
2020-12-12-16-42-13.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/metzgeria-violacea/
Introduction
The world of mosses is a fascinating one, filled with tiny, intricate plants that often go unnoticed by the casual observer. Among these unsung heroes of the plant kingdom is the Metzgeria violacea (Ach.) Dumort., a member of the Metzgeriaceae family, commonly known as Metzgeria. This unassuming moss has captured the attention of enthusiasts and scientists alike, thanks to its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the details of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand its place in the grand scheme of things. Metzgeria violacea
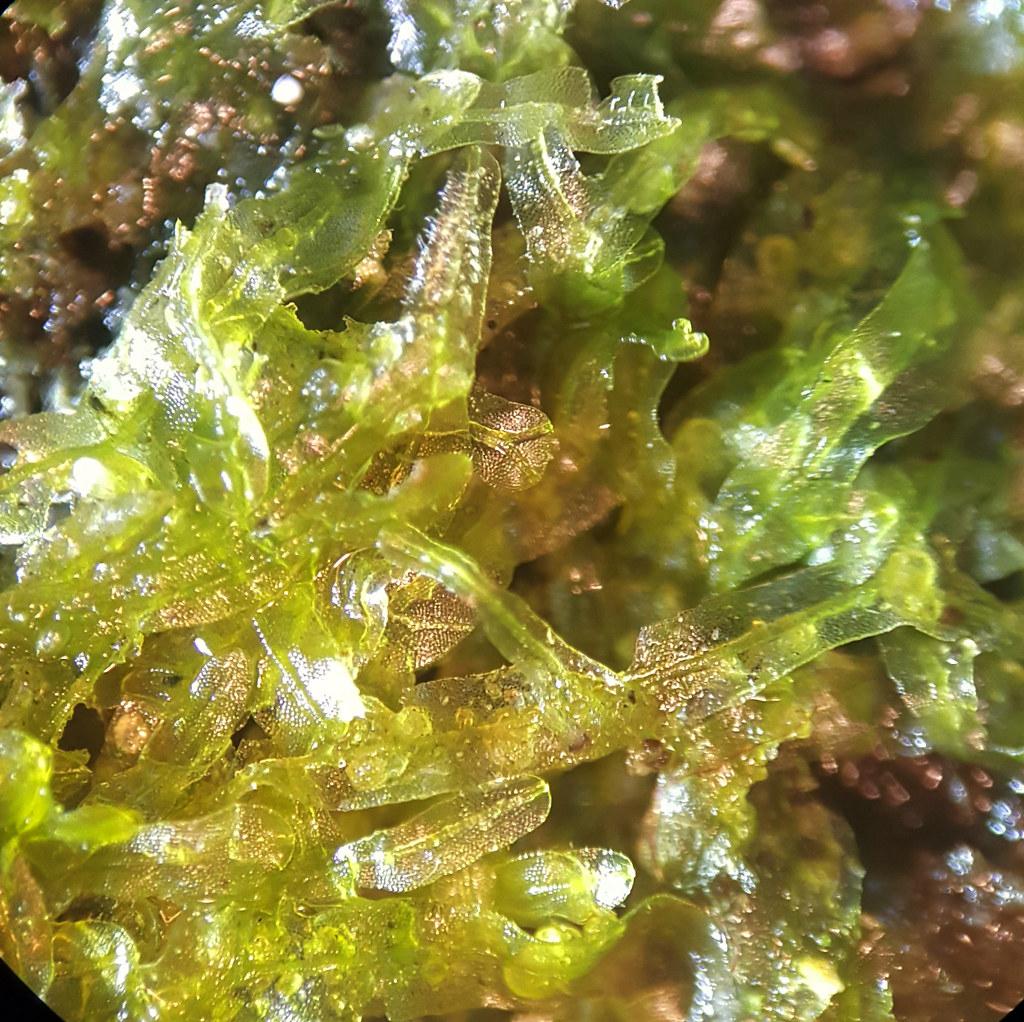

49846177683_dc27560406_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/49846177683/
belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, which