
f6ed28b75c510d3fc7af0d235036e523bd82ba03.jpg from: https://photocontest.smithsonianmag.com/photocontest/detail/hall-of-moss-olympic-np/
Mniadelphus Müll.Hal.: The Marvelous Moss of the Daltoniaceae Family
Introduction
Today we’re diving into the fascinating world of
Morphology-of-androecium-A-Tipuana-tipu-monadelphous-androecium-unfolded-with_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphology-of-androecium-A-Tipuana-tipu-monadelphous-androecium-unfolded-with_fig4_337592507
Mniadelphus Müll.Hal., a captivating moss species belonging to the Daltoniaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant plays important ecological roles and boasts some remarkable adaptations. Join me as we explore the morphology, habitat, distribution and significance of marvelous Mniadelphus!
Background on Bryophytes
Before we get to Mniadelphus specifically, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. Unlike other land plants, they lack true roots, stems and leaves. Instead, they have root-like rhizoids, stem-like structures called seta, and leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses are found in diverse habitats worldwide, from arctic tundra to tropical rainforests. There are over 12,000 moss species, including our star Mniadelphus.
Morphology and Identification

monadelphous-diadelphous-polyadelphous-concise-biology-solutions-icse-class-9-638×375.png from: https://www.knowledgeboat.com/question/explain-the-terms-monadelphous-diadelphous-and-polyadelphous–114096118646283040
Mniadelphus mosses are small but eye-catching. Their phyllids are ovate to oblong-lanceolate in shape and have a strong midrib that extends to the apex. The seta is smooth and the capsules are inclined to pendulous. Under a microscope, you can see that Mniadelphus leaf cells are rounded-hexagonal and the marginal cells form a distinct border.

Monadelphous-contracts.jpg from: https://im-mining.com/2022/12/20/monadelphous-group-secures-work-with-bhp-in-western-australia-chile/
One of the most identifiable features is the double peristome. The peristome is the ring of tooth-like structures surrounding the mouth of the capsule. In Mniadelphus, there is an inner peristome with segments and an outer peristome with teeth. This double peristome is a key characteristic of the

Monadelphous-Trackem.jpg from: https://im-mining.com/2020/01/07/monadelphous-signs-trackem-construction-material-management/
Daltoniaceae family to which Mniadelphus belongs.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Mniadelphus has a wide distribution, found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. Species diversity is especially high in the neotropics of Central and South America.
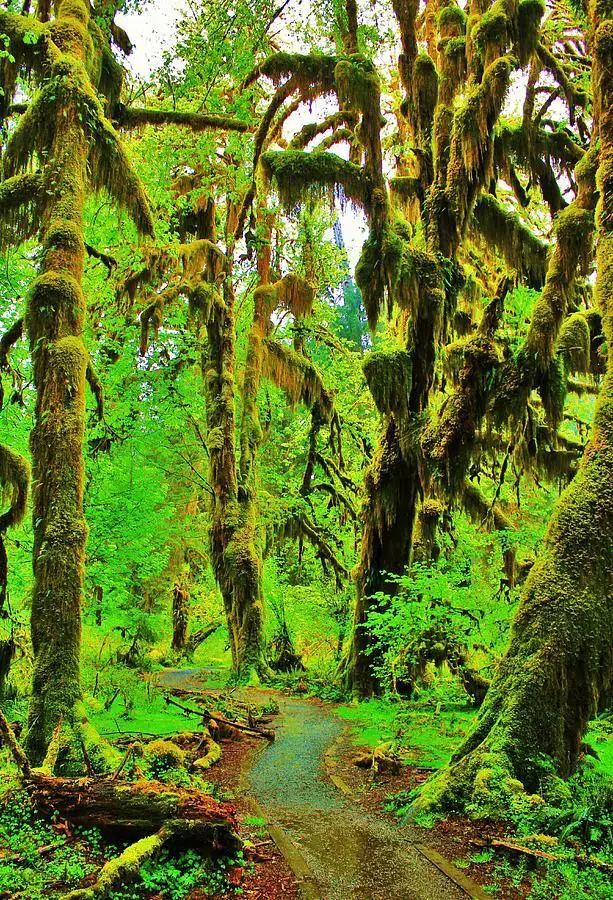
These mosses are most commonly found growing on tree trunks and branches

