
8935933698_d5f8c4d84f_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/40132175@N06/8935933698/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Pohlia clavicaulis Moss

4847582608_e4a322f805_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/40132175@N06/4847582608/
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth. One particularly interesting species is Pohlia clavicaulis (Broth.) F.J.Herm., a small but mighty moss in the Mniaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the unique features and ecological importance of this fascinating bryophyte.

34388040582_2b33798f80_b.jpg from: https://www.flickriver.com/photos/annkelliott/34388040582/
Background on Mosses
Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. Unlike other land plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have rhizoids, a stem-like structure called a caulidium, and leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in diverse habitats worldwide.

219232.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4881
Morphology and Identification

pear-moss-pohlia-nutans-2H3J74A.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/pear-moss-pohlia-nutans-image449714282.html
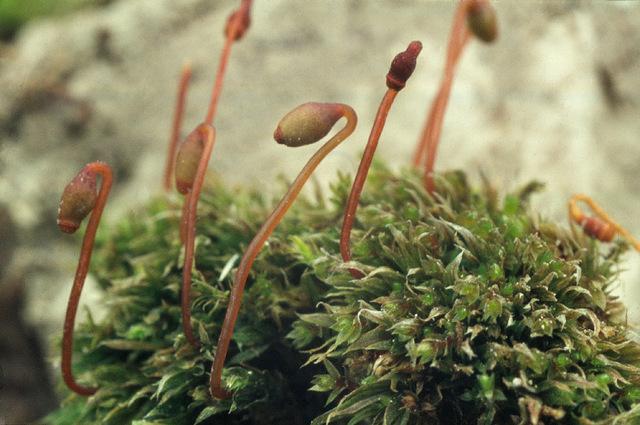
Pohlia clavicaulis is a small, tufted moss that forms dense mats. Its scientific name comes from the Latin words “clavi” meaning club-shaped and “caulis” meaning stem, referring to the distinctive shape of its caulidia. Key identifying features include:
- Phyllids (leaves) that are ovate-lanceolate and taper to a fine point
- A costa (midrib) that extends to the leaf tip
- Club-shaped, nodding capsules on long setae (stalks)
- Spores that are small and yellow

A-J-Propagules-of-Pohlia-proligera-Lindb-ex-Breidl-Lindb-ex-Arn-from-Zhu-Rui-liang.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-J-Propagules-of-Pohlia-proligera-Lindb-ex-Breidl-Lindb-ex-Arn-from-Zhu-Rui-liang_fig2_282380566
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide distribution, found in many regions around the world including:
- Europe
- Asia
- North America
- South America
- Australia
- New Zealand
P. clavicaulis grows on soil, rocks, logs, and tree bases in various forest types. It prefers moist, shaded sites but can tolerate some disturbance.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

Pohlia_melanodon,I_MWS46048.jpg from: https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20o?search=Pohlia&flags=glean:&mobile=close
Like other mosses, Pohlia clavicaulis plays important ecological roles:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms and small invertebrates
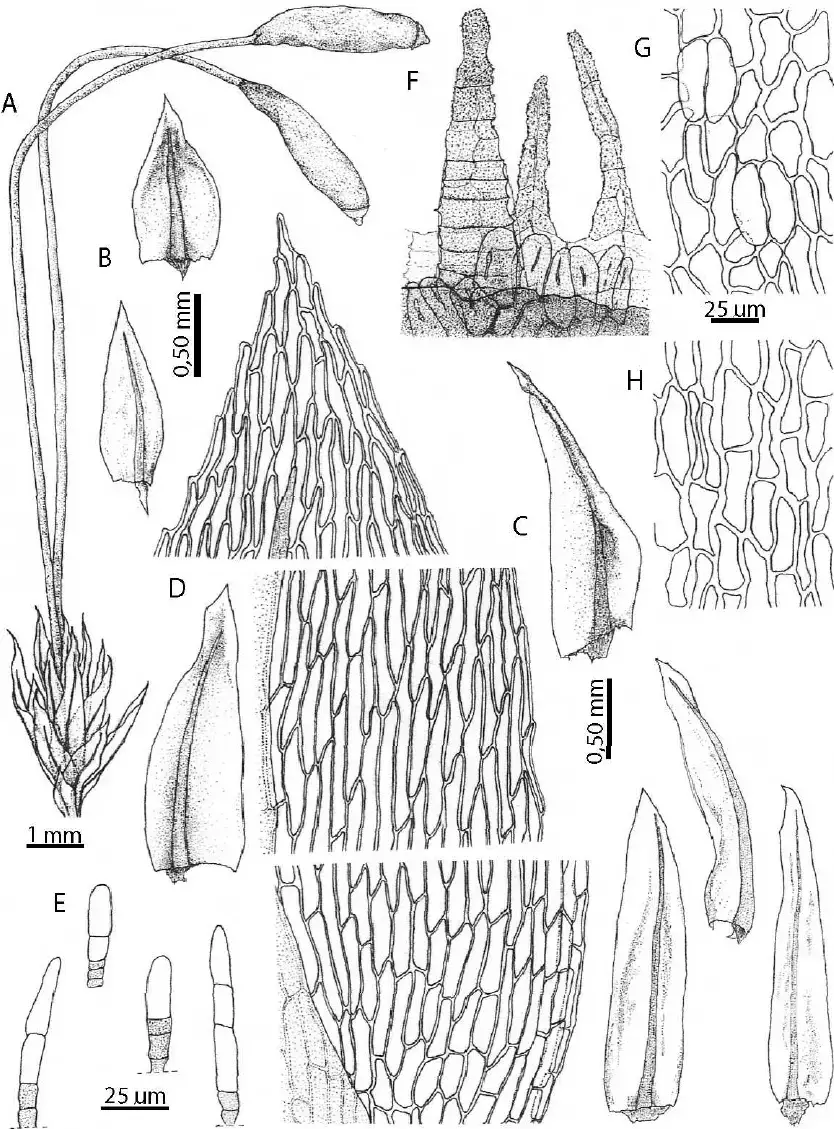
Pohlia-chilensis-A-Habit-B-Basal-leaves-C-Apical-leaves-D-Laminal-cells-apical.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pohlia-chilensis-A-Habit-B-Basal-leaves-C-Apical-leaves-D-Laminal-cells-apical_fig1_232665466

Propagules-variation-A-Pohlia-lutescens-from-Chen-SK-5145-PE-B-E-Pohlia_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Propagule-variation-A-F-Pohlia-camptotrachela-from-Chen-JF-63001a-IFP-G-K-Pohlia_fig4_330945417
- Pioneers disturbed sites and aids succession
It has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:

Pohlia-drummondii-MUB-18549-a-d-bulbils-P-filum-MUB-21458-e-g-bulbils-P_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pohlia-drummondii-MUB-18549-a-d-bulbils-P-filum-MUB-21458-e-g-bulbils-P_fig1_28162547
- Rhizoids anchor it to substrates and absorb water and nutrients
- Phyllids have a high surface area to efficiently capture light for photosynthesis
- Tolerates desiccation by entering dormancy and reviving when moisture returns
Conclusion
Pohlia clavicaulis may be small, but this mighty moss is an important component of ecosystems worldwide. Its unique morphology, wide distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating species to study and appreciate. Next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you may just spot some Pohlia making its home on a log or forest floor! What other mighty mosses have you encountered?