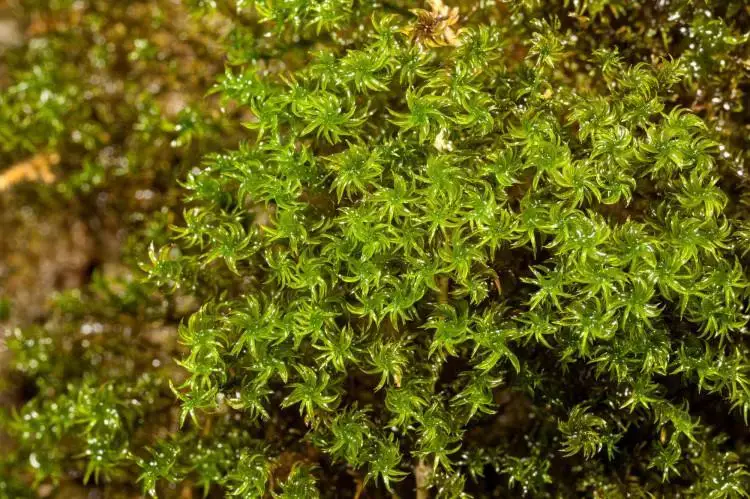

Gymnostomum-aeruginosum-101-750×499.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-gymnostomum-aeruginosum/
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Gymnostomum aeruginosum Sm., a captivating member of the Pottiaceae family. This unassuming moss, also known simply as Gymnostomum, might not be the showiest of its kind, but it holds a special place in the hearts of bryologists and nature lovers alike.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Gymnostomum aeruginosum Sm. belongs to the phylum Bryophyta, which encompasses all mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These tiny, non-vascular plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the dinosaurs! Despite their diminutive size, they play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers and stabilizers in harsh environments.
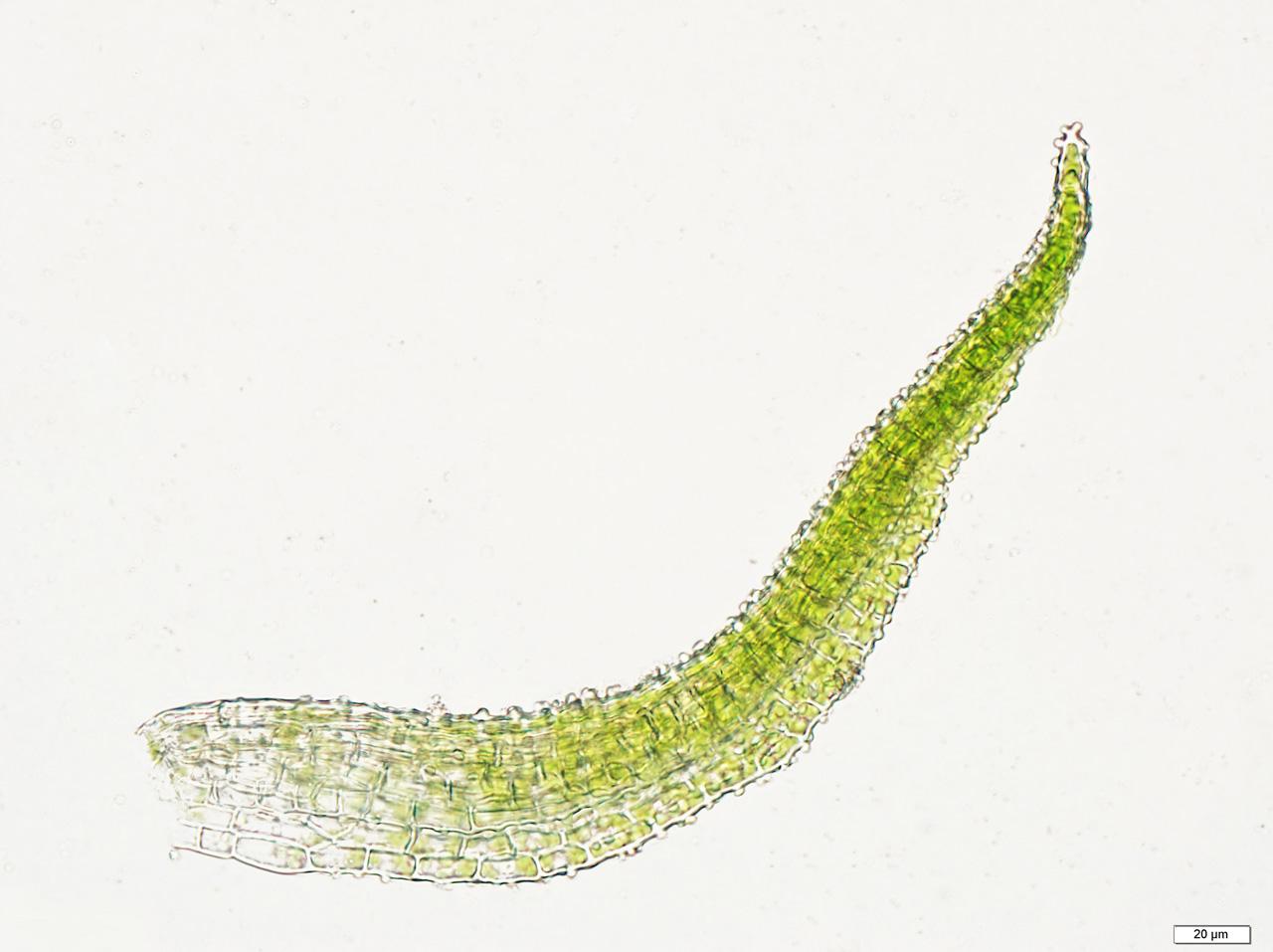
g_aeruginosum1.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/gymnostomum_aeruginosum.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Gymnostomum aeruginosum Sm. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts. Its leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and keeled (with a prominent midrib), giving it a distinctive appearance. When dry, the leaves are crisped and contorted
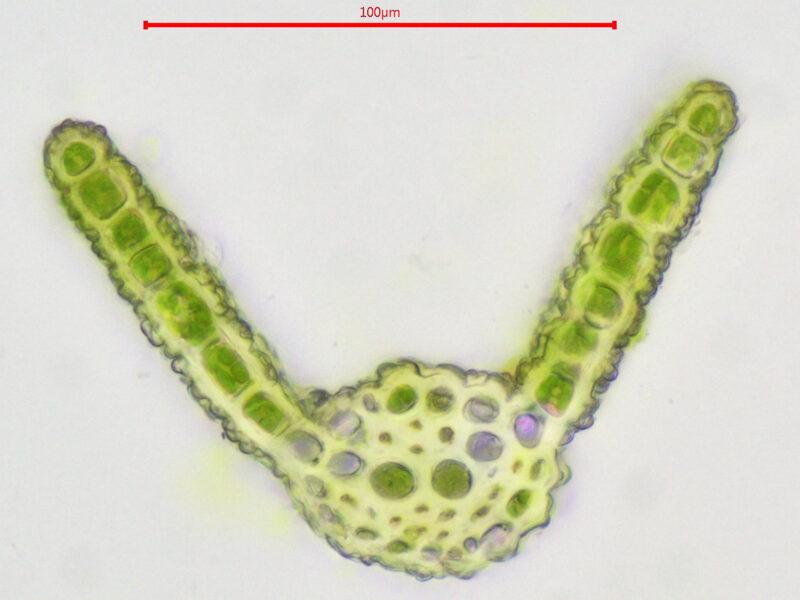
2023-01-10-11-16-17-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/gymnostomum-aeruginosum/
, but upon hydration, they become erect and spreading. The capsules (spore-bearing structures) are erect, cylindrical, and gymnostomous (without a peristome, the tooth-like structures that aid in spore dispersal).
Global Distribution and Habitat
This unassuming moss has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from calcareous soils and rock crevices to disturbed areas and even urban environments. Its ability to colonize and persist in these diverse settings is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small stature, Gymnostomum aeruginosum Sm. plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, it can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This trait allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Gymnostomum aeruginosum Sm. has been observed growing on concrete and brick walls, demonstrating its resilience and ability to colonize human-made structures. This moss has also been found in post-industrial sites

