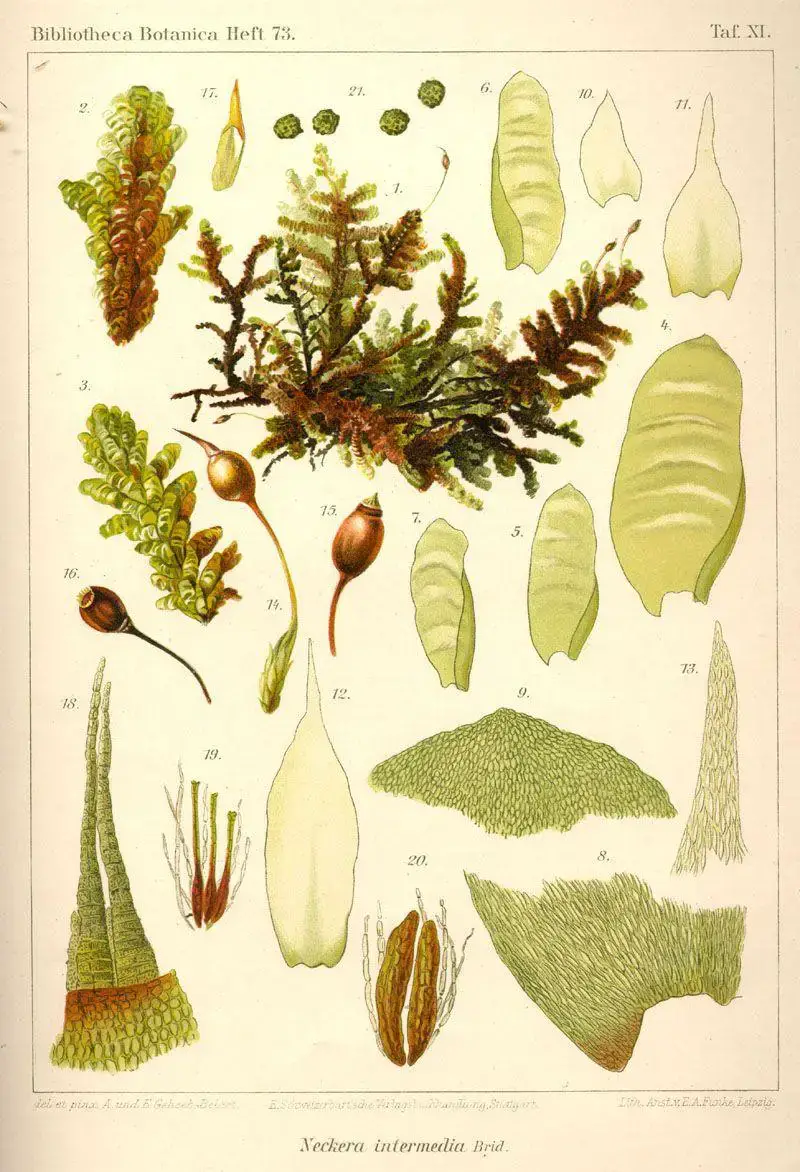

ae6858c8d5670d4200393212faf577d8.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com.au/pin/neckeraintermedia–292311832062721324/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Neckera intermedia Brid.
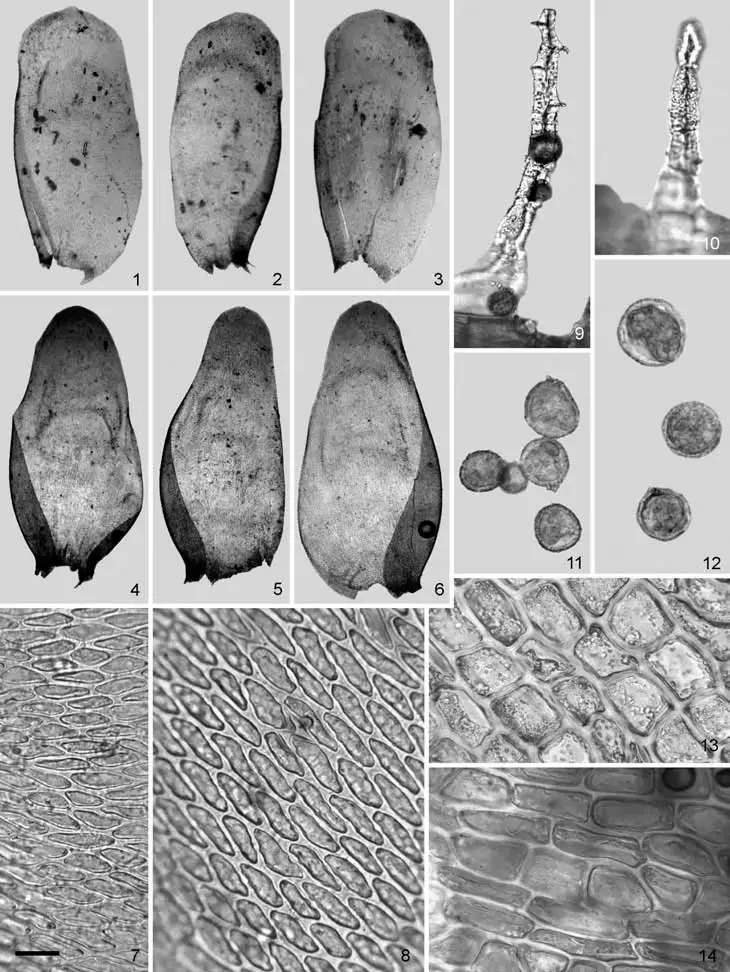
Neckera-intermedia-1-2-3-8-10-11-13-MUB-15644-1-3-Stem-leaves-8-Mid-leaf.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Neckera-intermedia-1-2-3-8-10-11-13-MUB-15644-1-3-Stem-leaves-8-Mid-leaf_fig1_233685073
moss stands out as a true marvel. Belonging to the Neckeraceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this remarkable species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Neckera intermedia Brid., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Neckera intermedia Brid., commonly known as Neckera, is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its vibrant green hue and delicate, feathery appearance make it a true delight to behold. The leaves of this moss are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinct midrib running along their length. One of the key identifying features of Neckera intermedia Brid. is the presence of paraphyllia, which are small, hair-like structures found on the stems.
Global Distribution and Habitat

