
Frullania-calcarifera-Steph-from-the-Crimean-Peninsula-5VI1964-Partyka-sn-1.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Frullania-calcarifera-Steph-from-the-Crimean-Peninsula-5VI1964-Partyka-sn-1_fig1_283100707
Exploring the Fascinating World of Frullania tenera Moss
Frullania tenera Lindb. ex Steph., commonly known as

0e2befe94abdd0e13049588f00645a62.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/frullania-image-details-771508–291045194657579822/
Frullania moss, is a captivating species belonging to the Frullaniaceae family. This tiny but mighty moss has captured the attention of enthusiasts and researchers alike due to its unique characteristics and ecological significance. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Frullania tenera

2021-02-25-11-50-47.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/frullania-tamarisci/
and uncover its secrets.
Background
Frullania tenera is a member of the Marchantiophyta division and Jungermanniopsida class of mosses. It was first described by Sextus Otto Lindberg and Franz Stephani

2020-11-22-13-00-24.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/frullania-teneriffae/
in the late 19th century. Since then, it has been studied for its distinctive morphology and wide global distribution.
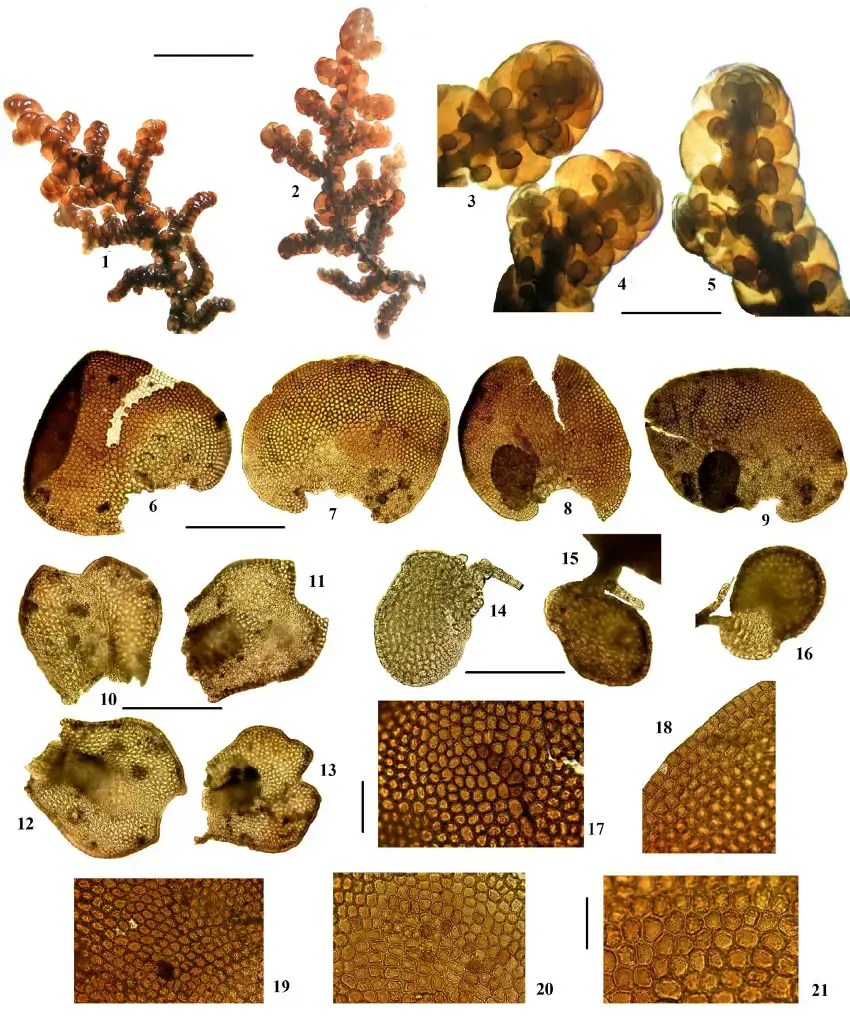
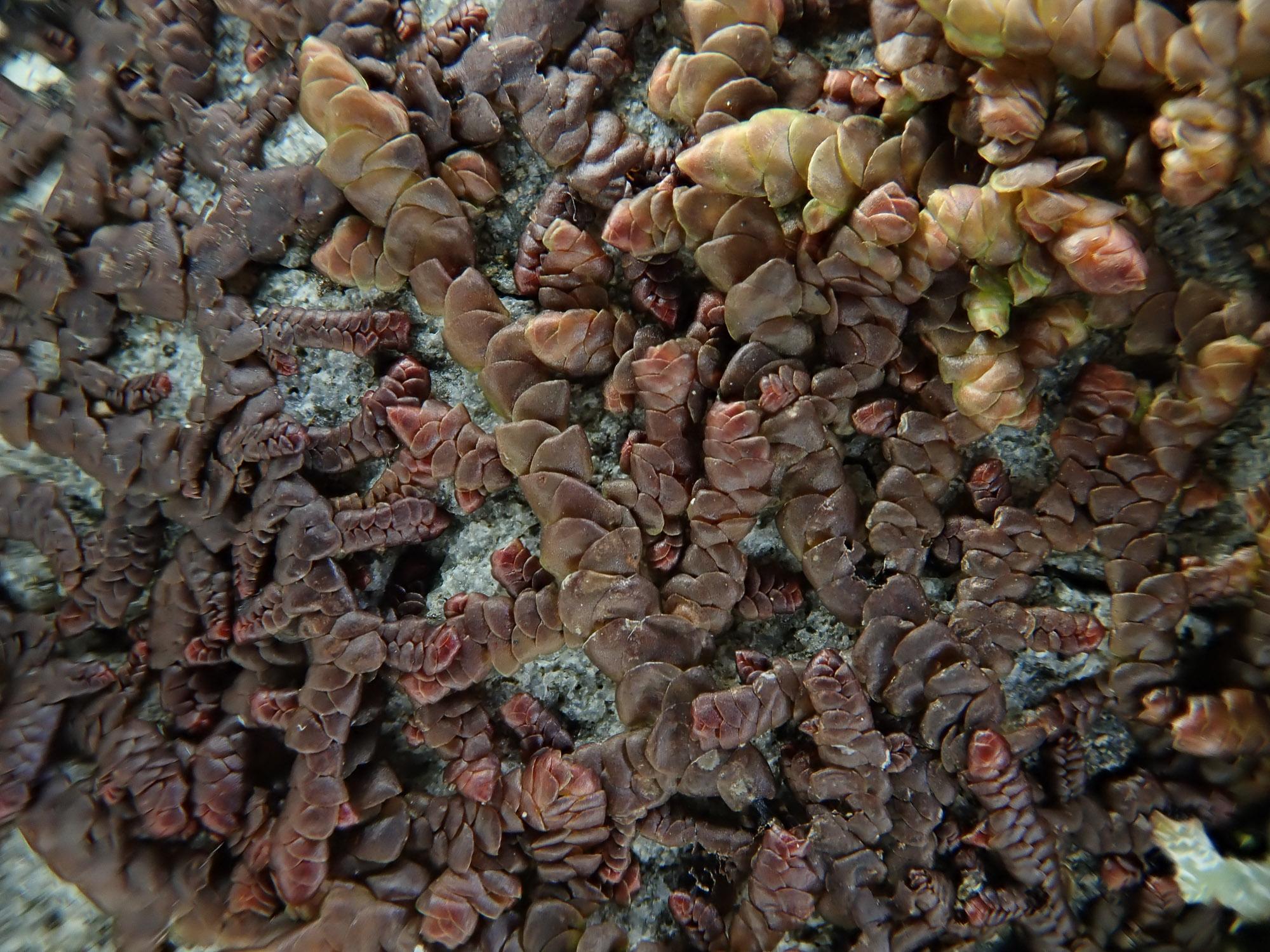
Morphology and Identification
One of the most striking features of Frullania tenera is its small size. The shoots typically measure between 0.5 to 2 cm
