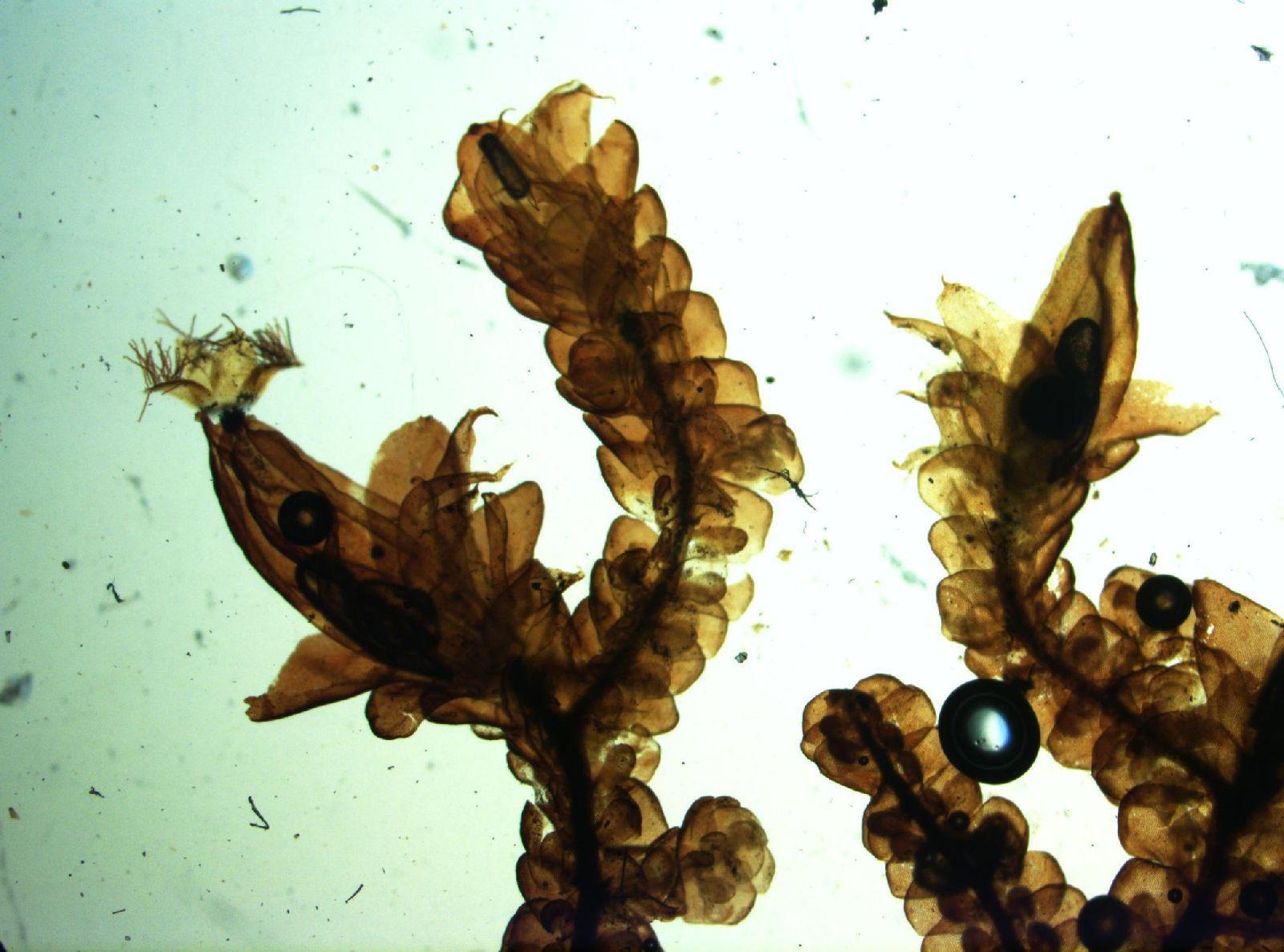
Frullania_arecae_pocs_697.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/frullania/taxa/index.php?taxon=165732
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Frullania arecae (Spreng.) Gottsche moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Frullaniaceae family. Often referred to simply as Frullania, this diminutive yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Marchantiophyta (liverwort) species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Frullania arecae, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, class Jungermanniopsida, order Jungermanniales, and family Frullaniaceae. Its scientific name, Frullania arecae (Spreng.) Gottsche, pays homage to the German botanist Carl Moritz Gottsche, who made significant contributions to the study of bryophytes.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Frullania arecae is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on various substrates. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with closely overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. The leaves are distinctive, with a rounded or ovate shape and a distinctive “saddle-shaped” appearance. They are often reddish-brown or greenish-brown in color, adding a touch of warmth to the moss’s overall appearance.