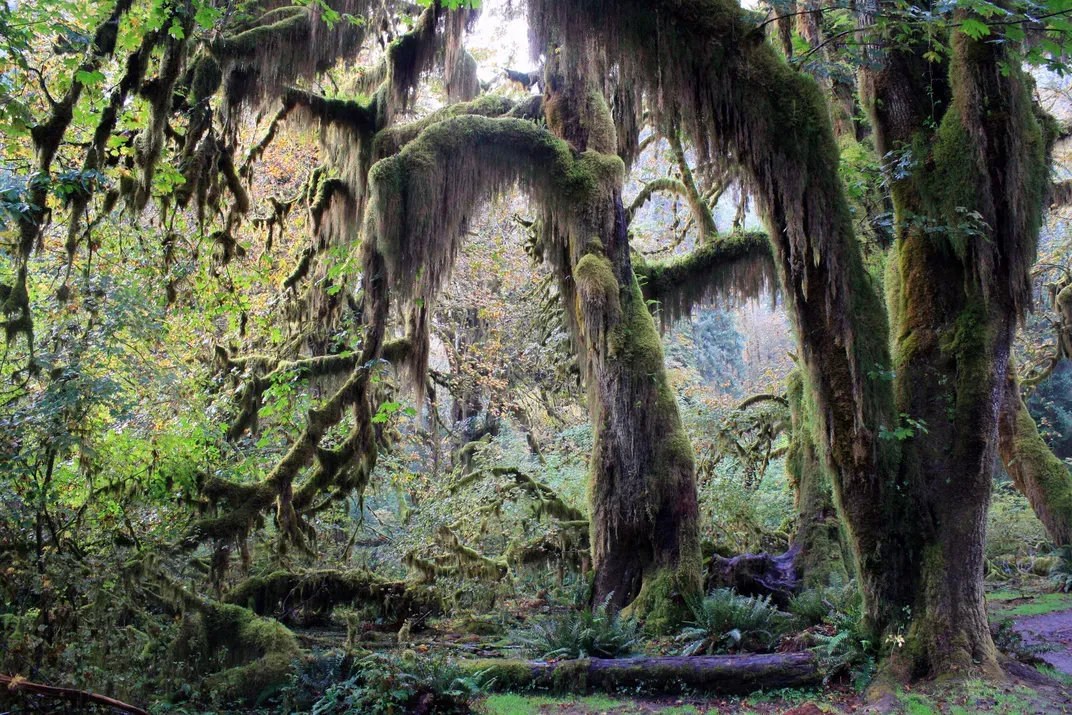
hall-of-moss-benjamin-yeager.jpg from: https://fineartamerica.com/featured/hall-of-moss-benjamin-yeager.html
in moist, shady forests. They are epiphytic, meaning they grow on other plants but are not parasitic. Some species also grow on rocks or soil banks. Mniadelphus prefers humid, low-light environments and is often found in cloud forests and along streams in rainforests.
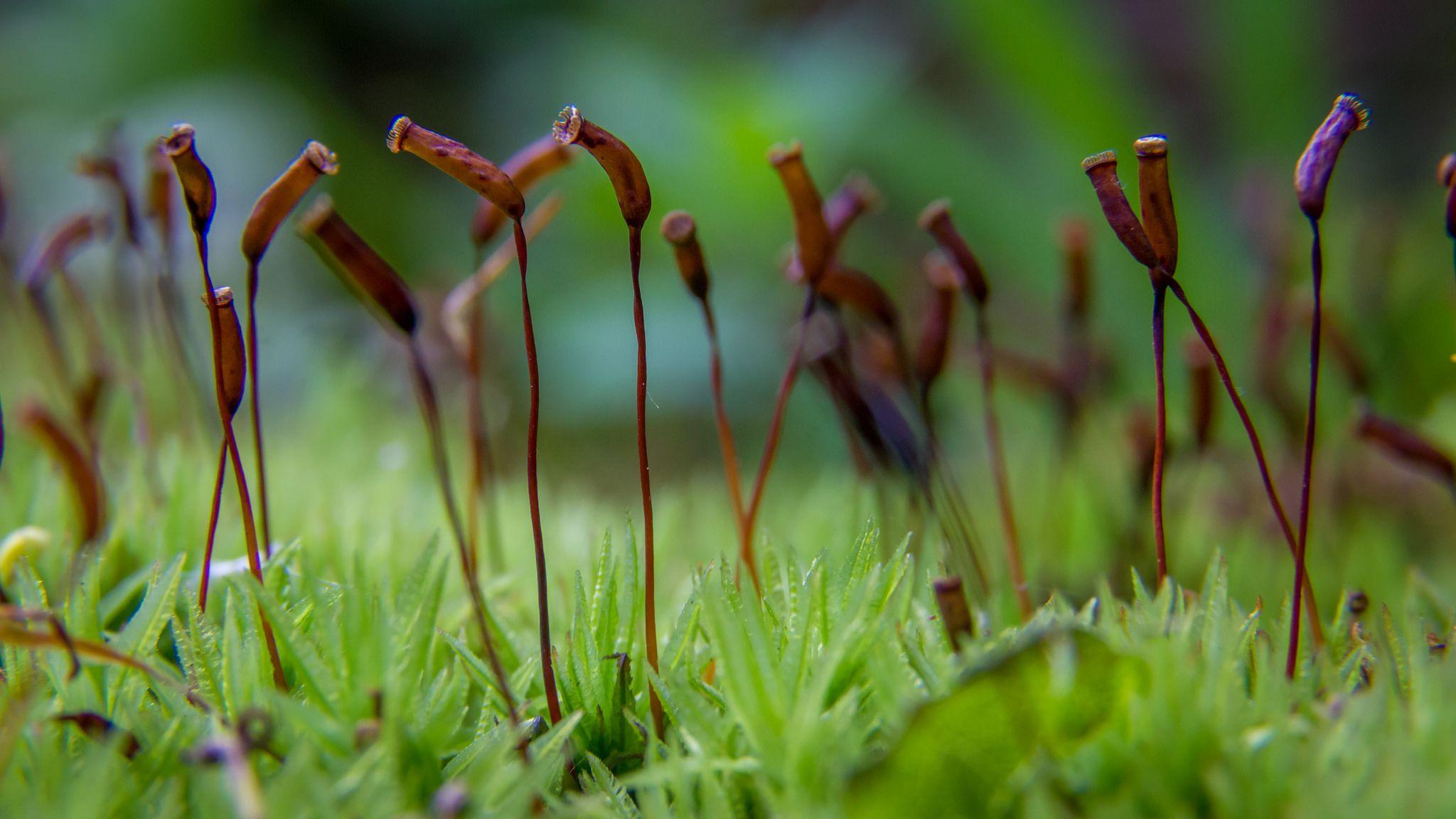

