Cairns-WT-379-showing-flattened-leaves-on-all.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Camptochaete-subporotrichoides-Meagher-Cairns-WT-379-showing-flattened-leaves-on-all_fig3_348871519
Global Distribution and Habitat
Camptochaete excavata is widely distributed across various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded rock surfaces

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/407668-Camptochaete-angustata
to decaying logs and soil in forests. This moss is often found in cool, temperate regions and is particularly abundant in areas with high humidity and moisture levels.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Camptochaete excavata plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates and serve as a moisture reservoir

camptochaetearbu1.jpeg from: https://www.kaimaibush.co.nz/mosses/lembophyllaceae.html
, helping to regulate water cycles in its environment.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Camptochaete excavata is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in habitats with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Camptochaete excavata played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of coniferous seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microclimate and retained moisture, creating favorable conditions for the germination and growth of tree seedlings.
Technical Table

fe4c899880f8ffbfe9fac7b6cbf1caf8.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/hoya-excavata–798192733933405429/
excavata-56d9e72f-1902-482c-91db-c25630d3178-resize-750.jpeg from: https://alchetron.com/Excavata
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales
 Hoya-excavata-2048×1542.jpg from: https://tropicsathome.com/product/hoya-excavata/ |
| Family | Lembophyllaceae |
| Genus | Camptochaete |
| Species | excavata |
Growth Form
 Ihlenfeldtia-excavata-2.jpg from: https://succulent.guide/types-of-succulents/ihlenfeldtia-excavata/ |
Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate, excavated or concave |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Costa | Single, excurrent |
| Sexuality | Dioicous |
Conclusion
The Camptochaete excavata (Taylor) A.Jaeger moss, a member of the Lembophyllaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. From its unique morphology to its ecological roles and global distribution, this unassuming bryophyte deserves our appreciation and admiration. As we continue to explore the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden wonders lie within the realm of bryophytes, waiting to be discovered and celebrated?