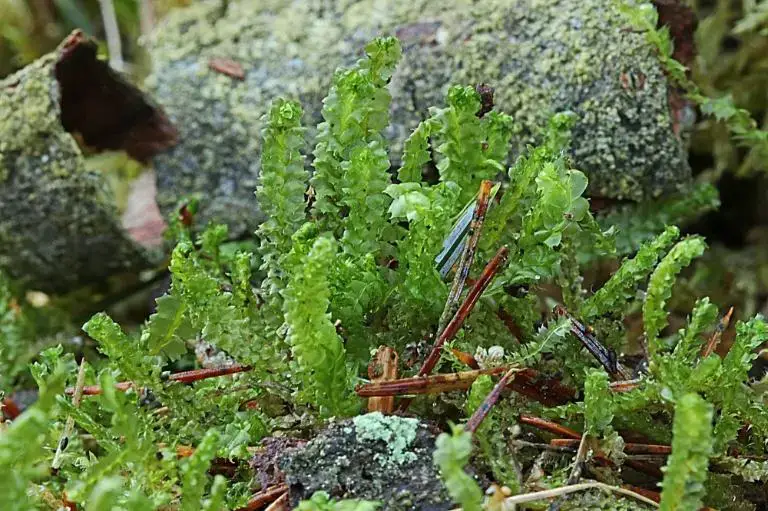

21801f37-9490-40ac-af97-afb60144698c_medium.jpg from: https://arter.dk/observation/record-details/2cd6b0dc-3d71-4430-bc96-afb601446a00
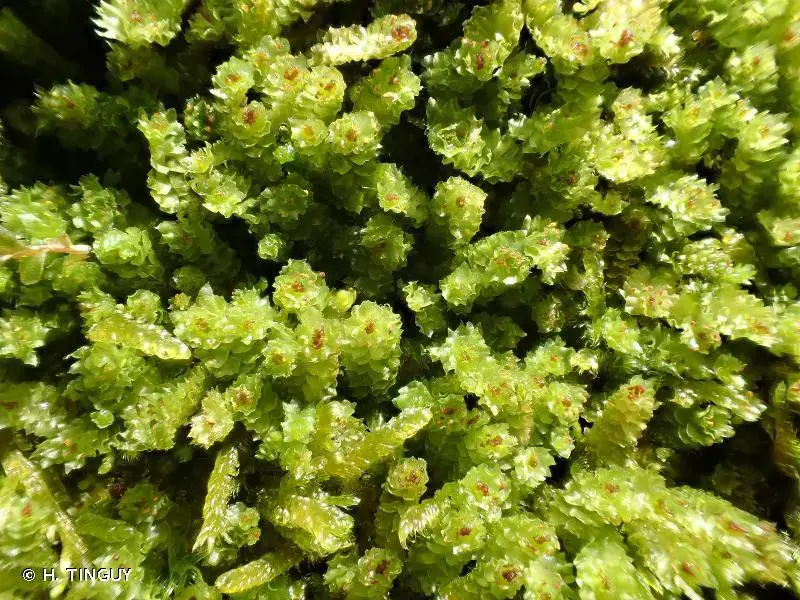

203943.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6317?lg=en
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophozia hatcheri (A.Evans) Steph. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Anastrophyllaceae family. Also known simply as Lophozia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Lophozia hatcheri, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses belong to the division Marchantiophyta, which encompasses the non-vascular land plants known as bryophytes. These ancient and resilient organisms have been around for millions of years, playing crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Lophozia hatcheri is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with closely overlapping leaves that are deeply divided into two or three lobes. The leaves are typically green to yellowish-green in color, and the plant can reach a height of just a few centimeters.
