Discover the Enchanting World of Tetralophozia setiformis Moss: A Guide for Enthusiasts
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
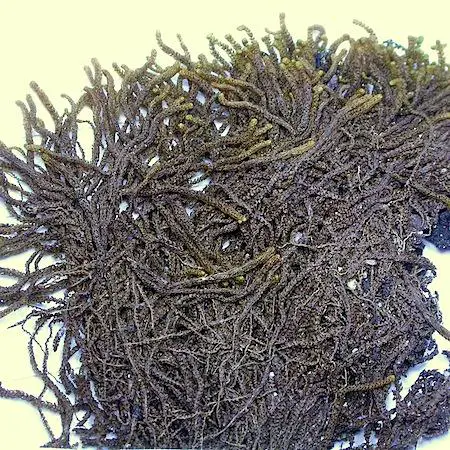

tetralophozia_setiformis1.jpg from: https://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/sammalet/louhusammal.html
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm of Tetralophozia setiformis (Ehrh.) Schljakov, a remarkable moss species belonging to the Anastrophyllaceae family. Often referred to simply as Tetralophozia, this diminutive plant holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be uncovered by enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
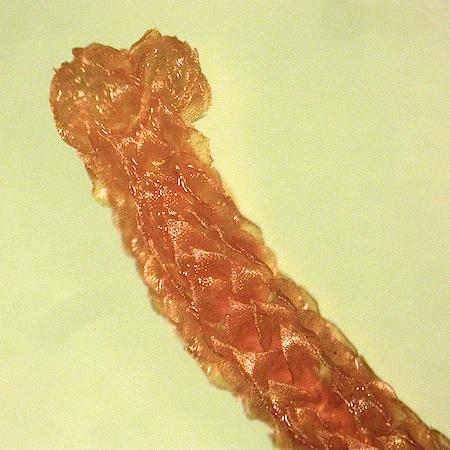
tetralophozia_setiformis2.jpg from: https://luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/louhusammal.html
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Tetralophozia setiformis
XvfoqrVSPTRe-RXcglnEw9OVW2WhocsXkAT7FUeD11T_fYlvypSOu0xHdYNiqPTG7sopMSBmAhwqNFo2llBFviKeLTlJNrehvzHmq-aG0SZqmB8qlZhQk797kmJXe7idT1ov6ym3 from: https://edge-ecology.com/2022/04/08/hunting-for-bryophytes-in-the-mountains/
, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of the plant kingdom. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, also known as liverworts, and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses leafy liverworts. Despite their small stature, these organisms play a crucial role in various ecosystems, often serving as pioneers in colonizing new environments.
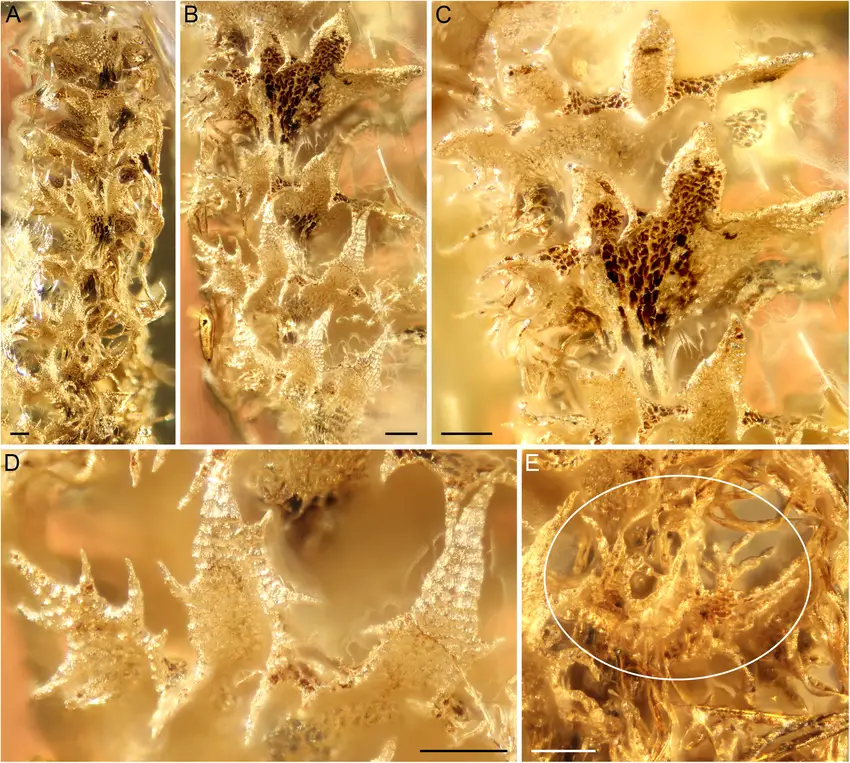
Holotype-of-Tetralophozia-groehnii-sp-nov-GPIH-4575-from-Baltic-amber-The-fossil-was.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Holotype-of-Tetralophozia-groehnii-sp-nov-GPIH-4575-from-Baltic-amber-The-fossil-was_fig3_283496446
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Tetralophozia setiformis is a delicate and intricate moss species that demands a keen eye for observation. Its slender stems, typically reaching lengths of 1-3 centimeters, are adorned with overlapping leaves arranged in a spiral pattern. These leaves are deeply divided into four lobes, giving the plant a distinctive, feathery appearance.