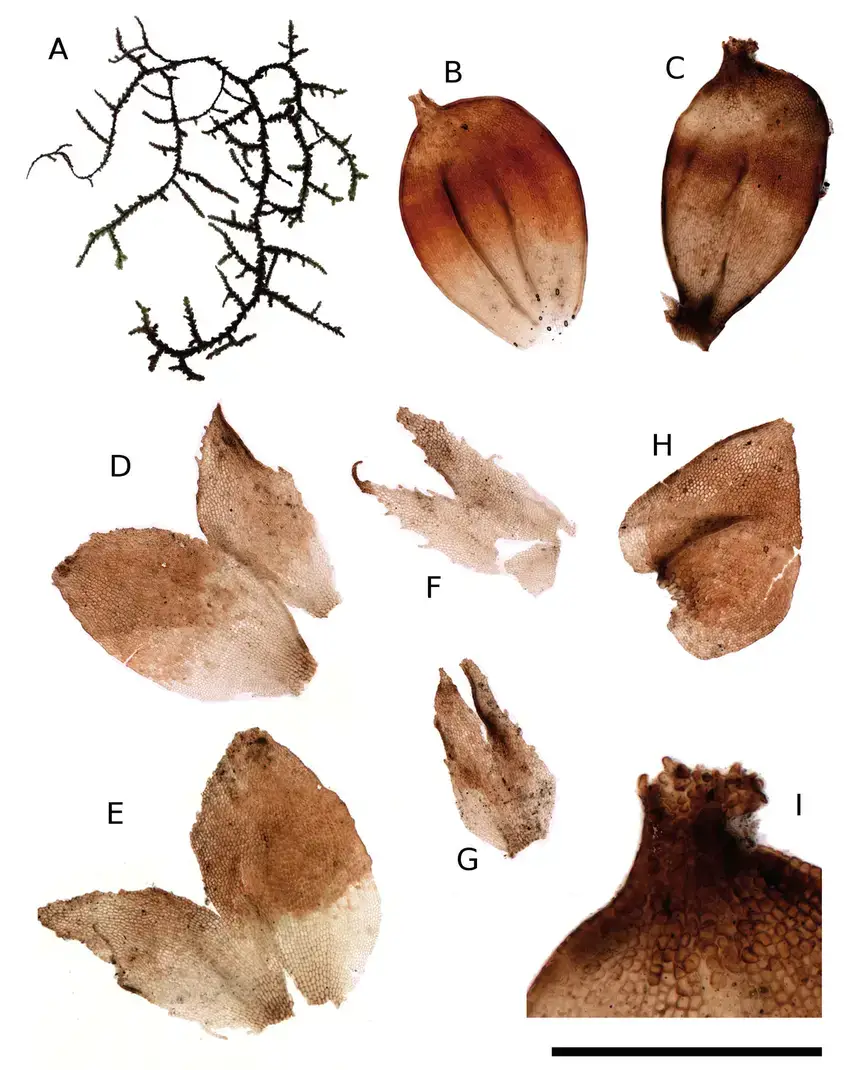
Frullania-weberbaueri-Steph-A-Habit-wet-dorsal-view-complete-plant-B-Perianth.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Frullania-weberbaueri-Steph-A-Habit-wet-dorsal-view-complete-plant-B-Perianth_fig1_305488292
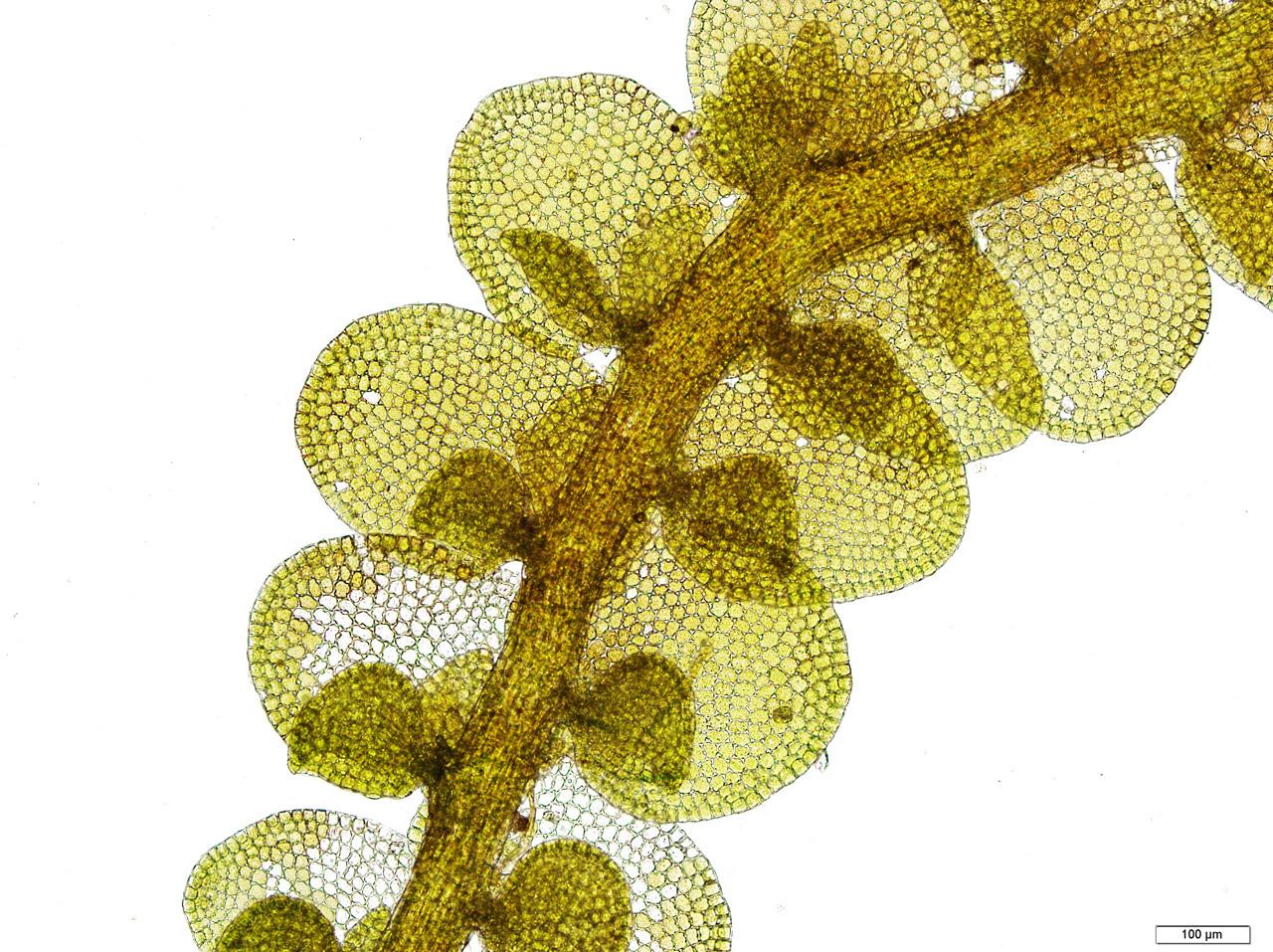
in length and are densely branched. The leaves are arranged in two rows and are deeply bilobed, with the upper lobe being larger than the lower one. The underleaves are also bilobed and are usually smaller than the leaves.
Identifying Frullania tenera requires careful observation of its microscopic features. The leaf cells are small and have thick walls, while the oil bodies are few and large. The perianths, which enclose the female reproductive structures, are obovoid and have a distinct beak.