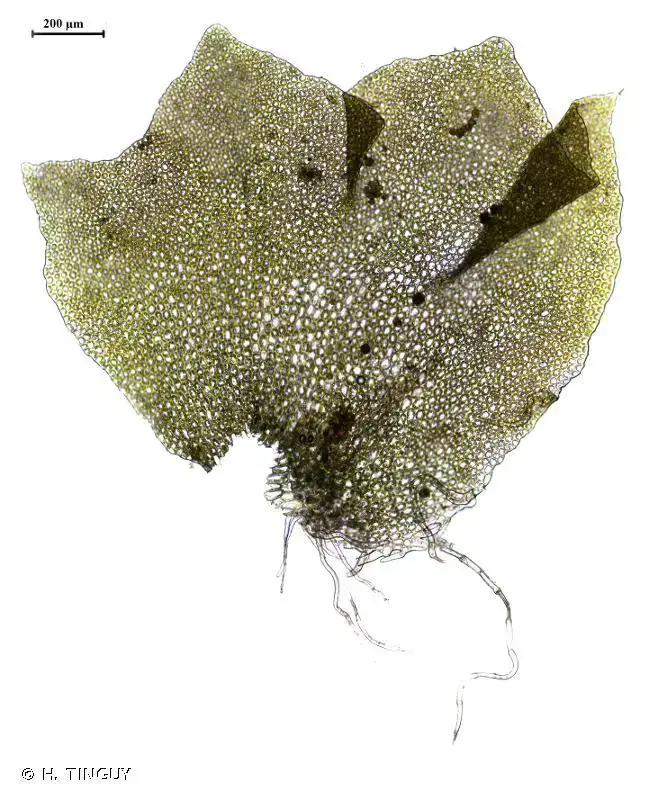

203945.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6317
One of the distinguishing features of Lophozia hatcheri is the presence of specialized reproductive structures called gametangia. These structures produce male and female gametes, which fuse to form a zygote and ultimately develop into a new generation of moss plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lophozia hatcheri is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist and shaded areas, rotting logs, and the bases of trees. This