Plectocolea-infusca-Mitt-var-memiadzei-1-habit-dorsal-view-2-male-branch-dorsal_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plectocolea-infusca-Mitt-var-memiadzei-1-habit-dorsal-view-2-male-branch-dorsal_fig1_275607657
Jungermannia infusca: The Fascinating Moss of the Solenostomataceae Family
Introduction
Have you ever noticed the tiny, delicate plants growing on rocks, trees, or soil in damp, shady areas? Chances are, you’ve seen moss. One particularly interesting species is Jungermannia infusca (Mitt.) Steph., also known simply as Jungermannia

Plectocolea-kurilensis-Bakalin-Bakalin-et-Vilnet-1-3-7-8-10-branch-with-perianth_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plectocolea-infusca-Mitt-1-5-sterile-branch-2-3-branch-with-perianth-4-branch_fig4_273487708
. This small but mighty plant is part of the Solenostomataceae family and the Marchantiophyta phylum. Let’s dive in and learn more about this fascinating organism!
Background
Mosses are small, non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and require moisture for reproduction. There are over 12,000 species of moss found worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
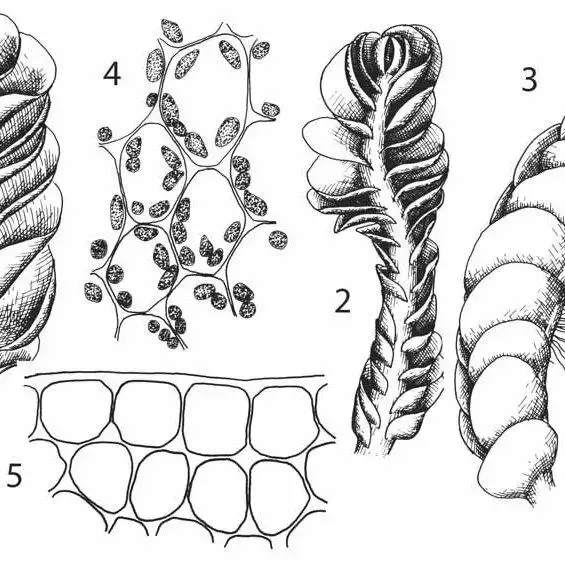
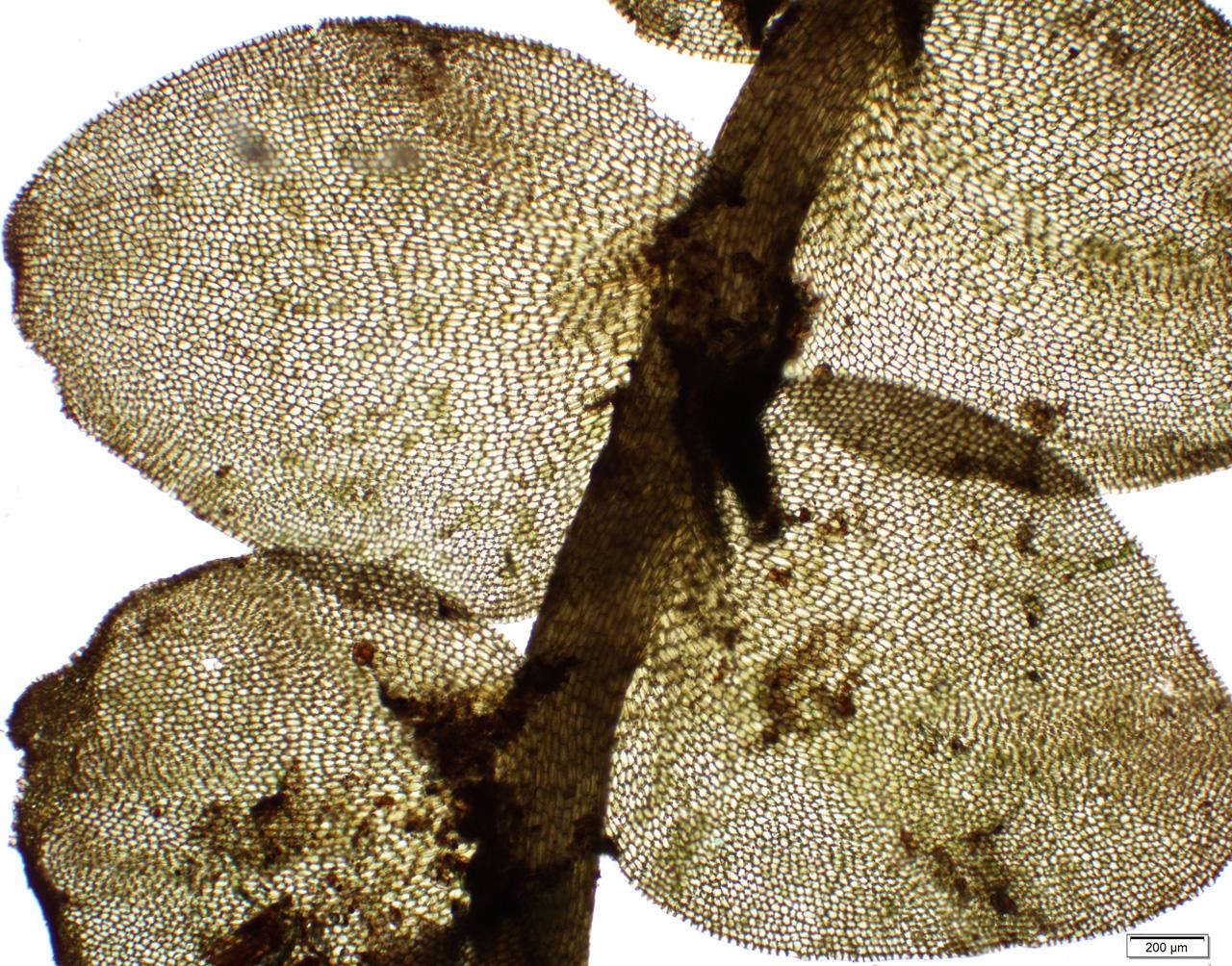
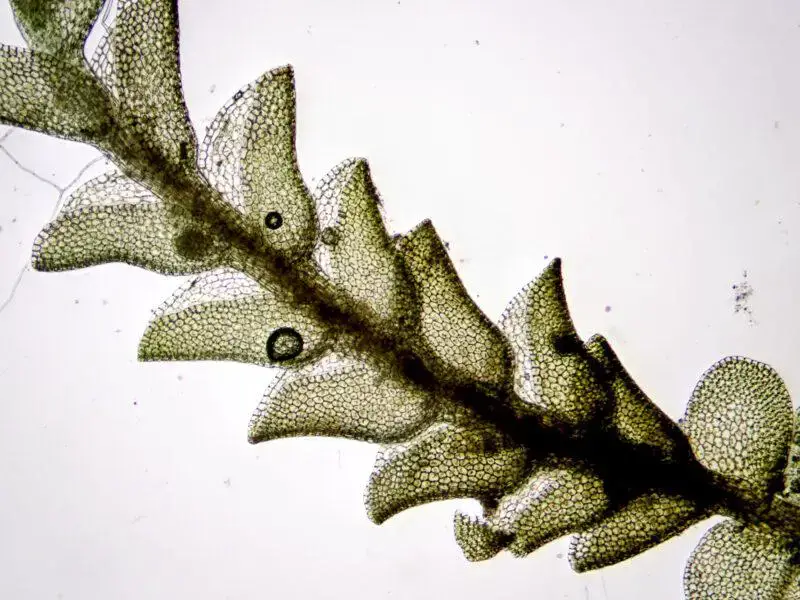
Jungermannia infusca is a leafy liverwort, meaning it has leaf-like structures arranged on a stem. The leaves are

