Syrrhopodon-japonicus-Besch-Broth-A-Plants-B-Cross-section-of-leaf-B-1-median_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Syrrhopodon-japonicus-Besch-Broth-A-Plants-B-Cross-section-of-leaf-B-1-median_fig1_283888063
Exploring the Fascinating World of Epipterygium thermale Moss
Introduction
Today we’re diving into the captivating realm of Epipterygium thermale (Besch.) Broth., a unique species of moss in the Bryaceae family. Also known simply as Epipterygium, this tiny but mighty plant plays important ecological roles. Let’s explore what makes Epipterygium thermale so special!

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iqVOncK2Cig
Background on Bryophytes
Before we get into the specifics of E. thermale, it’s helpful to understand what bryophytes are. Bryophytes are small, non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses like E. thermale are classified under Bryopsida.
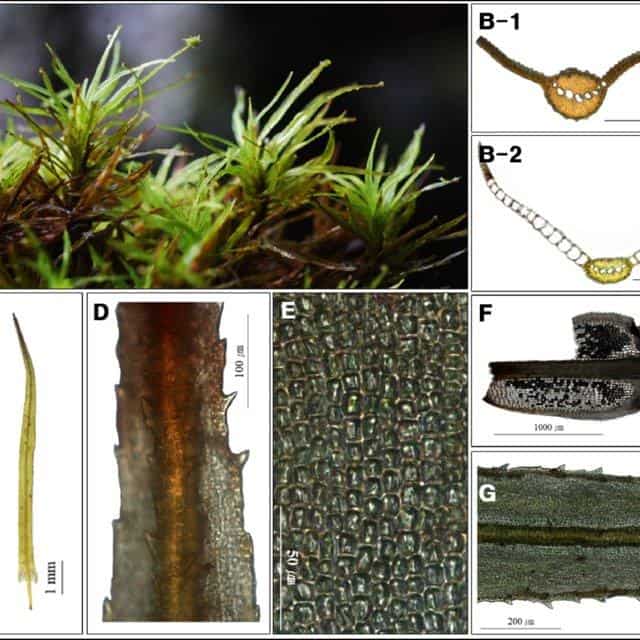
Morphology and Identification
Epipterygium thermale is a small, delicate moss. Its phyllids are ovate-lanceolate in shape and have a costa (midrib) that extends to the tip. The seta (stalk) is reddish-brown and supports a cylindrical capsule. Spores are released from the capsule to reproduce.
Identifying E. thermale requires microscopic examination of its cellular structure. Key features to look for include:
- Rhomboidal leaf cells
- Lack of a peristome (toothed structure around capsule mouth)
- Presence of an annulus (ring of cells where capsule opens)
Global Distribution and Habitat
Epipterygium thermale has a widespread but scattered distribution
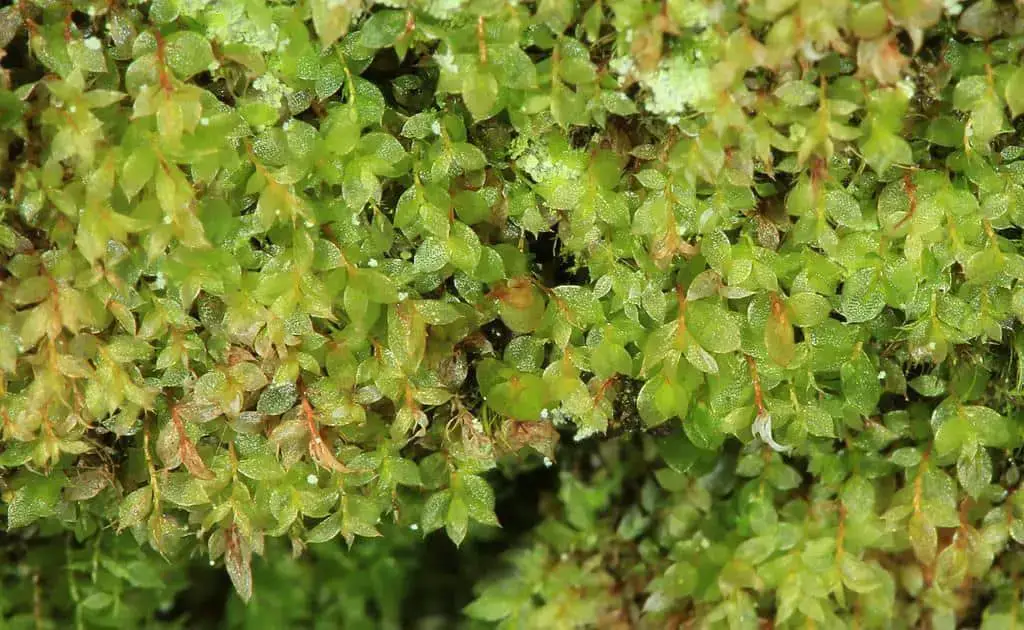

epipterygium_tozeri.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Bryaceae/epipterygium-tozeri/en/
. It is found in:
- Europe

