
Dichelyma-falcatum-general-view.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Dichelyma-falcatum-general-view_fig1_251513601
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Dichelyma falcatum (Hedw.) Myrin. Belonging to the Fontinalaceae family, this aquatic moss is commonly referred to as Dichelyma. Prepare to embark on a fascinating journey as we delve into the intricate details of this remarkable plant.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Dichelyma falcatum

dichelyma_falcatum.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/fontinalaceae/dichelyma-falcatum/en/
, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back over 400 million years, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
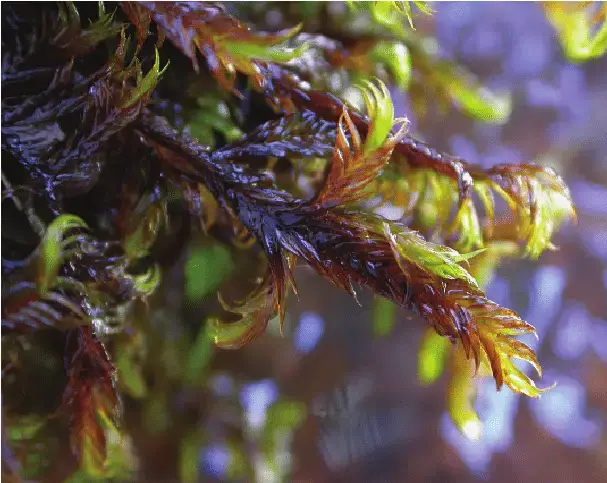
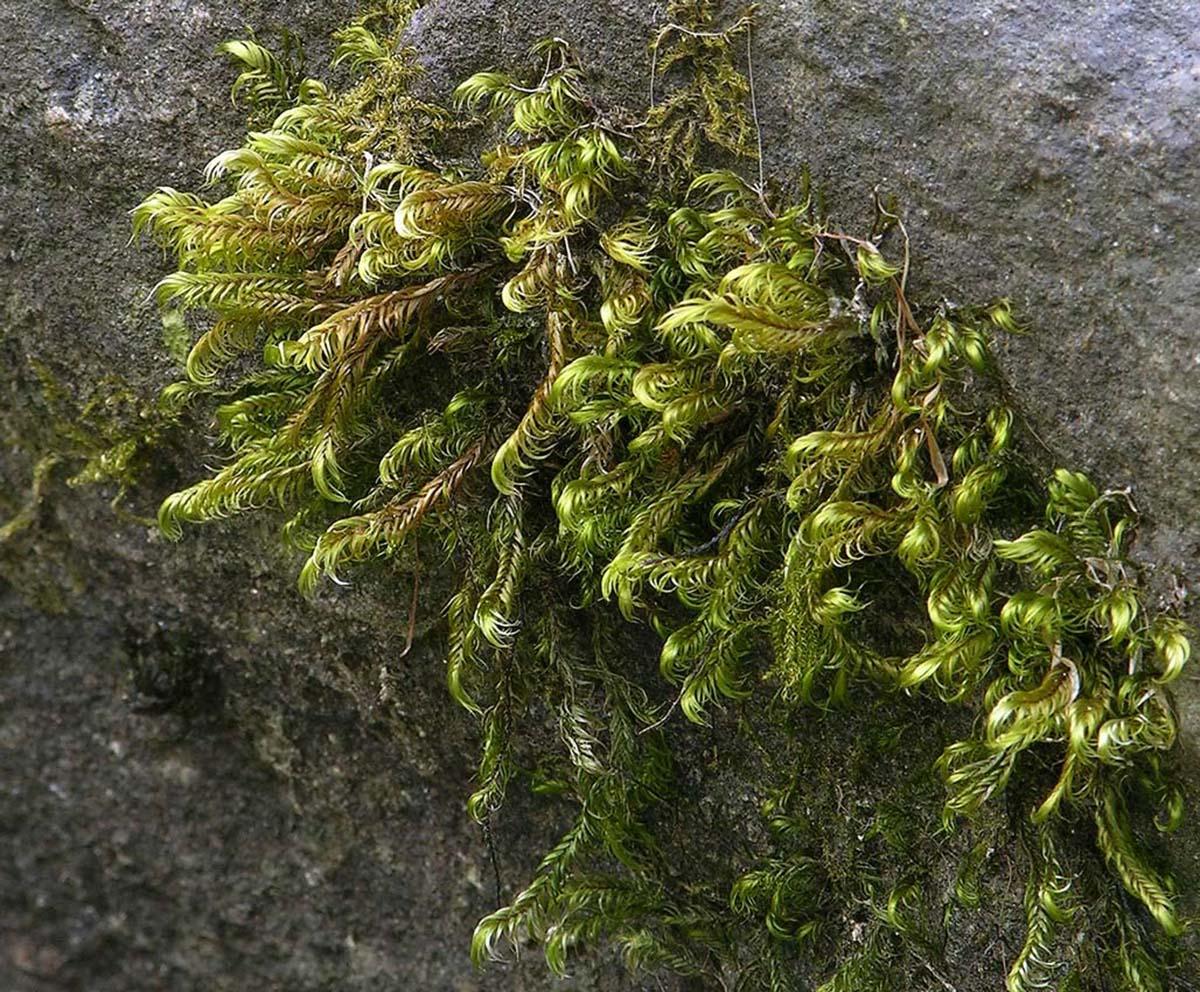
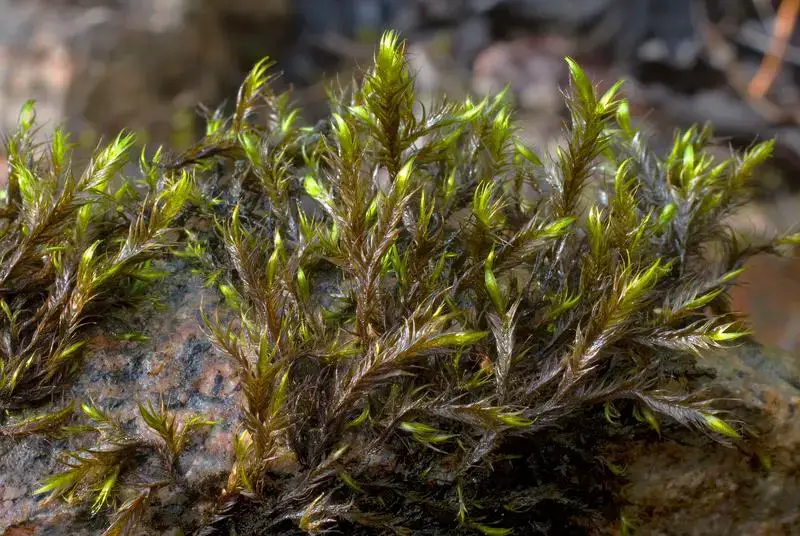
Dichelyma falcatum is a striking moss species that can reach impressive lengths of up to 30 centimeters. Its vibrant green hue and distinctive falcate (sickle-shaped) leaves make it easily recognizable. The leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem, creating a beautiful, feathery appearance. This moss is dioicous, meaning that male and female reproductive structures are found on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat

27630_2664_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/dichelyma-1004602
Dichelyma falcatum is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in cool, flowing streams and rivers. It is particularly abundant in regions with high humidity and consistent water flow, such as mountainous areas and forested streams. This aquatic moss prefers to anchor itself to submerged rocks or logs, where it can access the necessary nutrients and moisture.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Dichelyma falcatum plays a vital role in aquatic ecosystems, serving as a habitat and food source for various invertebrates and fish species. Its dense mats provide shelter and breeding grounds for aquatic organisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.