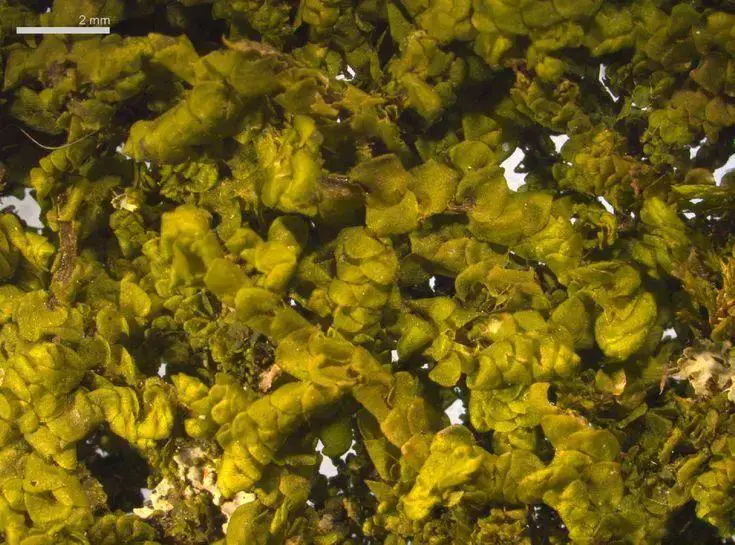
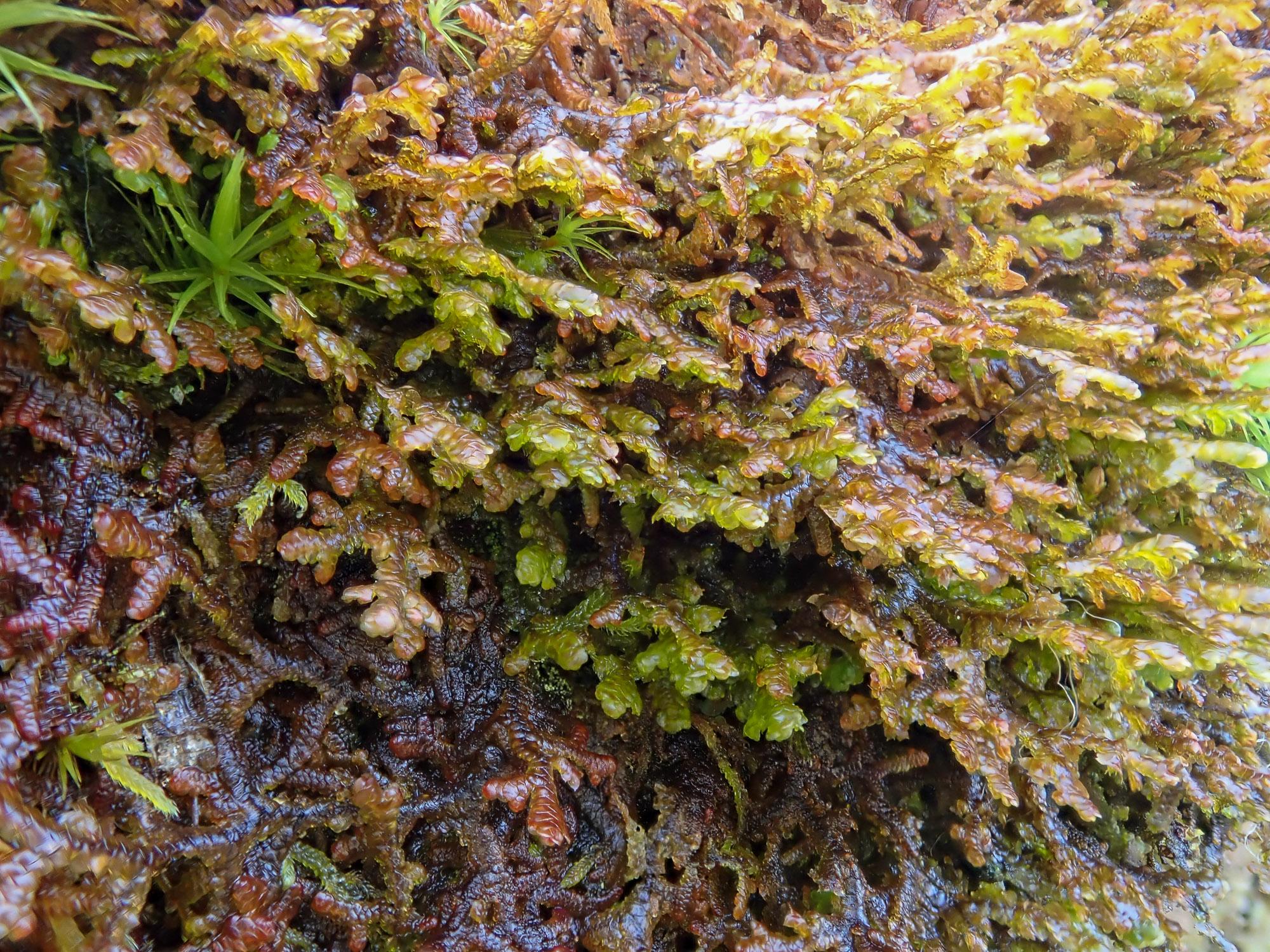
Global Distribution and Habitat
Frullania tenera

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/509502
has a wide global distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including:
- Temperate forests
- Subtropical regions
- Montane areas
- Coastal environments
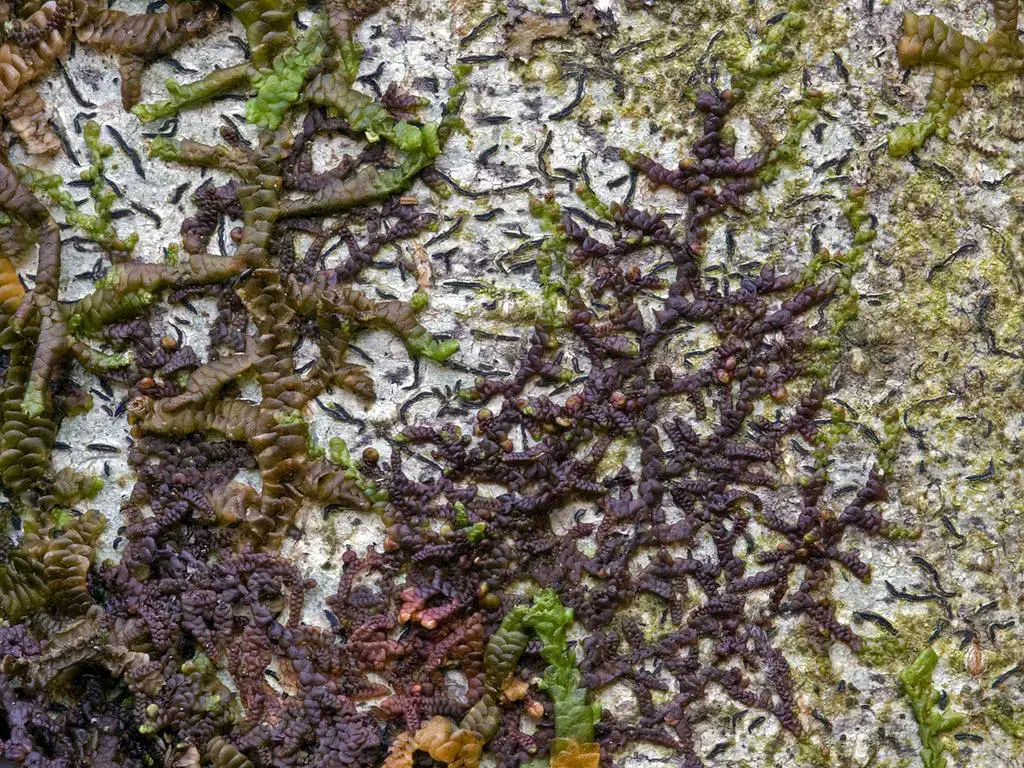
This adaptable moss can grow on various substrates, such as tree bark, rocks, and even man-made structures like walls and fences. Its ability to tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions has contributed to its success and widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Frullania tenera plays significant ecological roles. It contributes to:
- Nutrient cycling
- Water retention
- Providing shelter for microorganisms
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Frullania tenera is its ability to survive periods of drought. When water is scarce, the moss can enter a dormant state, curling its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly rehydrates and resumes growth.

f_riparia.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/frullania_riparia.html

49815176657_a7179daf3a_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/49815176657/
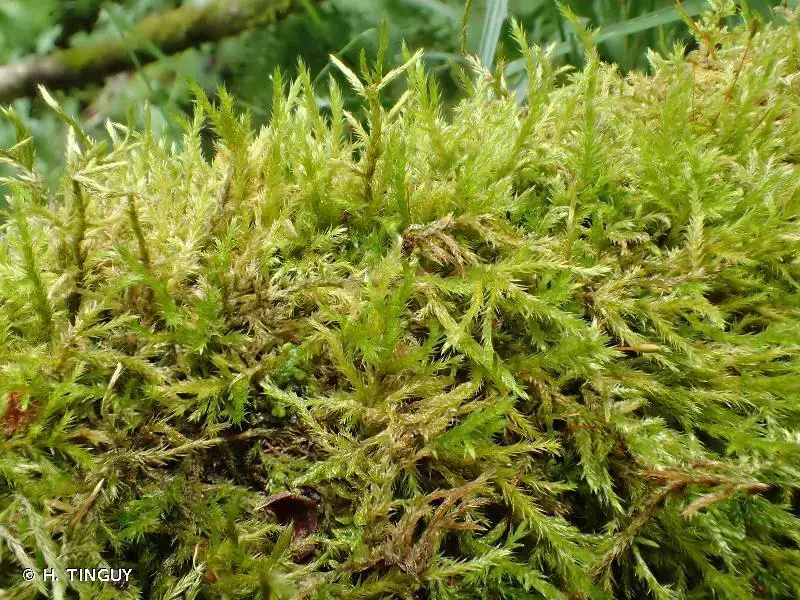

203949.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/787188
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Shoot length | 0.5 – 2 cm |
| Leaf arrangement | Two rows, deeply bilobed |
| Underleaves | Bilobed, smaller than leaves |
| Leaf cells | Small, thick-walled |
| Oil bodies | Few, large |
| Perianths | Obovoid, with distinct beak |
Conclusion
Frullania tenera Lindb. ex Steph. may be small, but it is a fascinating and important component of ecosystems worldwide. Its unique morphology, wide distribution, and ecological roles make it a subject of interest for moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. The next time you encounter this tiny moss, take a moment to appreciate its beauty and resilience. Who knows what other secrets it may hold?