B094-02_0.jpg from: http://taibif.tw/zh/namecode/200877
- Asia
- Africa

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/67875-Epipterygium-tozeri
- North and South America
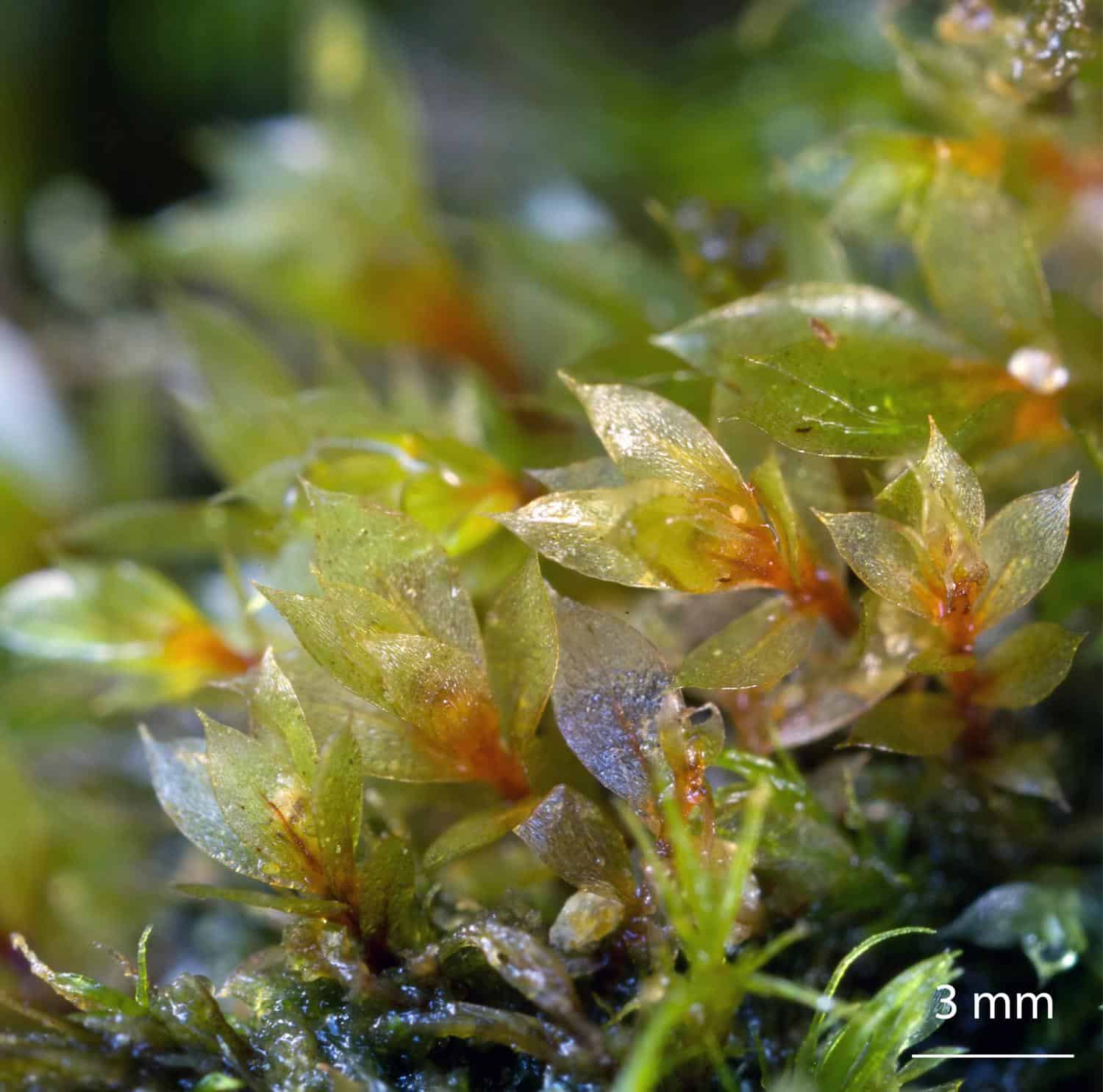

Epipterygium-tozeri-moss.jpg from: https://elmusgo.blogspot.com/2012/12/epipterygium-tozeri.html?m=0
- Australia
This moss grows on damp, shaded soil and rocks, often near streams or in forests. It prefers humid, temperate climates and is less common in arid regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, E. thermale plays several important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture in the soil
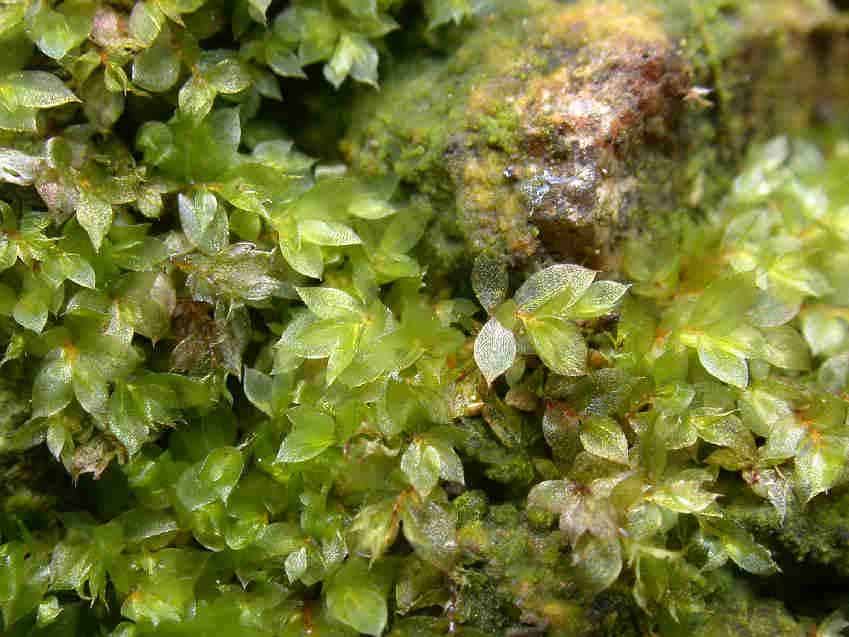

