382147.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6513?lg=en
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the
211663.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6513
Scapania aequiloba (Schwägr.) Dumort. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Scapaniaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Scapania aequiloba belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. These bryophytes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, serving as indicators of environmental health and contributing to the intricate web of life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Scapania aequiloba is a thallose liverwort, characterized by its distinctive flattened, ribbon-like appearance. Its gametophyte stage consists of a prostrate, irregularly branched thallus, ranging in color from deep green to reddish-brown. The thallus is typically 1-3 cm long and 2-4 mm wide, with a distinct midrib running along its length.
One of the most remarkable features of this moss is its gemma cups, which are small, cup-shaped structures found on the upper surface of the thallus. These cups produce numerous gemmae, tiny, disc-shaped propagules that aid in asexual reproduction. The presence of these gemma cups is a key identifying characteristic of Scapania aequiloba.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Scapania aequiloba is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in temperate and boreal regions. It can be found in various habitats, including moist, shaded areas such as coniferous and deciduous forests, stream banks, and rocky outcrops. This moss prefers acidic, well-drained soils and often grows in association with other bryophytes, forming intricate carpets on the forest floor.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Scapania aequiloba plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance for these tiny creatures.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Scapania aequiloba is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up and appearing lifeless. However, upon rehydration, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a unique association between Scapania aequiloba and certain species of fungi. This symbiotic relationship, known as mycorrhizal association, enhances the moss’s ability to absorb nutrients from the soil, highlighting the intricate connections within ecosystems.
Technical Table
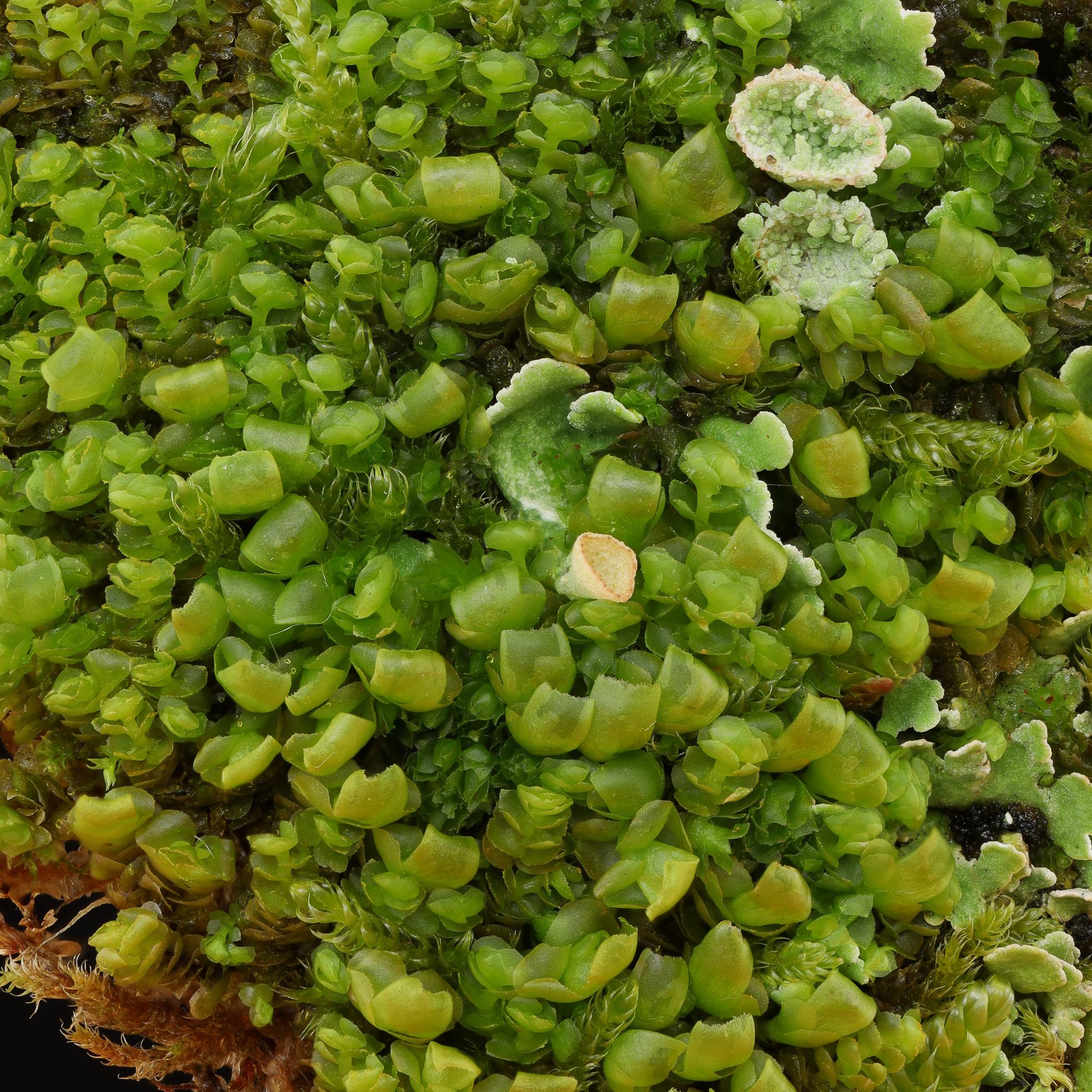

2020-10-09-12-05-11.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/scapania-compacta/
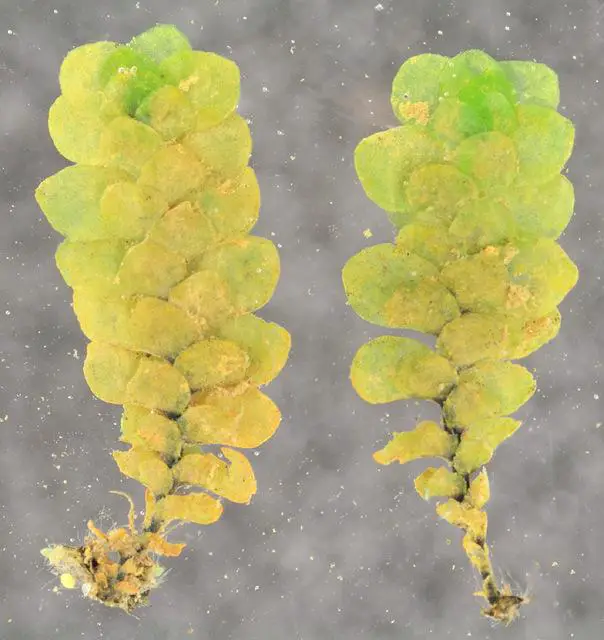

Scapania_undulata,I_MWS76069.jpg from: https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Scapania&flags=col2:&res=640
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Scapaniaceae |
| Genus | Scapania |
| Species | aequiloba |
| Common Name | Scapania moss |
| Gametophyte | Thallose liverwort |
| Thallus | Flattened, ribbon-like, 1-3 cm long, 2-4 mm wide |
| Color | Deep green to reddish-brown |
| Gemma Cups | Present, for asexual reproduction |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, coniferous and deciduous forests, stream banks, rocky outcrops |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere, temperate and boreal regions |
| Ecological Role | Soil formation, stabilization, microhabitat for invertebrates |
| Adaptation | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy during drought |
Conclusion
The Scapania aequiloba (Schwägr.) Dumort. moss, a member of the Scapaniaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the intricate tapestry that surrounds us, inviting us to delve deeper into the mysteries of life. Perhaps the next time you venture into a shaded forest, you’ll pause and appreciate the resilience and beauty of this remarkable bryophyte.