JR68113_thumb.jpg from: https://laji.fi/taxon/MX.43520
Distribution-of-Dichelyma-falcatum-Hedw-Myrin-circles-and-D-japonicum-Card.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-of-Dichelyma-falcatum-Hedw-Myrin-circles-and-D-japonicum-Card_fig3_273928652
One of the remarkable adaptations of Dichelyma falcatum is its ability to withstand and thrive in fast-flowing water. Its sturdy stems and falcate leaves allow it to remain anchored and resist the force of the current. Additionally, this moss possesses specialized structures called rhizoids, which help it adhere to surfaces and absorb nutrients from the water.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, researchers discovered that Dichelyma falcatum played a crucial role in maintaining the health of stream ecosystems. The moss provided a stable habitat for various aquatic invertebrates, which in turn served as food sources for fish and other wildlife. This highlights the importance of preserving and protecting the habitats where this remarkable moss thrives.
Technical Table

dichelyma_falcatum4.jpg from: http://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/koskikoukkusammal.html
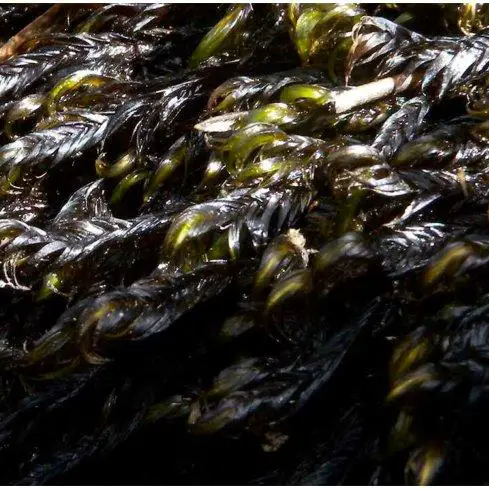