Epipterygium_tozeri_003C.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Epipterygium_tozeri.html
- Provides shelter and food for micro-organisms and insects
- Pioneers the growth of other plants by stabilizing soil
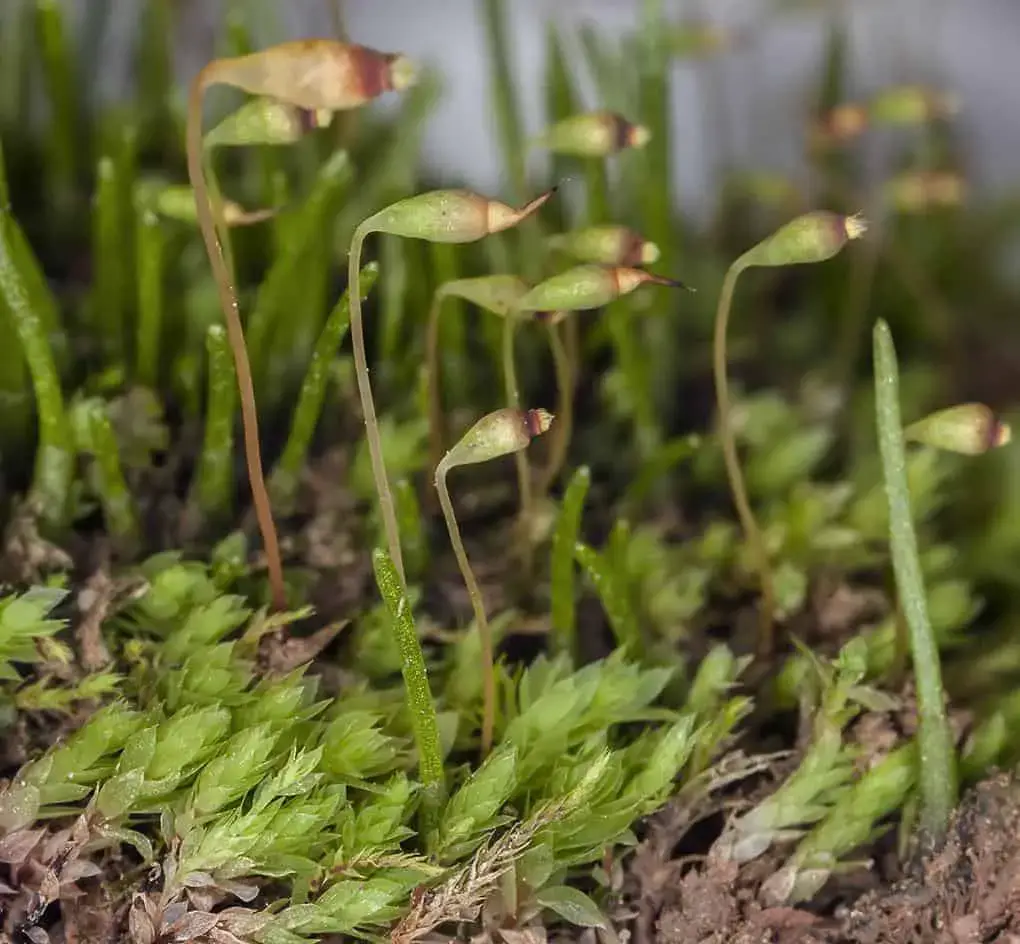

2603.jpeg from: https://www.calflora.org//cgi-bin/species_query.cgi?where-calrecnum=12459
Epipterygium has adapted to regulate water efficiently. Its phyllids can absorb moisture from rain and dew. During dry periods, the moss goes dormant to conserve resources.

ephemerumcrassinervium.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Ephemeraceae/ephemerum-crassinervium/en/
Conclusion
From its tiny stature to its global presence, Epipterygium thermale is a prime example of how even the most unassuming species can have an outsized ecological impact. The next time you see a patch of moss, take a closer look – you may be gazing at an Epipterygium! What other secrets do you think these ancient plants hold?

41149959871_8f7e1a082b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/131742409@N02/41149959871