moss prefers acidic soils and is often found in coniferous or mixed forests, where it contributes to the intricate tapestry of the forest floor.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lophozia hatcheri plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance.
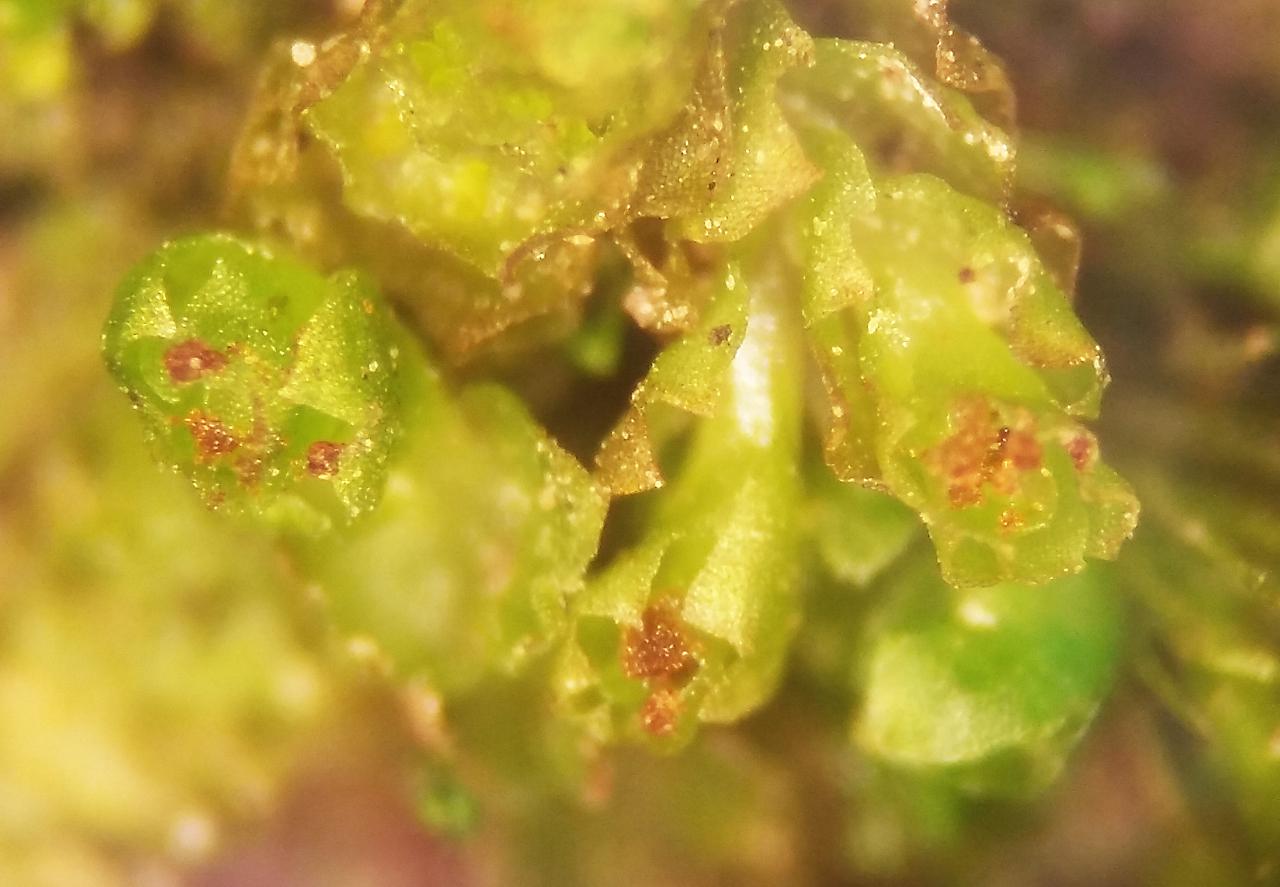

b_hatcheri.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/barbilophozia_hatcheri.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophozia hatcheri is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found Lophozia hatcheri to be a