236147.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5324/tab/taxo
, acting as a pioneer species in the process of ecological succession.
Technical Table
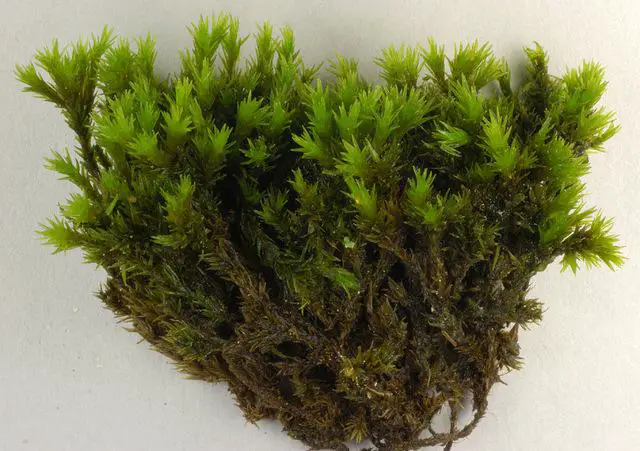

Gymnostomum_aeruginosum,I_MWS49072.jpg from: https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20p?see=I_MWS49072&res=640

240px-Gymnostomum_aeruginosum_(d%2C_144704-474818)_0714.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Gymnostomum_aeruginosum