a-Philonotis-hastata-Gametophyte50x-b-Jungermannia-appressifolia-Mitt-Gametophyte.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-Philonotis-hastata-Gametophyte50x-b-Jungermannia-appressifolia-Mitt-Gametophyte_fig5_344717960

j_exsertifolia.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/jungermannia_exsertifolia.html
succubous (lying flat, not overlapping), ovate (egg-shaped), and bilobed (divided into two lobes). They are a dark green to brownish

haitubomigoke-saibou2.jpg from: https://mikawanoyasou.org/koke/haitubomigoke.htm
color. The stems grow prostrate (lying flat) and are irregularly branched. Jungermannia produces capsules on setae (stalks) for reproduction.

jungermannia-pseudocyclop-rosa-moss-1-510×510.jpg from: https://www.premiumbuces.com/en/jungermannia-pseudocyclop-rosa-moss/
Global Distribution and Habitat
This species is found across Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It grows on damp soil, rocks, logs, and tree bases in shady forests and along streams from lowlands to subalpine elevations. Jungermannia thrives in humid microclimates with indirect light.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Jungermannia plays important roles in its ecosystem:

2020-08-30-16-33-23-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/jungermannia-atrovirens/
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides shelter and food for invertebrates
- Pioneers the colonization of bare substrates

jungermannia-pseudocylop1_600x600.jpg from: https://www.aquascape.de/natureholic-moospad-jungermannia-pseudocyclop-rose-moss-3-x-3cm
- Contributes to nutrient cycling
- Serves as a bioindicator of air and water quality
Jungermannia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Poikilohydry: can survive desiccation by suspending metabolic activity when dry
- Ectohydry: absorbs water and nutrients over its surface
- Clonal growth: can reproduce asexually via fragmentation

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237586845_The_first_synthesis_of_-secocuparenal_a_sesquiterpene_isolated_from_the_liverwort_Jungermannia_infusca
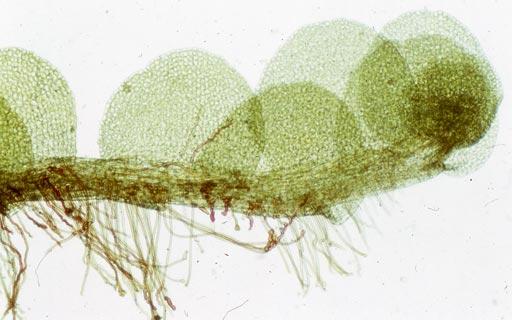
jungermannia_infusca01l.jpg from: https://www.digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/hepa_habit/Jungermannia infusca/Jungermannia_infusca.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Solenostomataceae |
| Genus | Jungermannia |
| Species | J. infusca |
Conclusion
Jungermannia infusca may be small, but it is a remarkable and important member of its ecosystem. Its unique adaptations and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for botanists and naturalists alike. Next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot some Jungermannia! What other amazing bryophytes have you encountered?