significant component of the bryophyte community in old-growth forests. Its presence was closely linked to the availability of decaying wood and the presence of specific tree species, highlighting its ecological preferences.
Technical Table
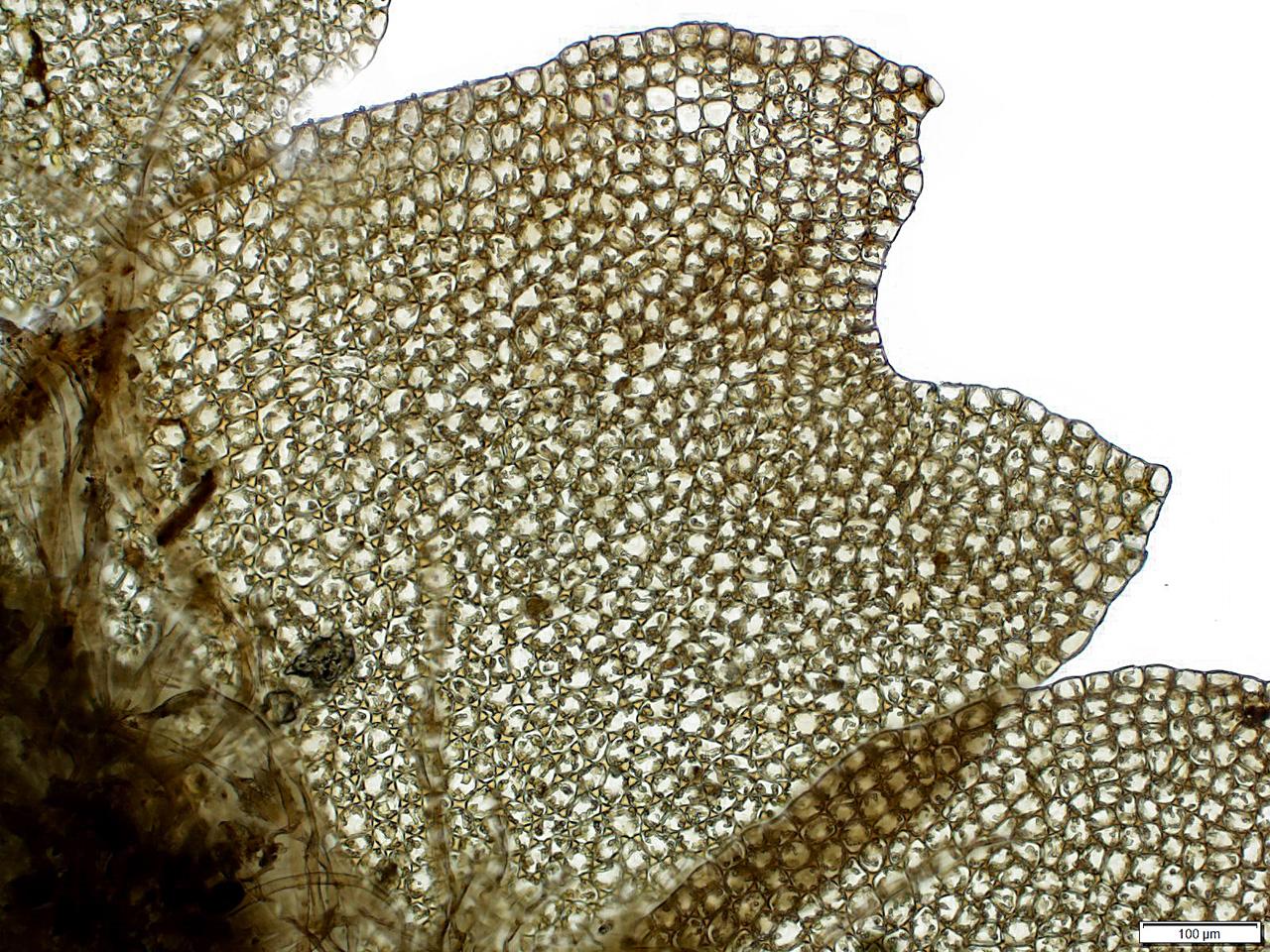

lo_obtusa1.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lophozia_obtusa.html
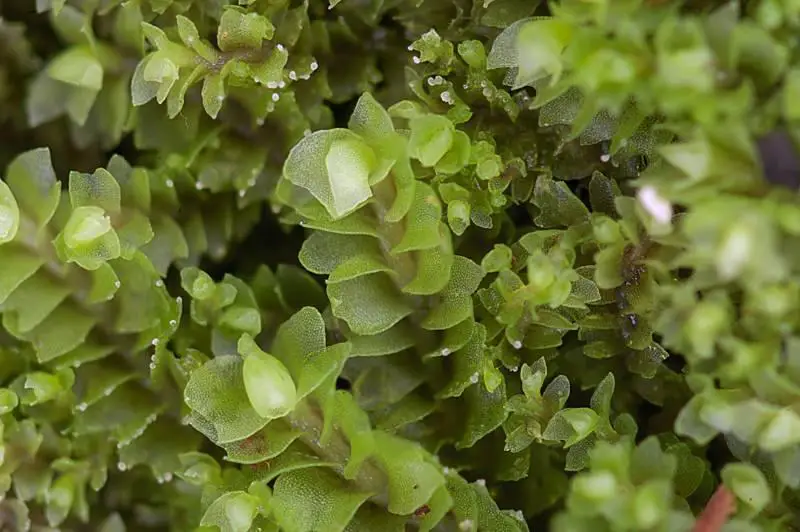

880971.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/880967.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Lophozia hatcheri (A.Evans) Steph.