One of the most remarkable features of Tetralophozia setiformis is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, it produces tiny, inconspicuous sporophytes that release spores, enabling the moss to disperse and colonize new areas. Asexually, it can propagate through fragmentation or the formation of specialized structures called gemmae.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Tetralophozia setiformis is a widely distributed species, found across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist, shaded rock crevices

29301455206_596abb9f00_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/silybum/29301455206
and decaying logs

Thelephora-terrestris-Ehrh.-1793-78594.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/hongos/Thelephora-terrestris-Ehrh.-1793-img78594.html
to acidic soils in coniferous forests.
This moss’s ability to adapt to different environments is a testament to its resilience and versatility. It often forms dense mats or cushions, creating a microhabitat for other organisms and contributing to the overall biodiversity of its surroundings.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Tetralophozia setiformis plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture retention, creating a favorable environment for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Tetralophozia setiformis is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, it can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows the moss to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Study: Tetralophozia setiformis in Boreal Forests
In the vast boreal forests of the Northern Hemisphere, Tetralophozia setiformis plays a crucial role in the ecosystem’s dynamics. These forests, characterized by their cool, moist conditions, provide an ideal habitat for this moss species to flourish.
Tetralophozia setiformis often forms dense mats on decaying logs and stumps, contributing to the decomposition process and nutrient cycling. Its presence also creates microhabitats for various invertebrates, such as springtails and mites, which play essential roles in the forest’s food web.
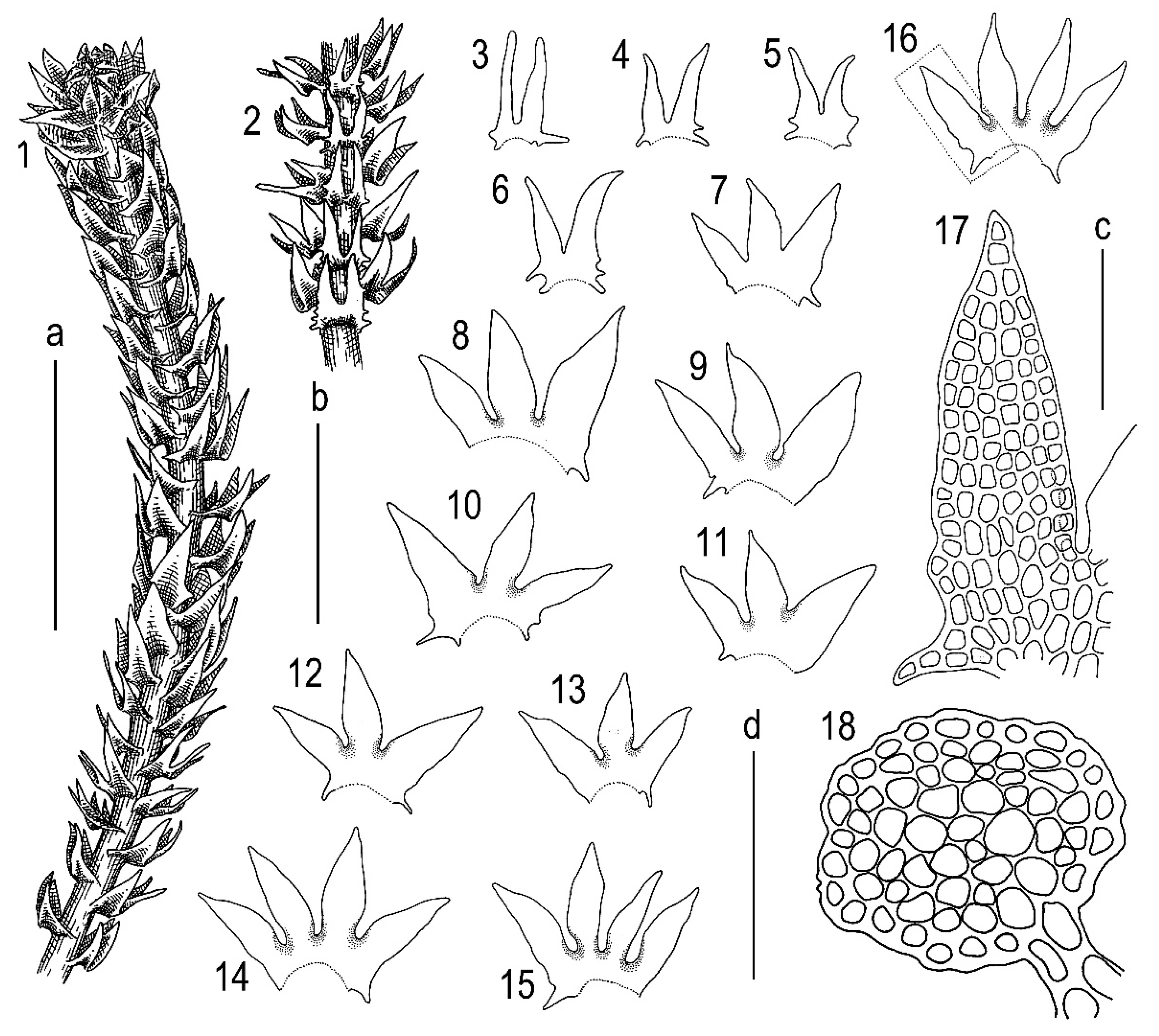
plants-11-03121-g003.png from: https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/11/22/3121/htm
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae |
| Scientific Name | Tetralophozia setiformis (Ehrh.) Schljakov
 Thyrostroma-celtidis-MFLU-16-1800-holotype-a-b-Sporodochia-on-host-surface-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Thyrostroma-celtidis-MFLU-16-1800-holotype-a-b-Sporodochia-on-host-surface-c_fig5_336916466 |
| Common Name | Tetralophozia |
| Growth Form | Dense mats or cushions |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral, deeply divided into four lobes |
| Reproduction | Sexual (sporophytes) and asexual (fragmentation, gemmae) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded rock crevices, decaying logs, acidic soils in coniferous forests |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
Tetralophozia setiformis (Ehrh.) Schljakov

2890287889.jpg from: https://www.orchideen-lehradt.de/shop/Tillandsia-setiformis-p436852530
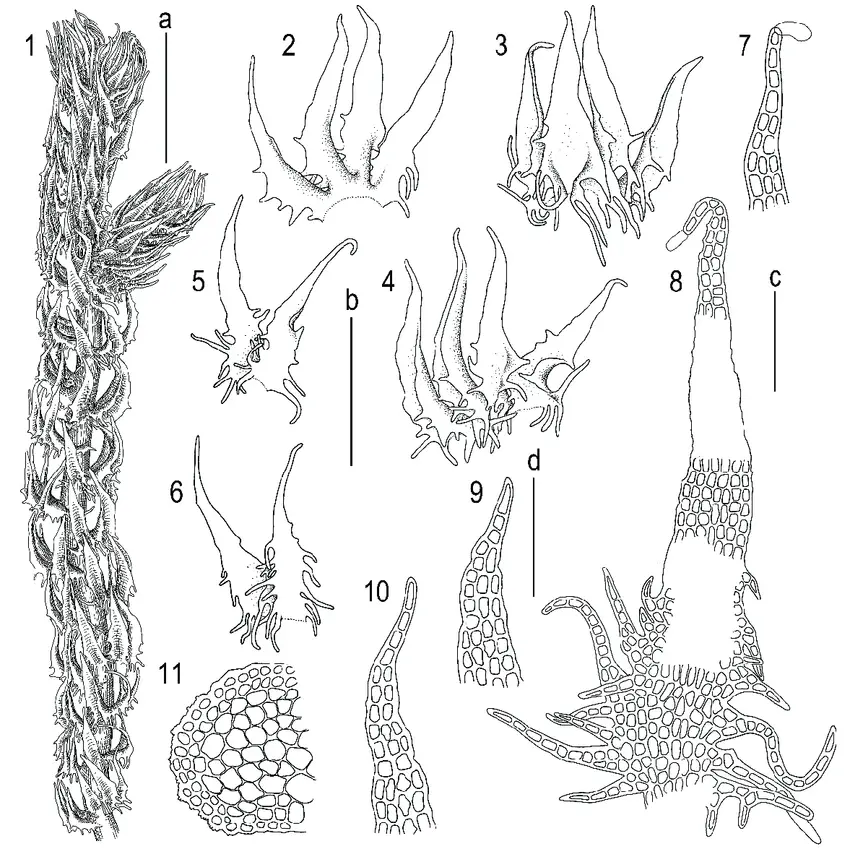
Tetralophozia-filiformis-Steph-Urmi-1-plant-habit-ventral-view-2-4-leaves.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Tetralophozia-filiformis-Steph-Urmi-1-plant-habit-ventral-view-2-4-leaves_fig4_365436760
, a remarkable moss species, may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its intricate morphology and diverse reproductive strategies to its vital ecological roles and adaptations, this moss serves as a testament to the wonders that can be found in the most unassuming of places.
As we bid farewell to this captivating journey, a thought-provoking question lingers: In a world where we often overlook the smallest of beings, what other marvels might we be missing, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?