One of the most remarkable features of Frullania arecae is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. The sexual reproductive structures, known as archegoniophores and antheridiophores, are borne on separate plants (dioicous). The asexual reproduction occurs through the formation of specialized structures called gemmae, which are small, disc-shaped propagules that can develop into new plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Frullania arecae is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from temperate to tropical regions, and can be found growing on tree bark, rocks, soil, and even man-made structures like walls and roofs.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to humid and shaded environments, making it a common sight in forests, woodlands, and other areas with high moisture levels. Its ability to colonize a wide range of substrates and tolerate varying environmental conditions contributes to its widespread distribution.
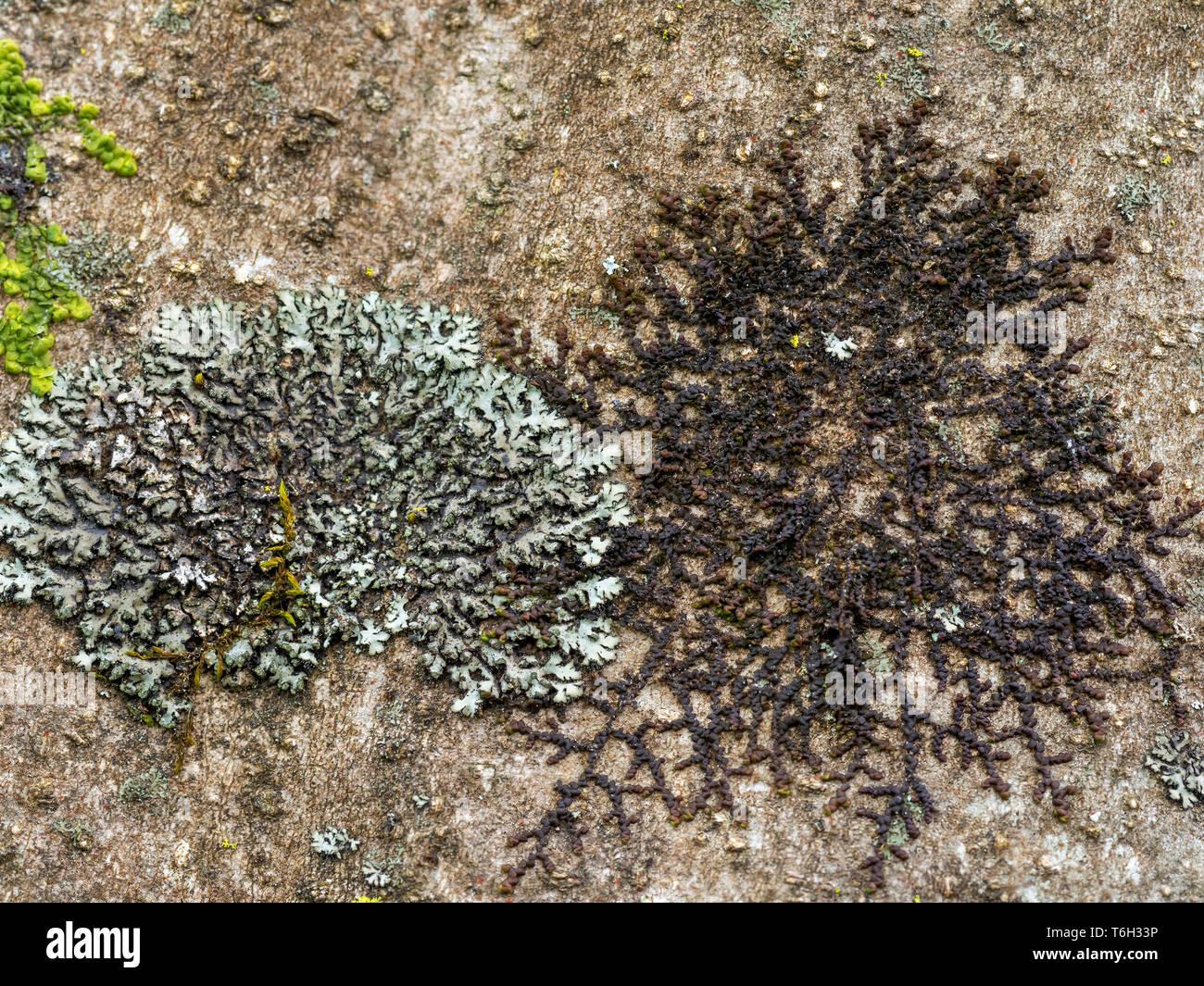

flechten-phaeophyscia-orbicularis-und-frullania-dilatata-wahrscheinlich-t6h33p.jpg from: https://www.alamy.de/flechten-phaeophyscia-orbicularis-und-frullania-dilatata-wahrscheinlich-image245008730.html
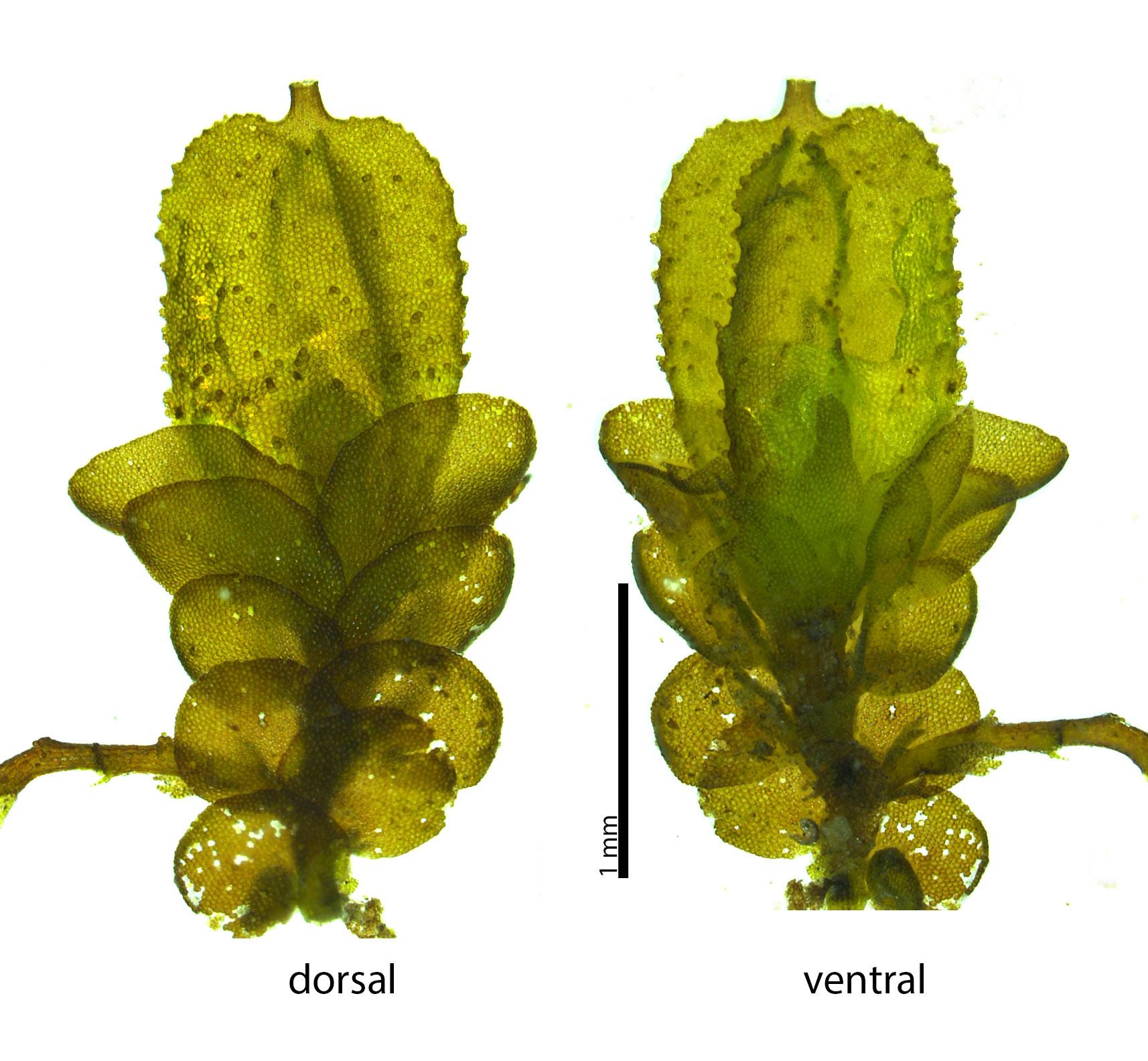

fruapp_pgd9311_web1.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/frullaniaappalachiana.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Frullania arecae plays crucial ecological roles within its habitats. As a primary producer, it contributes to the overall productivity of the ecosystem by converting carbon dioxide into organic matter through photosynthesis. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, supporting biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Frullania arecae is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and reducing metabolic activity. Once moisture becomes available again, it quickly revives and resumes its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
Frullania arecae has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its ecological importance and potential applications. For instance, researchers have investigated the moss’s ability to accumulate heavy metals, making it a potential biomonitor for environmental pollution. Additionally, its antimicrobial properties have been explored, with some studies suggesting potential applications in the pharmaceutical industry.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Frullaniaceae |
| Genus | Frullania |
| Species | arecae |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, overlapping |
| Leaf Shape | Rounded or ovate, saddle-shaped |
| Color | Reddish-brown or greenish-brown |
| Reproduction | Sexual (dioicous) and asexual (gemmae) |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, soil, man-made structures |
| Distribution | Widespread across various regions |
Conclusion
The Frullania arecae (Spreng.) Gottsche moss, a member of the Frullaniaceae family, is a remarkable and captivating species that has captured the interest of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. From its distinctive morphology and reproductive strategies to its global distribution and ecological roles, this moss offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricate world of bryophytes.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of mosses, Frullania arecae serves as a reminder of the intricate beauty and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a dense mat of reddish-brown or greenish-brown moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the wonders of this unassuming yet remarkable plant.
Thought-provoking question: In an ever-changing world, how can we ensure the preservation of species like Frullania arecae and the invaluable ecological services they provide?