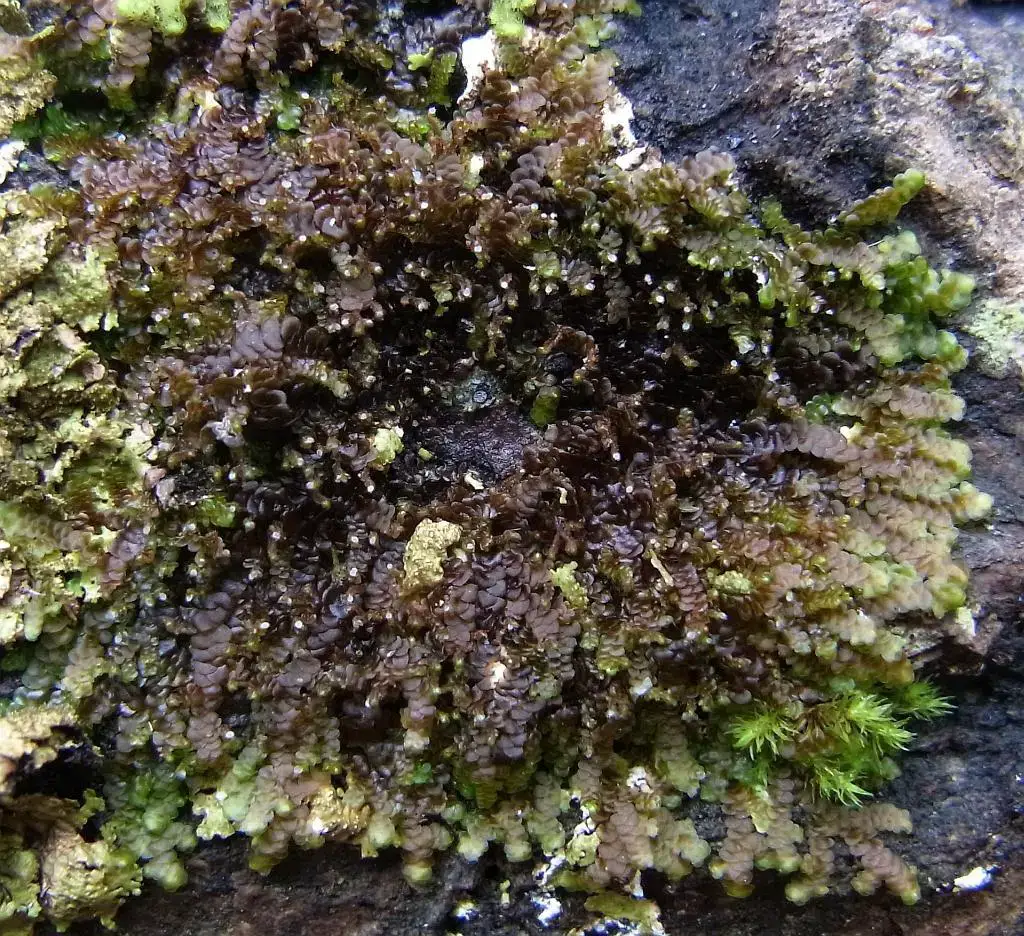

RIMG0733_Frullania_boland.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/frullania/taxa/index.php?taxon=159142