
iberian-tree-frog-hyla-molleri-in-valdemanco-madrid-spain-2ARG63F.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/iberian-tree-frog-hyla-molleri-in-valdemanco-madrid-spain-image341490115.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Leucophanes molleri Müll.Hal. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is

4e64bef677163d6779dbd17b0d8d474e.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/fotografia/anfibios-y-reptiles/hyla-molleri-2/26946.html
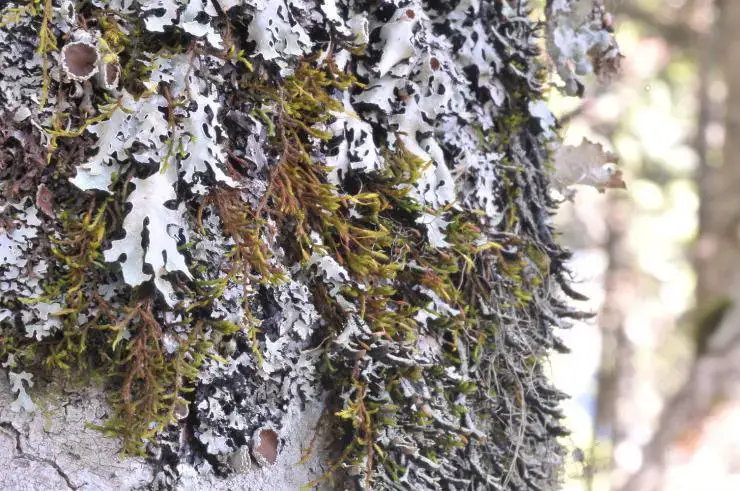

5856d54f21c593d9017a4c708465902e.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/944be5363af1050246cc941b5ca41998
Leucophanes molleri Müll.Hal.
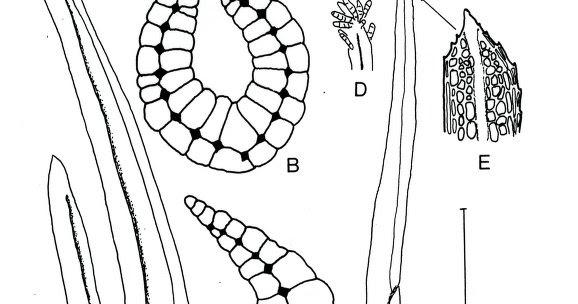
LEUCOPHANES%2BMOLLERI%2BN.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-leucobryaceae-leucophanes-molleri.html
, a moss in the Calymperaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its morphology to its ecological importance.
Background
Leucophanes molleri is a species of moss first described by German botanist Carl Müller in 1879. It belongs to the genus Leucophanes and the family Calymperaceae. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta, which also includes liverworts and hornworts. The class Bryopsida contains the “true mosses” like Leucophanes.
Morphology and Identification
Leucophanes molleri forms loose, pale green to whitish tufts. The leaves are oblong-lanceolate and have a distinct border of elongated cells. The leaf margins are entire (smooth). A key identifying feature is the presence of
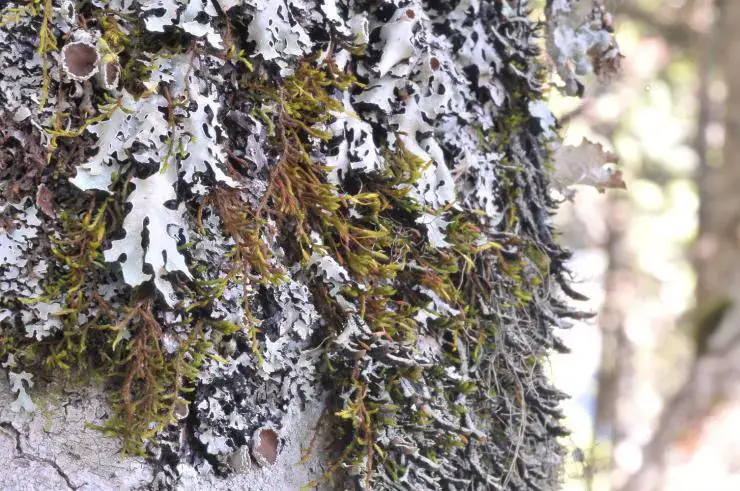

5856d54f21c593d9017a4c708465902e.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/944be5363af1050246cc941b5ca41998
leucocysts – large, empty, hyaline cells that help the moss retain water.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including parts of Africa, Asia, Australia, and South America
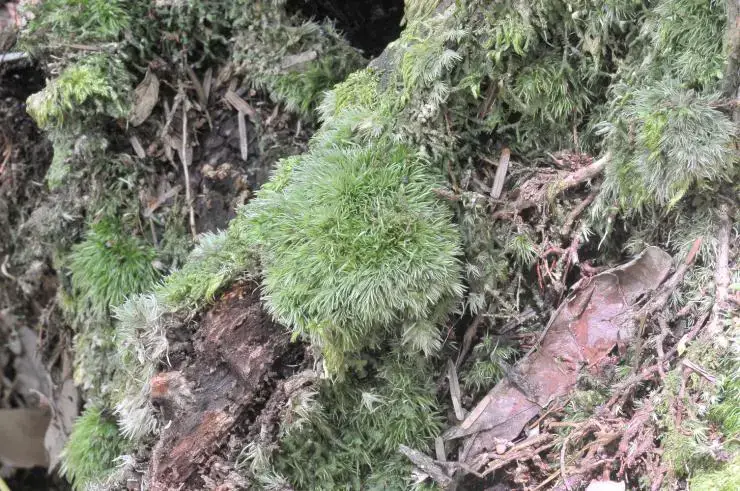

7037e79d418c961c5141889e083833ce.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/2355523fe7d6b11d4b7a8ac495911fd7
. It typically grows on tree trunks, branches, and sometimes on rocks in humid forests at low to moderate elevations.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Leucophanes molleri plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms
- Participates in nutrient cycling
- Serves as a bioindicator of air quality
The leucocysts help the moss survive periodic drying by storing water. The plant can enter a dormant state when moisture is scarce.
Moss Morphology Comparison
| Moss Genus | Leaf Shape | Leaf Margin | Leucocysts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leucophanes | oblong-lanceolate | entire | present |
| Octoblepharum | ligulate | serrulate | present |
| Syrrhopodon | linear-lanceolate | serrulate | absent |
Conclusion
Leucophanes molleri is a prime example of how even tiny, inconspicuous organisms can have outsized ecological importance. The next time you see moss growing on a tree, take a closer look – you may be gazing at a miniature but mighty Leucophanes! What other secrets do you think these amazing plants hold?