
Porella-obtusata-growing-in-yellowish-green-glossy-patches-with-a-characteristic.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Porella-obtusata-growing-in-yellowish-green-glossy-patches-with-a-characteristic_fig1_284733226
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Porella elegantula (Mont.) E.A.Hodgs. moss stands out as a true marvel. Belonging to the Porellaceae family, this unassuming yet extraordinary plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this Marchantiophyta member and unravel its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Porella elegantula, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.

lch-464a4.jpg from: https://www.dorsetnature.co.uk/pages-lichen/lch-464.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
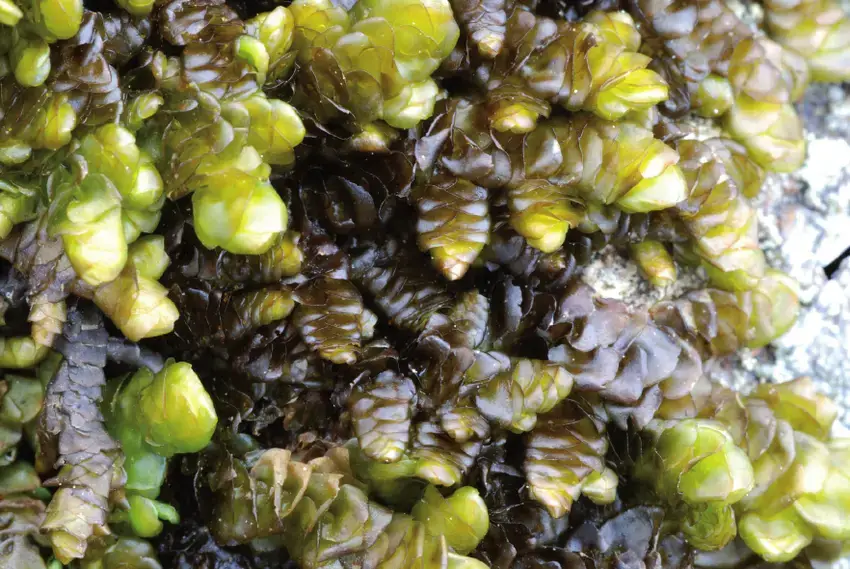
Porella elegantula is a pleurocarpous moss
A17674.jpg from: https://fungi.myspecies.info/all-fungi/melanohalea-elegantula
, meaning its branches grow horizontally from the main stem. Its delicate, feathery appearance is a sight to behold, with overlapping leaves arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. The leaves themselves are ovate to lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running through their length. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a hexagonal pattern, adding to the intricate beauty of this moss.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This Jungermanniopsida member is widely distributed across various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on rocks, tree trunks, and decaying logs in forests and woodlands. Porella elegantula is particularly fond of areas with high humidity and moderate temperatures, making it a common sight in temperate and subtropical regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many bryophytes,
medium. from: https://inaturalist.nz/taxa/405195-Porella-elegantula
Porella elegantula plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation by breaking down organic matter and retaining moisture, creating a suitable environment for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance for these tiny creatures.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Porella elegantula is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, researchers discovered that Porella elegantula played a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the forest ecosystem. The moss acted as a buffer, regulating moisture levels and providing a suitable environment for other plant species to flourish.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Porellales |
| Family | Porellaceae |
| Genus | Porella |
| Species | Porella elegantula (Mont.) E.A.Hodgs. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Midrib | Present |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
Conclusion
The Porella elegantula (Mont.) E.A.Hodgs. moss is a true testament to the wonders of nature. Its delicate beauty, ecological significance, and remarkable adaptations make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these invaluable members of our ecosystems for generations to come?