encompasses liverworts, a group of bryophytes (non-vascular plants) closely related to mosses. These tiny plants play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

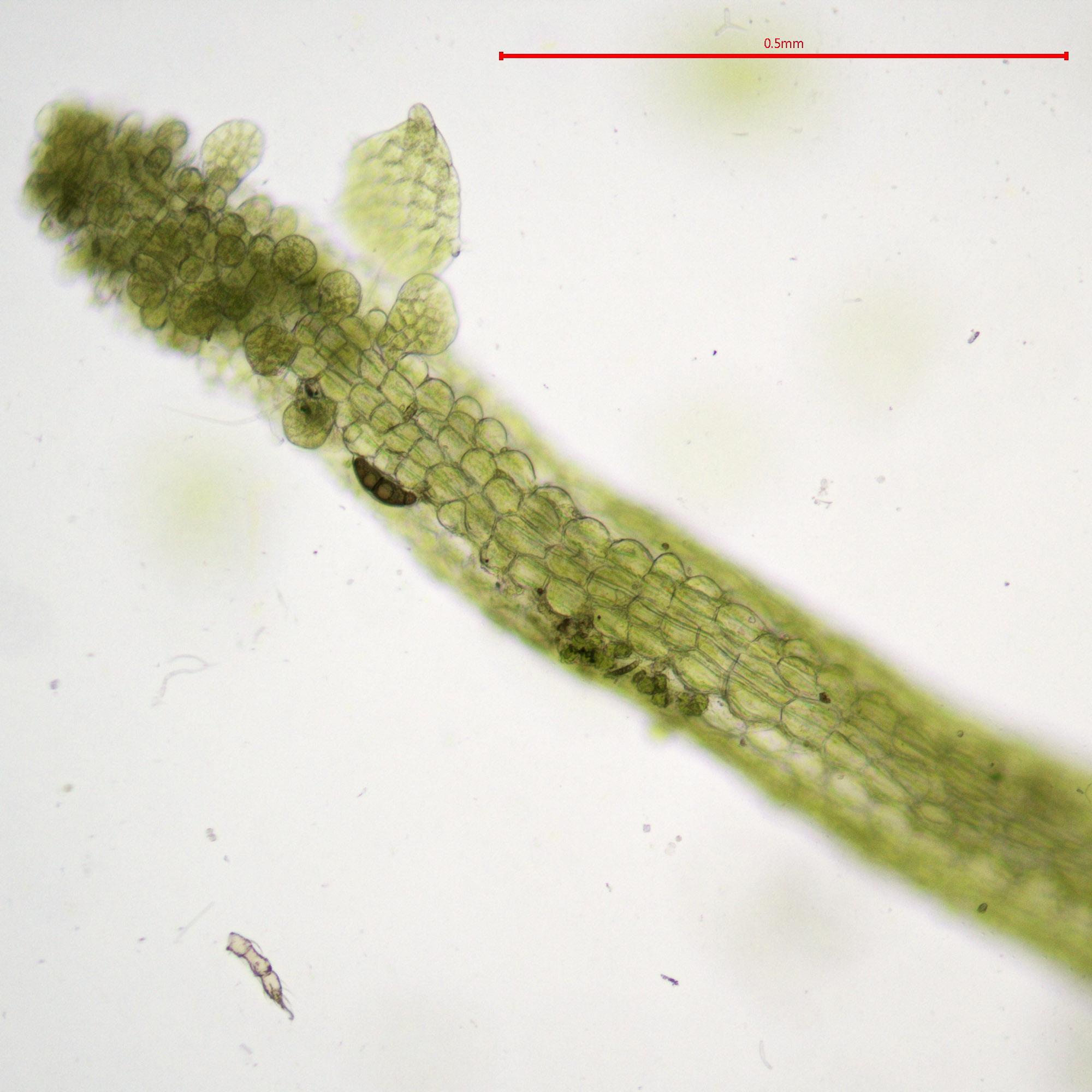
Metzgeria-furcata-(L.)-Dumort.-325612.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Metzgeria-furcata-(L.)-Dumort.-img325612.html
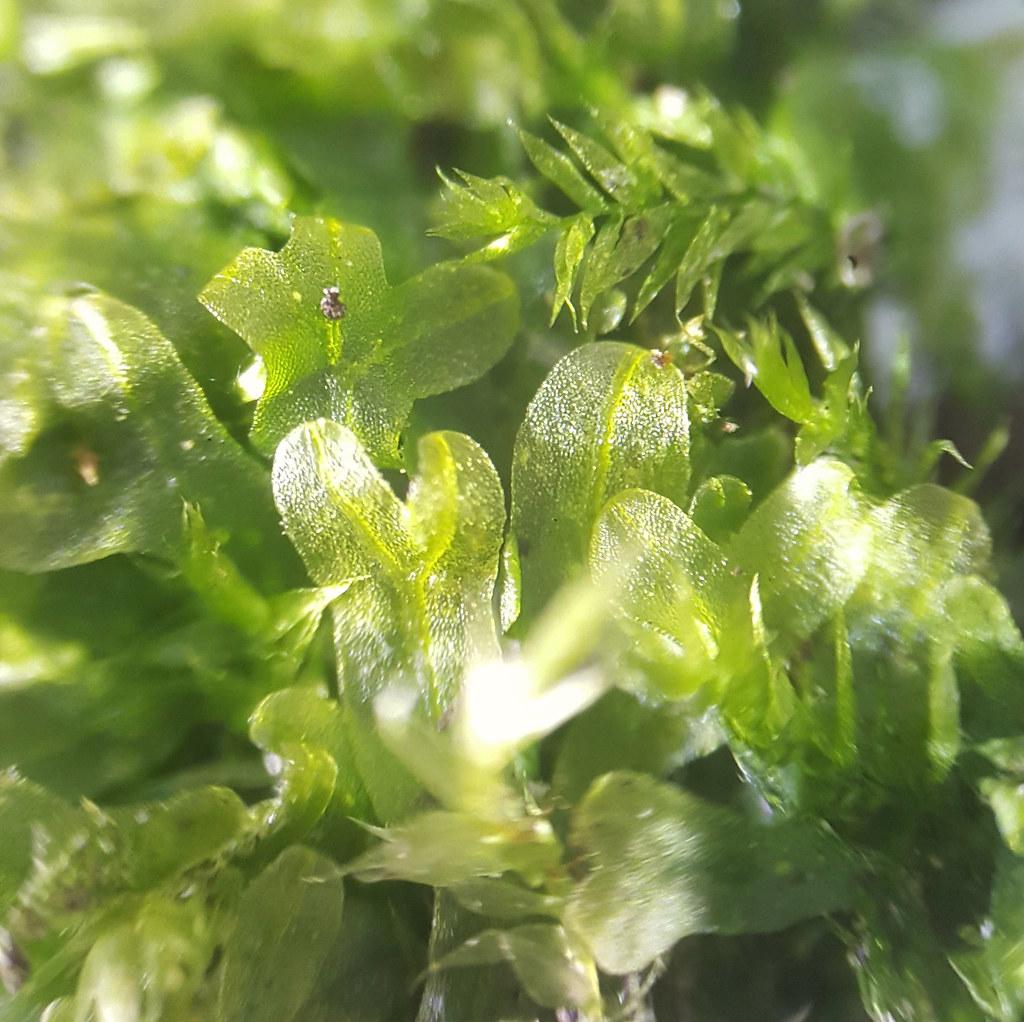
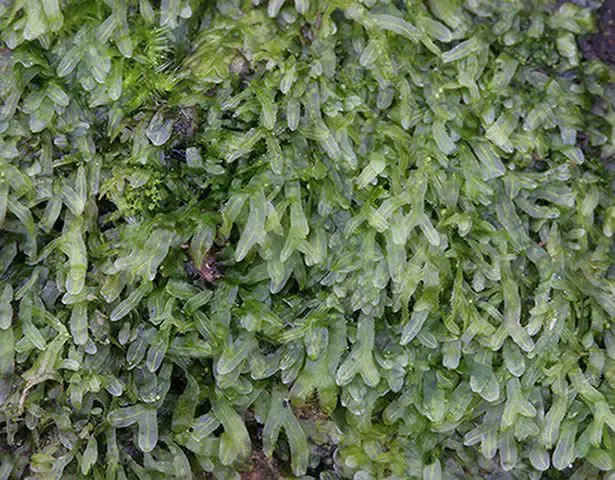