3399-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21818

3399-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21819
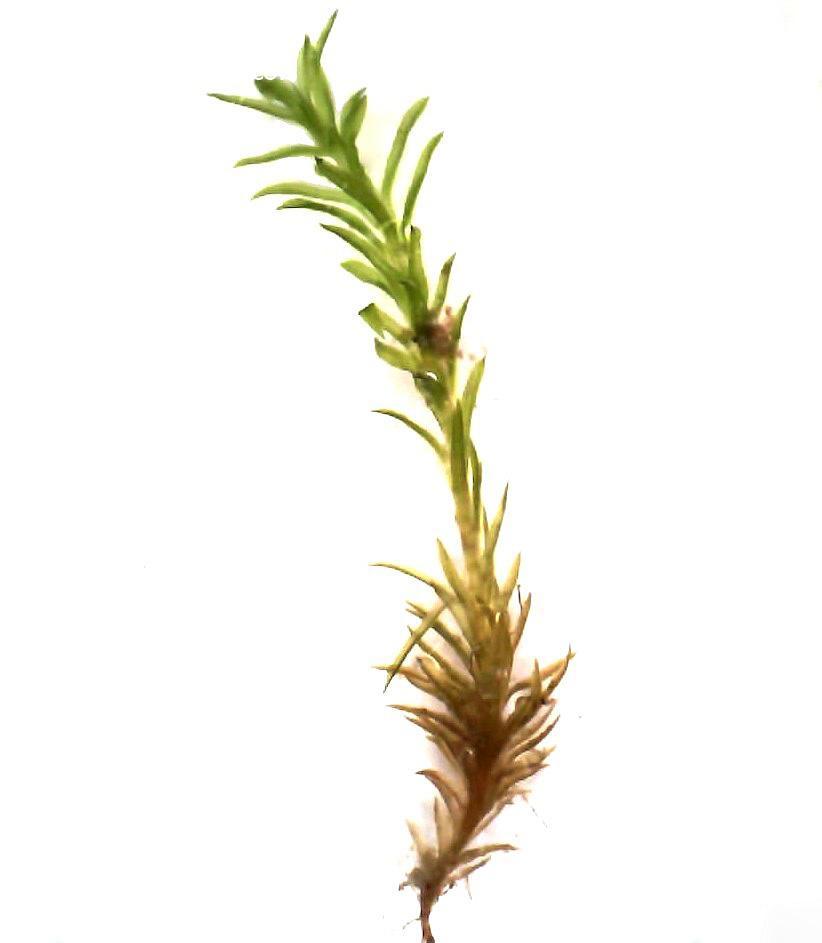

3399-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=22122
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Gymnostomum |
| Species | aeruginosum Sm.
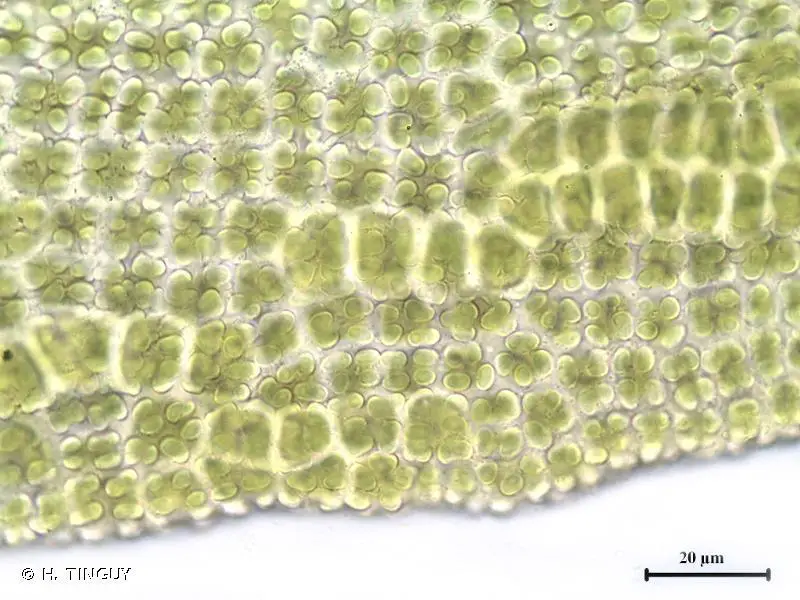 236153.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5324/tab/habitats |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, keeled |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical, gymnostomous |
| Distribution | Widespread (Europe, Asia, Africa, North America) |
| Habitat | Calcareous soils, rock crevices, disturbed areas, urban environments |
| Ecological Role | Pioneer species, soil stabilizer, microhabitat |
| Adaptation | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
Gymnostomum aeruginosum Sm. might be small, but its impact on the natural world is anything but insignificant. From stabilizing soils to providing microhabitats, this unassuming moss plays a vital role in the intricate web of life. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden wonders lie within the realm of mosses, waiting to be discovered and celebrated?