Dichelyma-falcatum-etang-du-Racou-espece-relicte_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Dichelyma-falcatum-etang-du-Racou-espece-relicte_fig1_348844175
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dichelyma falcatum (Hedw.) Myrin |
| Family | Fontinalaceae
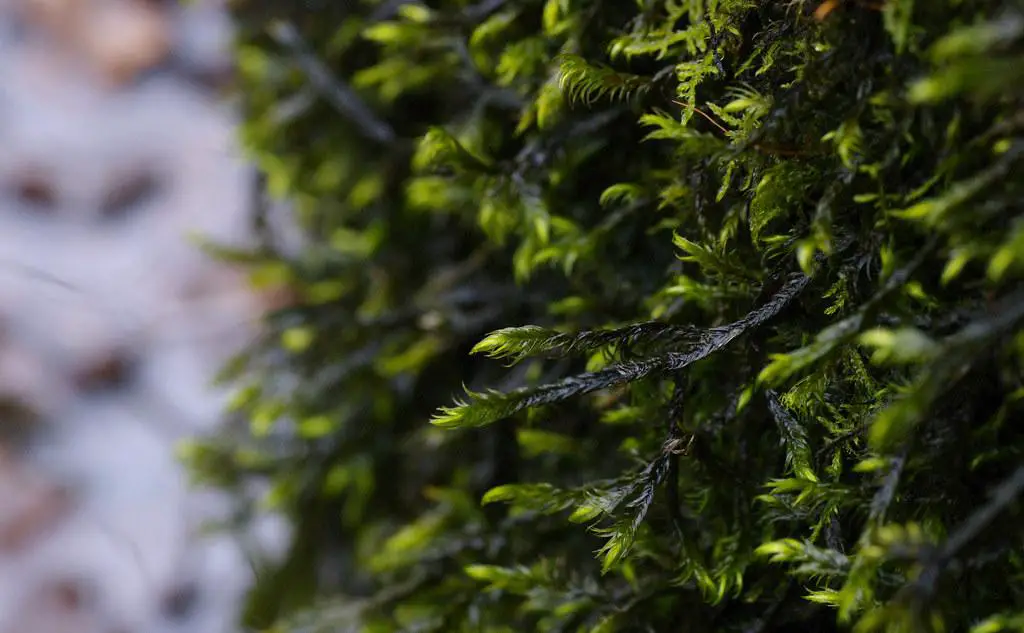 25826317380_d1df97c7b6_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/25826317380/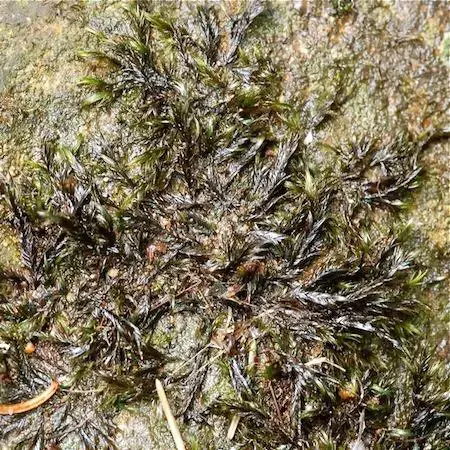  dichelyma_falcatum2.jpg from: https://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/koskikoukkusammal.html |
| Common Name | Dichelyma |
| Growth Form | Aquatic moss |
| Leaf Shape | Falcate (sickle-shaped) |
| Habitat | Cool, flowing streams and rivers |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere |
| Ecological Role | Habitat and food source for aquatic organisms |
Conclusion
Dichelyma falcatum (Hedw.) Myrin, a true gem of the Fontinalaceae family, is a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject of study for botanists, ecologists, and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve the habitats that support these remarkable moss species and the ecosystems they sustain?
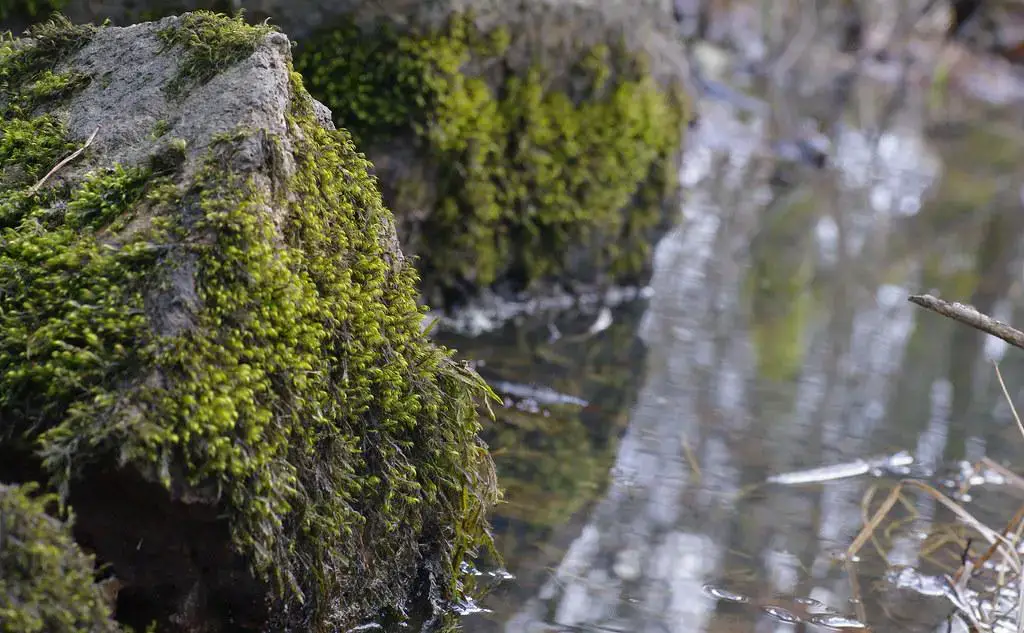

26006829532_b2366faf8e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/26006829532/