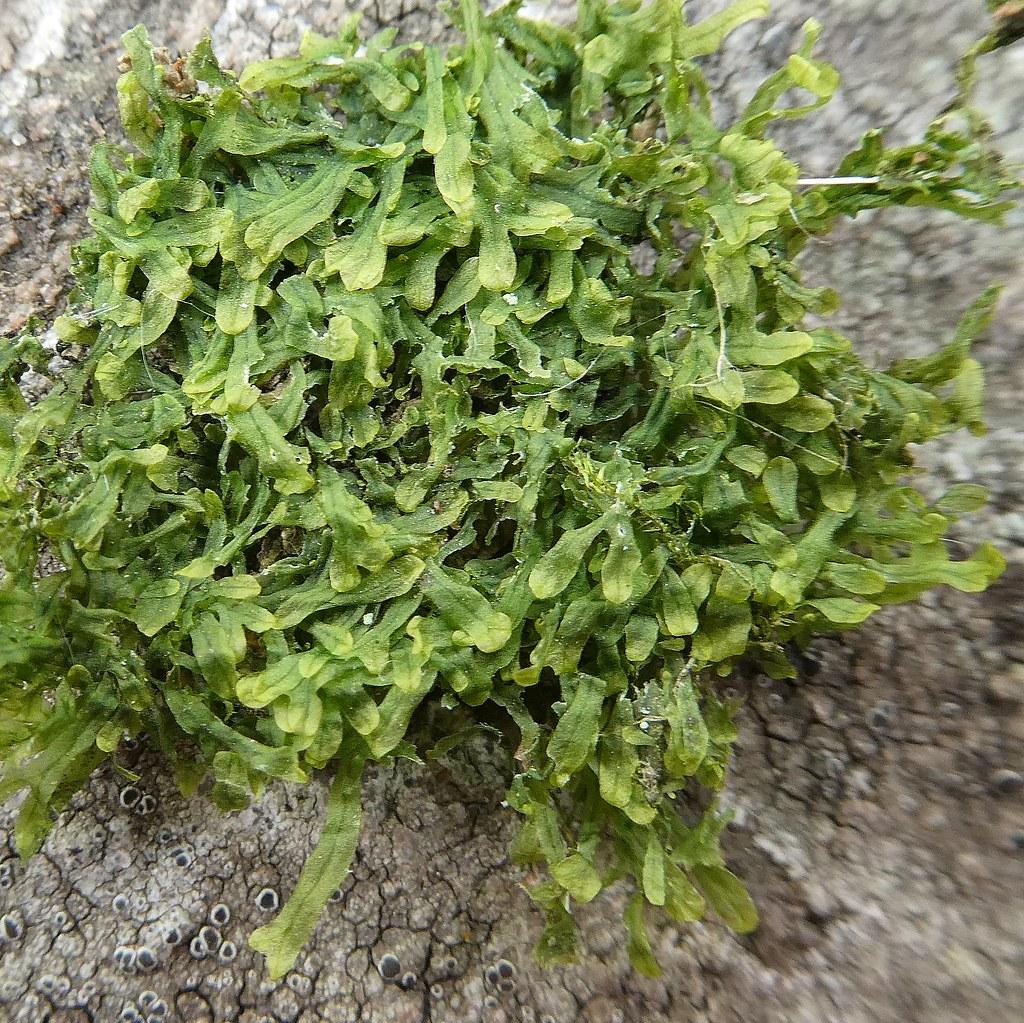
Metzgeria violacea is a thalloid liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form rather than the more familiar upright stems of true mosses. Its thalli are typically dark green to purplish-brown in color, with a distinctive violet tinge that gives the species its name. The thalli are irregularly branched and can grow up to 10 cm long, forming dense mats on the surfaces they colonize.