Neckera_intermedia.jpg from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/exsertotheca-intermedia-12050/
This remarkable moss species has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. Neckera intermedia Brid. thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on the bark of trees, rocks, or decaying logs in forests and woodlands. Its preference for cool, humid conditions makes it a common sight in temperate and boreal regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Neckera intermedia Brid. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It serves as a microhabitat for numerous tiny organisms, providing shelter and sustenance for a diverse array of invertebrates, such as mites, springtails, and even tardigrades (water bears). Additionally, this moss acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps regulate the local microclimate and prevent soil erosion.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Neckera intermedia Brid. is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
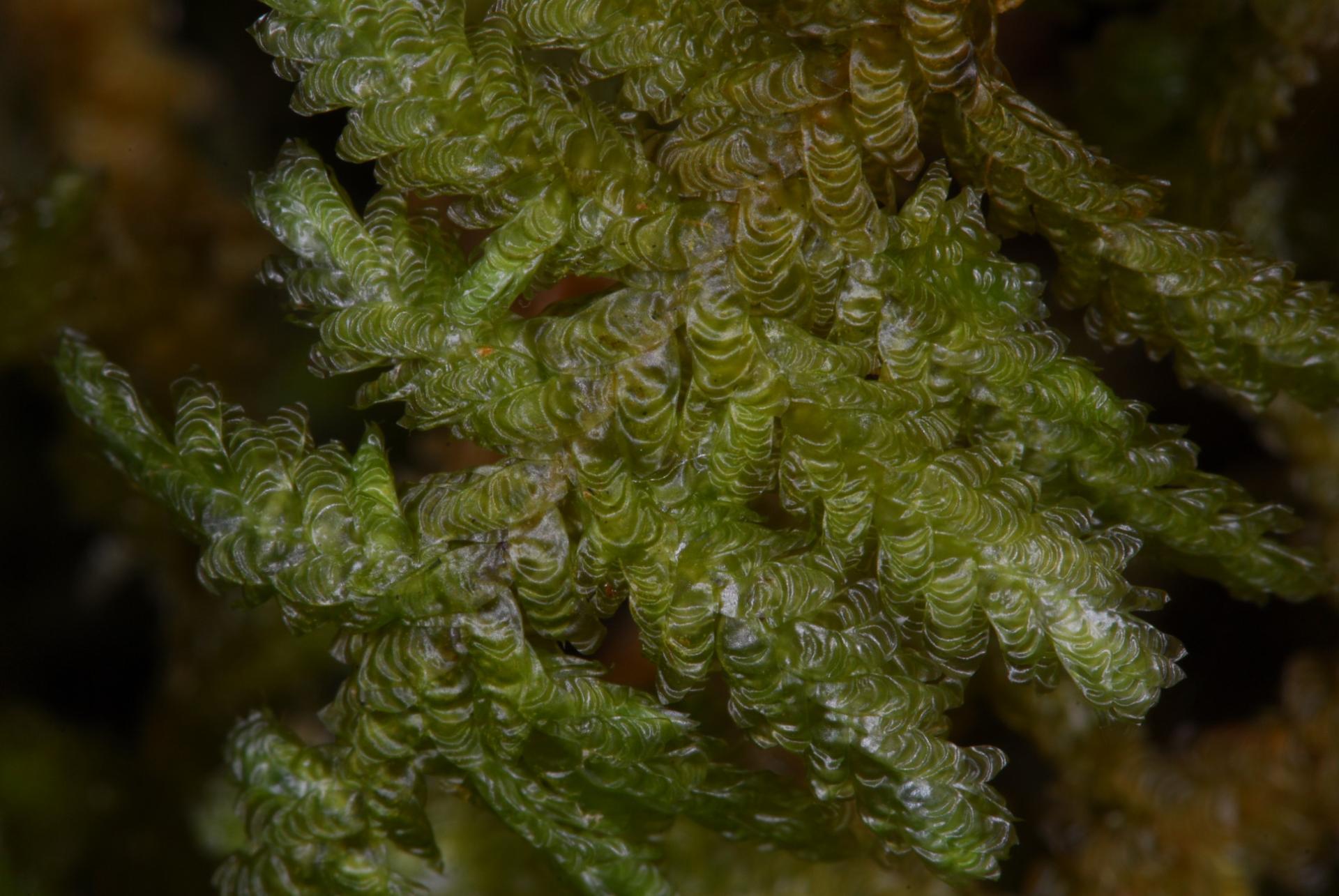

exsertotheca-intermedia-t00376-115.jpg from: http://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/exsertotheca-intermedia-12050/
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Neckera intermedia Brid. played a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of epiphytic (tree-dwelling) bryophyte communities. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and provide a suitable microhabitat for other species contributed to the overall richness and diversity of these unique ecosystems.

medium.JPG from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/132674-Neckera-pennata
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Neckeraceae |
| Genus | Neckera |
| Species | Neckera intermedia Brid. |
| Common Name | Neckera |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
Conclusion
The Neckera intermedia Brid. moss is a true testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its delicate beauty to its vital ecological roles, this species captivates moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other fascinating and overlooked species are waiting to be discovered and celebrated?