 24-19-Colura-tenuicornis-A-Evans-Steph-ca-x-440-20-Drepanolejeunea-erecta.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24-19-Colura-tenuicornis-A-Evans-Steph-ca-x-440-20-Drepanolejeunea-erecta_fig4_321824568 |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae |
| Common Name | Lophozia |
| Growth Form | Creeping moss, forming dense mats or cushions |
| Leaf Morphology | Deeply divided into two or three lobes |
| Reproductive Structures | Gametangia (male and female) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, rotting logs, tree bases |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia |
Conclusion
The Lophozia hatcheri (A.Evans) Steph. moss, a member of the Anastrophyllaceae
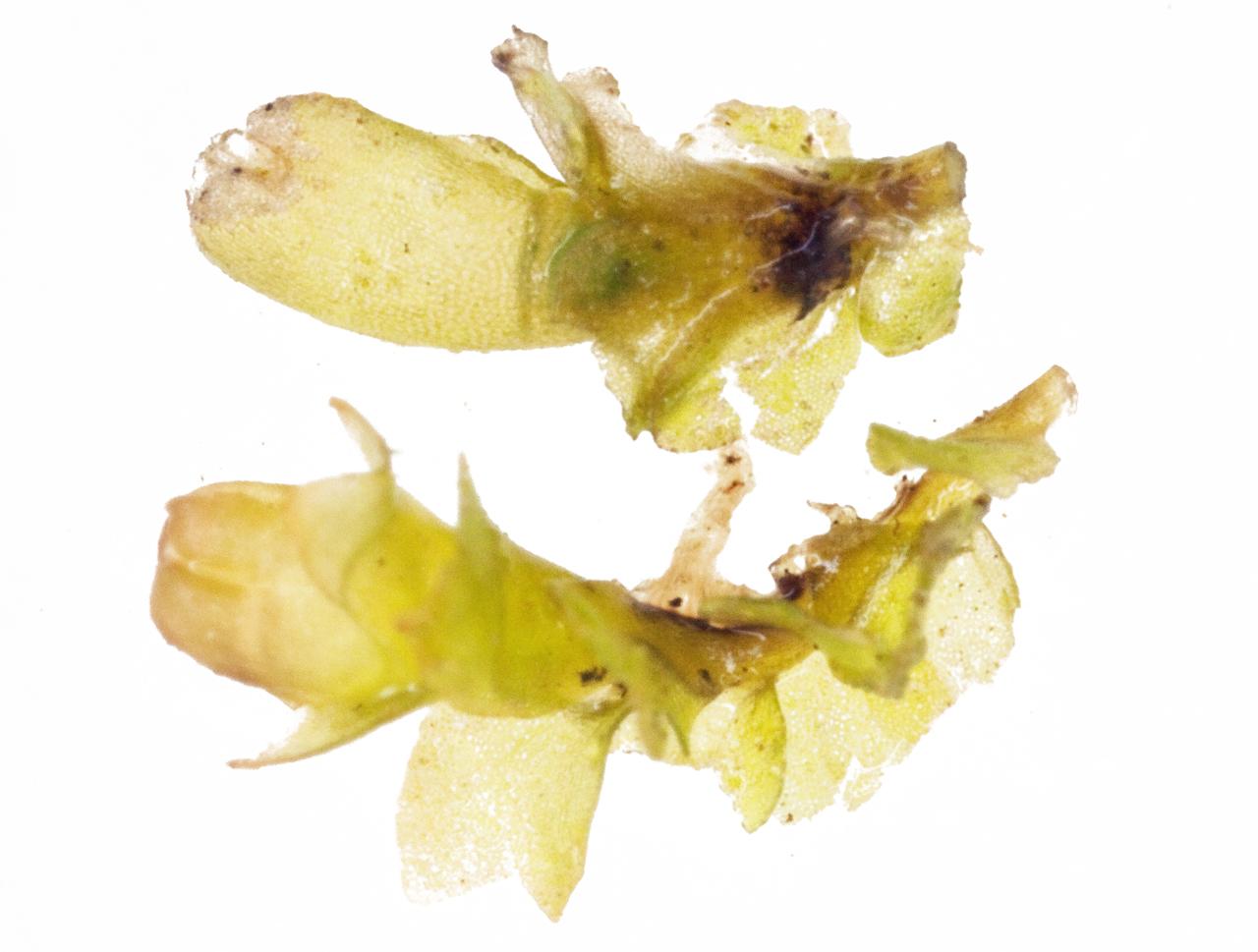

lo_sp2.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lophozia_sp.html
family, is a remarkable example of the diversity and resilience found in the world of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, mosses like Lophozia hatcheri serve as reminders of the incredible complexity and interconnectedness that surrounds us.
Ponder this: In a world where every organism plays a vital role, how can we better appreciate and protect the often overlooked but essential members of our ecosystems?