One of the most striking features of Metzgeria violacea is its gemma cups, which are small, cup-shaped structures that produce asexual reproductive units called gemmae. These gemmae are essentially miniature plantlets that can detach and develop into new individuals, allowing the moss to spread and colonize new areas efficiently.
Global Distribution and Habitat
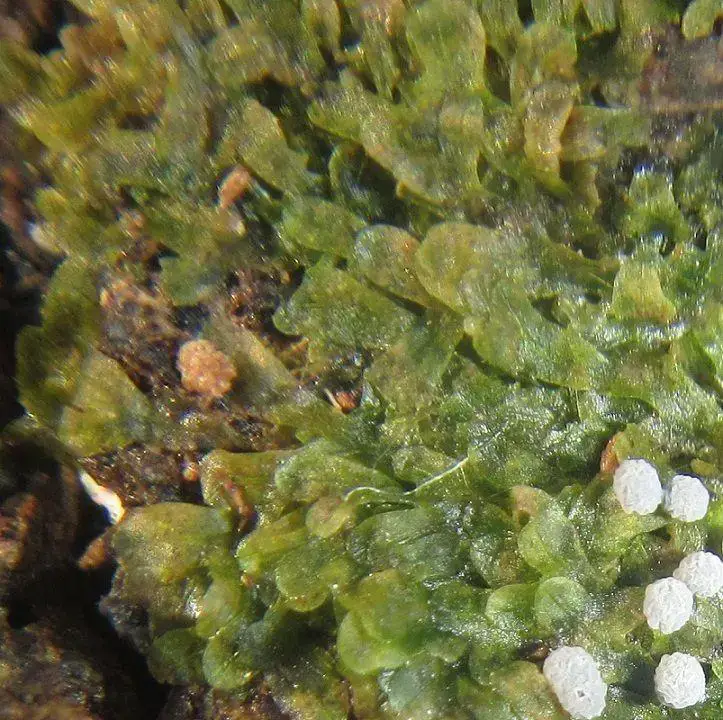
Metzgeria violacea is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on almost every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from temperate to tropical regions, and can be found growing on various substrates, including tree bark, rocks, and soil.

49837484571_b93c219cb9_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/49837484571/
This moss is particularly well-adapted to humid environments and is often found in moist, shaded areas such as forests, ravines, and stream banks. Its ability to colonize a variety of surfaces and its tolerance for a wide range of environmental conditions contribute to its widespread distribution.

62a9ea03d5d0bd5e0303022459b259a3.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/especie/metzgeria-furcata
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Metzgeria violacea plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps to stabilize and prepare the way for other plants to establish themselves. Its dense mats can retain moisture and create a microclimate suitable for other organisms, such as fungi and invertebrates.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Metzgeria violacea is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can enter a dormant state, curling up and becoming brittle. However, when moisture returns, it can quickly rehydrate and resume its normal growth and metabolic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Metzgeria violacea played a crucial role in the recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as logging or wildfires. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize bare surfaces and create a suitable environment for other plants made it a valuable ally in the process of ecological succession.