f6706d8a270099400740f77062b35c3f.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/332773859945309197/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Mniadelphus plays several important roles in its ecosystem:

7bb7078ce6d1cdc1dfc9a7dbae99f6f0.jpg from: https://eunis.eea.europa.eu/species/167751
Moisture retention: The dense mats formed by Mniadelphus help trap and retain moisture in the environment. This benefits the moss as well as other organisms in the habitat.
Nutrient cycling: As part of the detritus food chain, mosses like Mniadelphus help break down organic matter and release nutrients back into the ecosystem.
hall-moss-trail-olympic-national-park-moss-covered-big-leaf-maple-tree-hall-moss-trail-olympic-national-park-104348835.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/hall-moss-trail-olympic-national-park-moss-covered-big-leaf-maple-tree-hall-moss-trail-olympic-national-park-image104348835
Providing habitat: The mats and cushions of Mniadelphus provide microhabitats for numerous small invertebrates like mites, springtails, and tardigrades.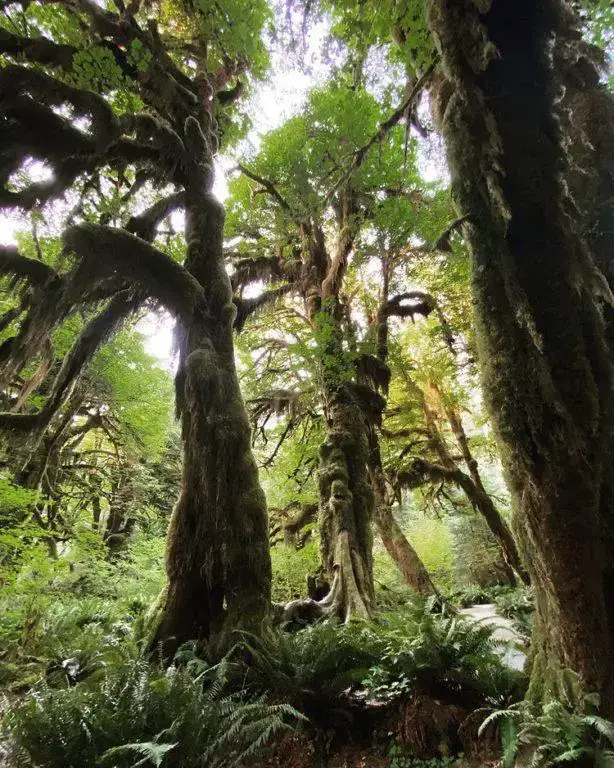
USA-Washington-Olympic-National-Park-Hoh-Rainforest-IG-planet.katie_-e1629907661481.jpg from: https://tracethetrail.com/usa/washington-olympic-national-park-hoh-rainforest-hall-of-moss/08/25/2021/
Erosion control: By colonizing bare soil and rock surfaces, Mniadelphus helps stabilize the substrate and prevent erosion.
Mniadelphus has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its habitat:
Poikilohydry: Like all mosses, Mniadelphus can tolerate desiccation. It can survive losing most of its moisture content and rehydrate when water is available again.
Leaf structure: The strong midrib and thick-walled leaf cells help the phyllids retain their structure and resist wilting.
Rhizoids: The rhizoids anchor the moss to its substrate and absorb water and nutrients.
Spore dispersal: The elevated capsules on seta help disperse the spores further in air currents.
Conclusion
Mniadelphus Müll.Hal. is a marvelous moss with a fascinating morphology, widespread distribution, and important ecological roles. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the epiphytes – you might just spot some mini Mniadelphus! These unassuming plants are vital components of their ecosystems.
I hope this post has piqued your curiosity about the world of mosses. What other cool bryophytes have you encountered? Let me know in the comments!