Technical Table

49858721431_2c72a66bbc_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/silybum/49858721431
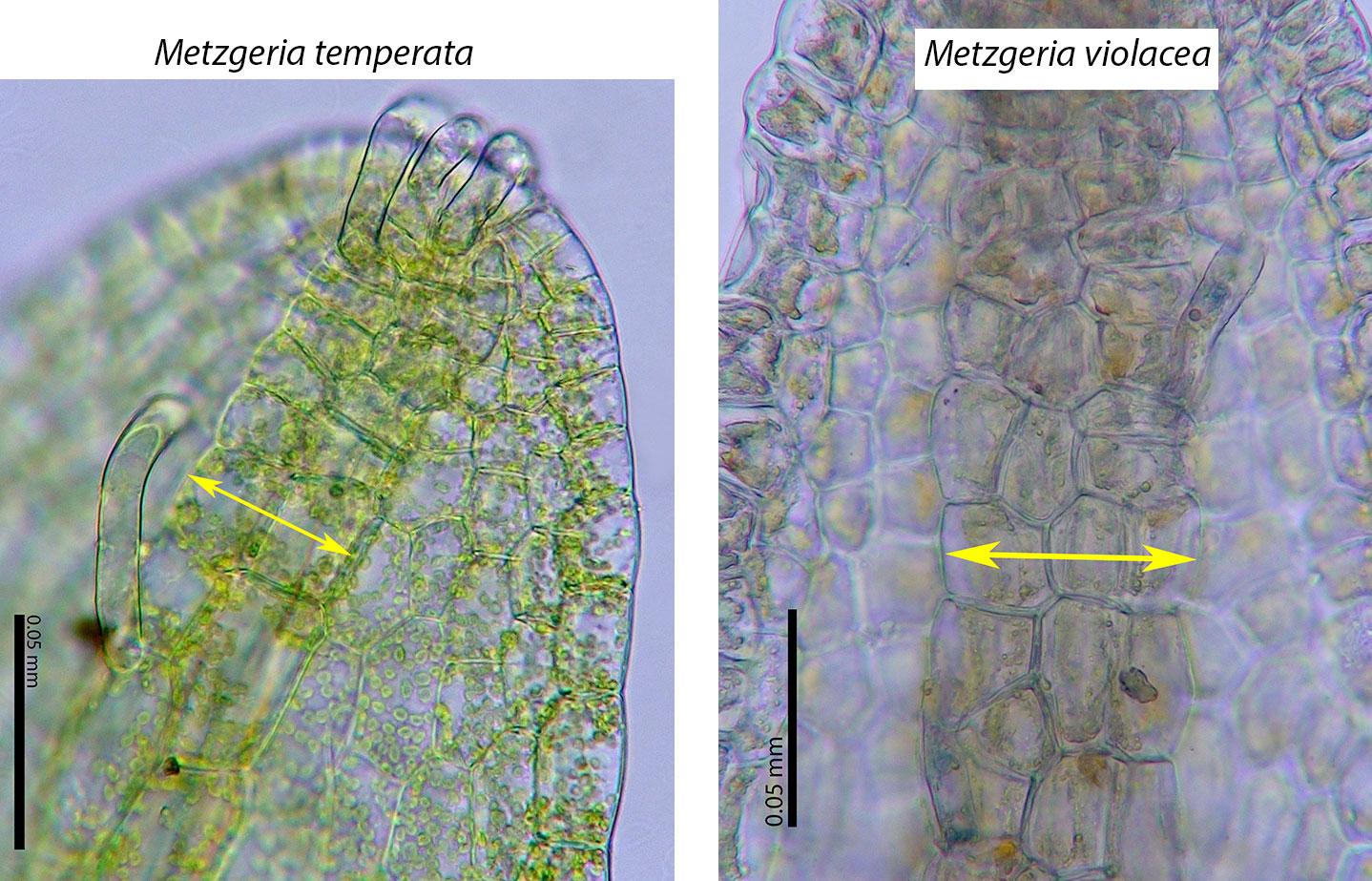
mettem_metvio_web1.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/metzgeriaviolacea.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Metzgeriales |
| Family | Metzgeriaceae |
| Genus | Metzgeria |
| Species | violacea |
| Growth Form | Thalloid liverwort |
| Color | Dark green to purplish-brown, with a violet tinge |
| Thallus Length | Up to 10 cm |
| Reproduction | Sexual (spores) and asexual (gemmae) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forests, ravines, stream banks) |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan (found on almost every continent except Antarctica) |
Conclusion
Metzgeria violacea is a remarkable moss that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its unique morphology, adaptations, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and scientists alike. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate world of bryophytes, this unassuming moss may hold the key to unlocking new insights into the resilience and diversity of life on our planet.
Ponder this: If such a tiny, unassuming plant can play such a vital role in its ecosystem, what other wonders might be hidden in the natural world, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?